J Korean Med Assoc.
2005 Aug;48(8):703-706. 10.5124/jkma.2005.48.8.703.
The Importance of Lifestyle in the Prevention and Trearment of Diabetes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Ajou University College of Medicine and Hospital, Korea. LKW65@ajou.ac.kr
- KMID: 2064935
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2005.48.8.703
Abstract
- The association between diabetes and lifestyle habit is well known. Recently many studies confirmed that lifestyle modification is effective in the prevention and treatment of diabetes.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
9. Harris MI, Flegal KM, Cowie CC, Eberhardt MS, Goldstein DE, Byrd-Holt DD, et al. Prevalence of diabetes, impaired fasting glucose, and impaired glucose tolerance in U.S. adults. The Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diabet Care. 1998. 21:518–524.
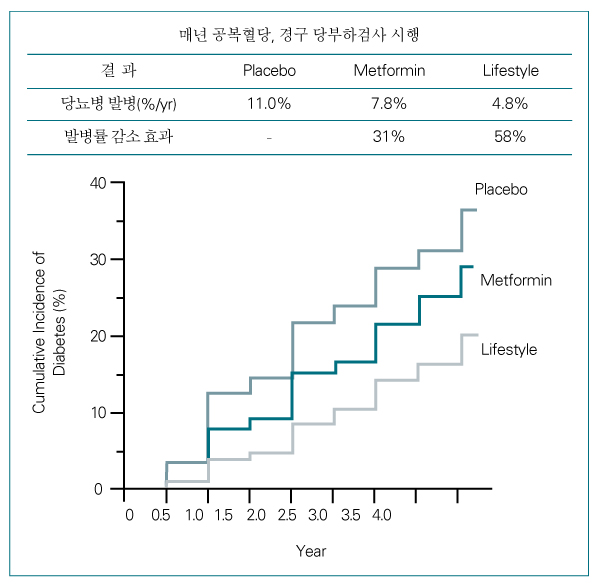
Article10. Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N Engl J Med. 2002. 346:393–403.11. Pan XR, Li GW, Hu YH, Wang JX, Yang WY, Howard BV, et al. Effects of diet and exercise in prevention NIDDM in people with impaired glucose tolerance: the Da Qing IGT and Diabetes Study. Diabet Care. 1997. 20:537–544.
Article12. Tuomilehto J, Lindstrom J, Eriksson JG, Valle TT, Hamalainen H, Ilanne-Parikka P. Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study Group. Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N Engl J Med. 2001. 344:1343–1350.
Article13. Boule NG, Haddad E, Kenny GP, Wells GA, Sigal RJ. Effects of exercise on glycemic control and body mass in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials. JAMA. 2001. 286:1218–1227.
Article