J Korean Diabetes.
2011 Dec;12(4):179-182. 10.4093/jkd.2011.12.4.179.
Satisfaction with High Deductible Policies among Patients with Diabetes in the Korean General/University Hospital System
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. djkim@ajou.ac.kr
- KMID: 2059847
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/jkd.2011.12.4.179
Abstract
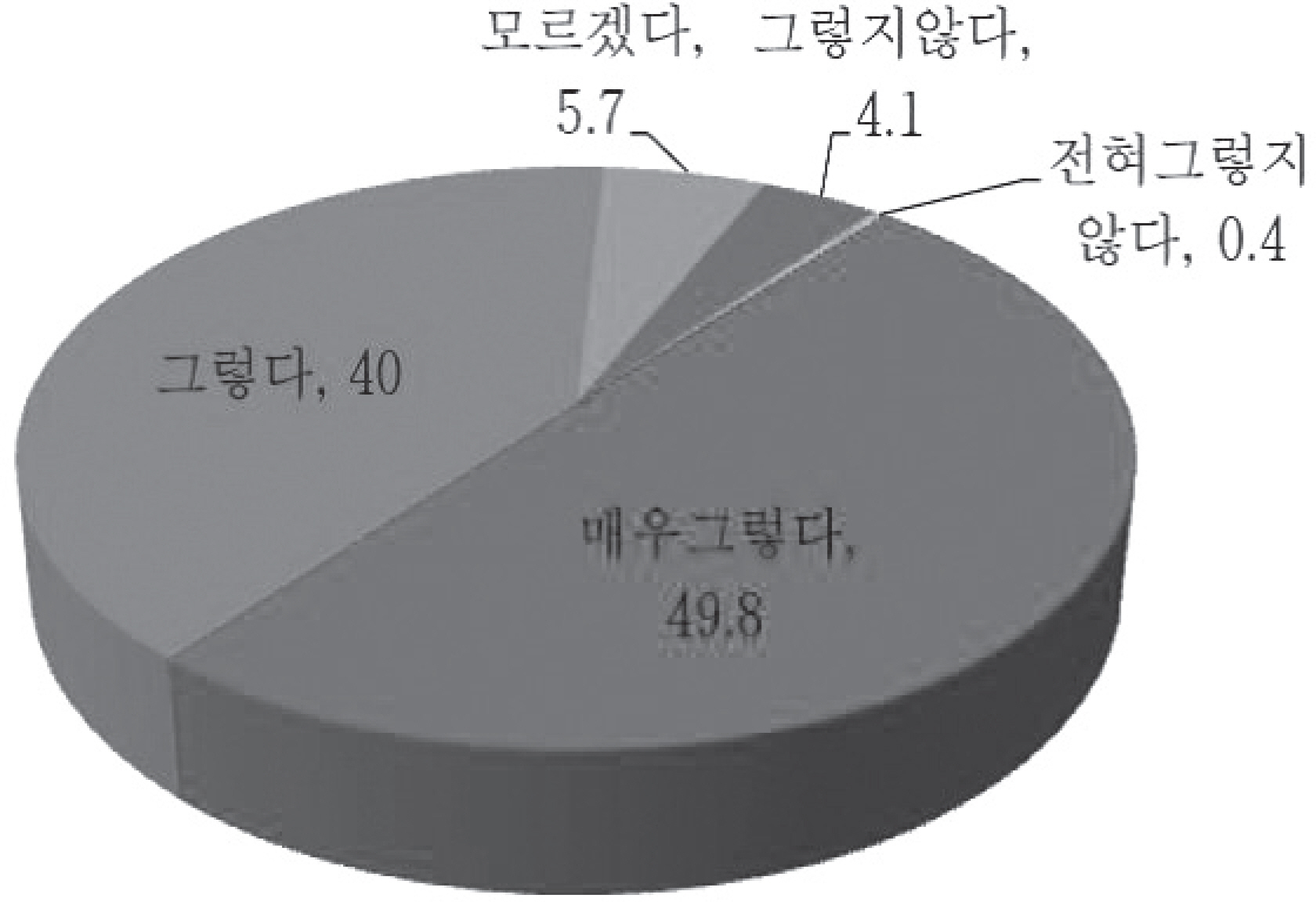
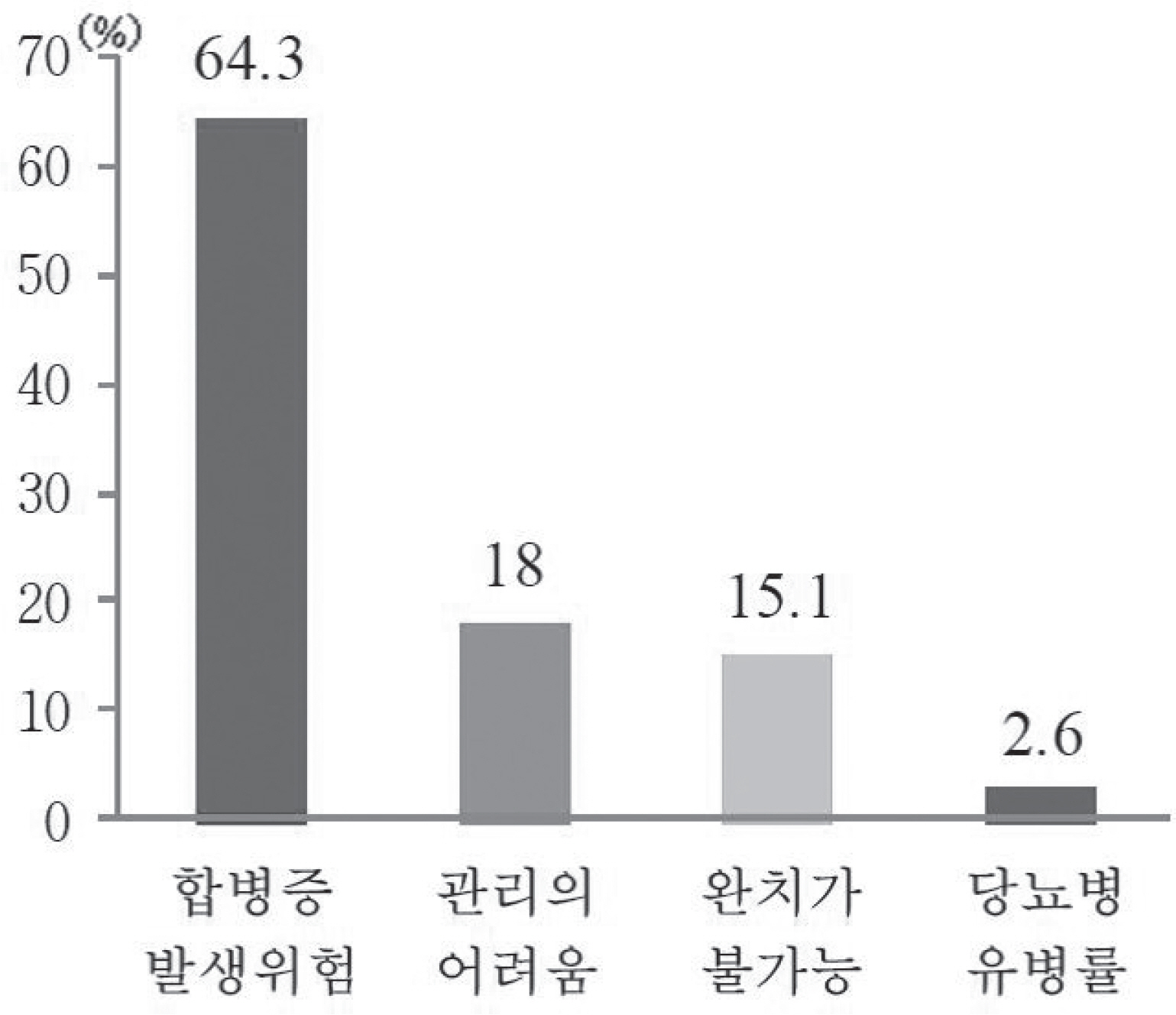
- The Korean government implemented a new policy on October 1st, 2011, requiring that patients with type 2 diabetes in the general or university hospital system pay 40% or 50% rather than 30% of total prescription drug costs. The Diabetes Association of Korea performed a survey regarding satisfaction with the new policy among patients with diabetes from August 24th to September 2nd, 2011. A total of 548 patients participated in the survey through one-to-one interviews. About 90% of patients with diabetes regarded diabetes as a serious disease, while only 4.5% regarded diabetes as a mild disease. The reasons why patients regarded diabetes as a serious disease were risks of developing diabetic complications (64.3%), difficulty of diabetes care (18.0%), and difficulty of cure (15.1%). About 70% of patients felt burdened by the increased prescription drug costs and deductibles, while only 12% did not. Finally, 85% of patients thought that the new policy was unfair to patients with diabetes and about 75% of patients regarded the new policy as inappropriate. In conclusion, the Korean government's new high deductible policy for patients with diabetes in the general/university hospital system should be withdrawn immediately.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rhee SY, Chon S, Kwon MK, Park IB, Ahn KJ, Kim IJ, Kim SH, Lee HW, Koh KS, Kim DM, Baik SH, Lee KW, Nam MS, Park YS, Woo JT, Kim YS. Prevalence of chronic complications in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus based on the Korean National Diabetes Program. Diabetes Metab J. 2011; 35:504–12.
Article2. Kim DJ. The epidemiology of diabetes in Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2011; 35:303–8.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Well-Being and Treatment Satisfaction of Diabetic Patients in an Outpatient Setting at a General Hospital in Korea
- User Satisfaction of Nursing Information System
- Hospital Avoidance and Associated Factors During the COVID-19 Pandemic
- 2024 Policy Revision for Support of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
- A Comparison of Patients' Nursing Service Satisfaction, Hospital Commitment and Revisit Intention between General Care Unit and Comprehensive Nursing Care Unit