J Bacteriol Virol.
2006 Dec;36(4):221-228. 10.4167/jbv.2006.36.4.221.
Comparison of Biological and Genetic Characteristics Between Sucrose-Fermenting and Sucrose-Nonfermenting Vibrio vulnificus Isolates
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, Wonkwang Health Science College, Iksan, Korea. smkim@wkhc.ac.kr
- 2Department of Microbiology, Jellabukdo Instituite of Health & Environmental, Jeonju, Korea.
- 3Department of Biology, Graduate School, Sunchon National University, Sunchon, Korea.
- 4Department of Biology, Graduate School, Jeonju University, Jeonju, Korea.
- 5Vestibulocochlear Research Center & Department of Miocrobiology, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea.
- 6Dermatology, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea.
- KMID: 2055030
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2006.36.4.221
Abstract
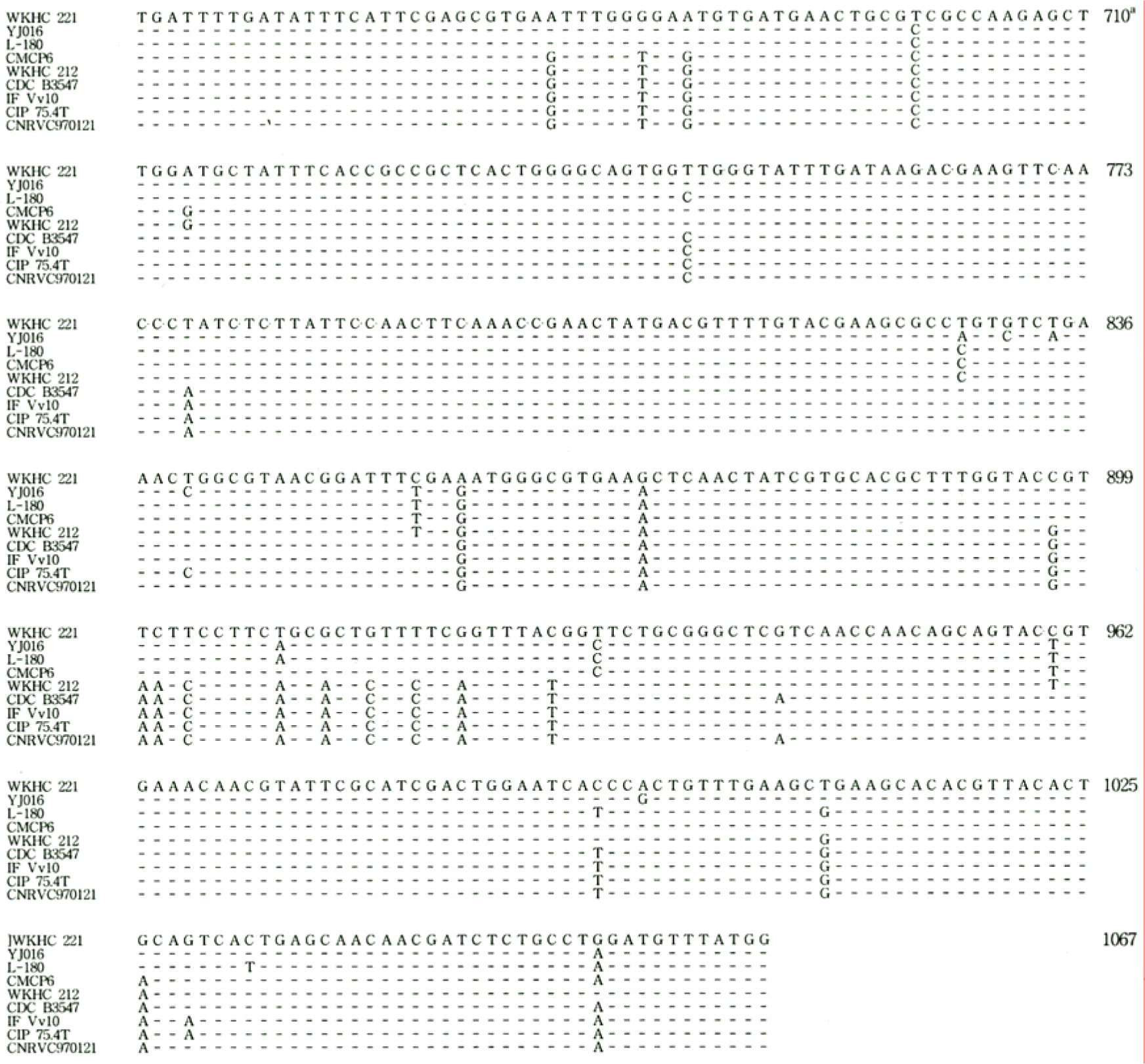
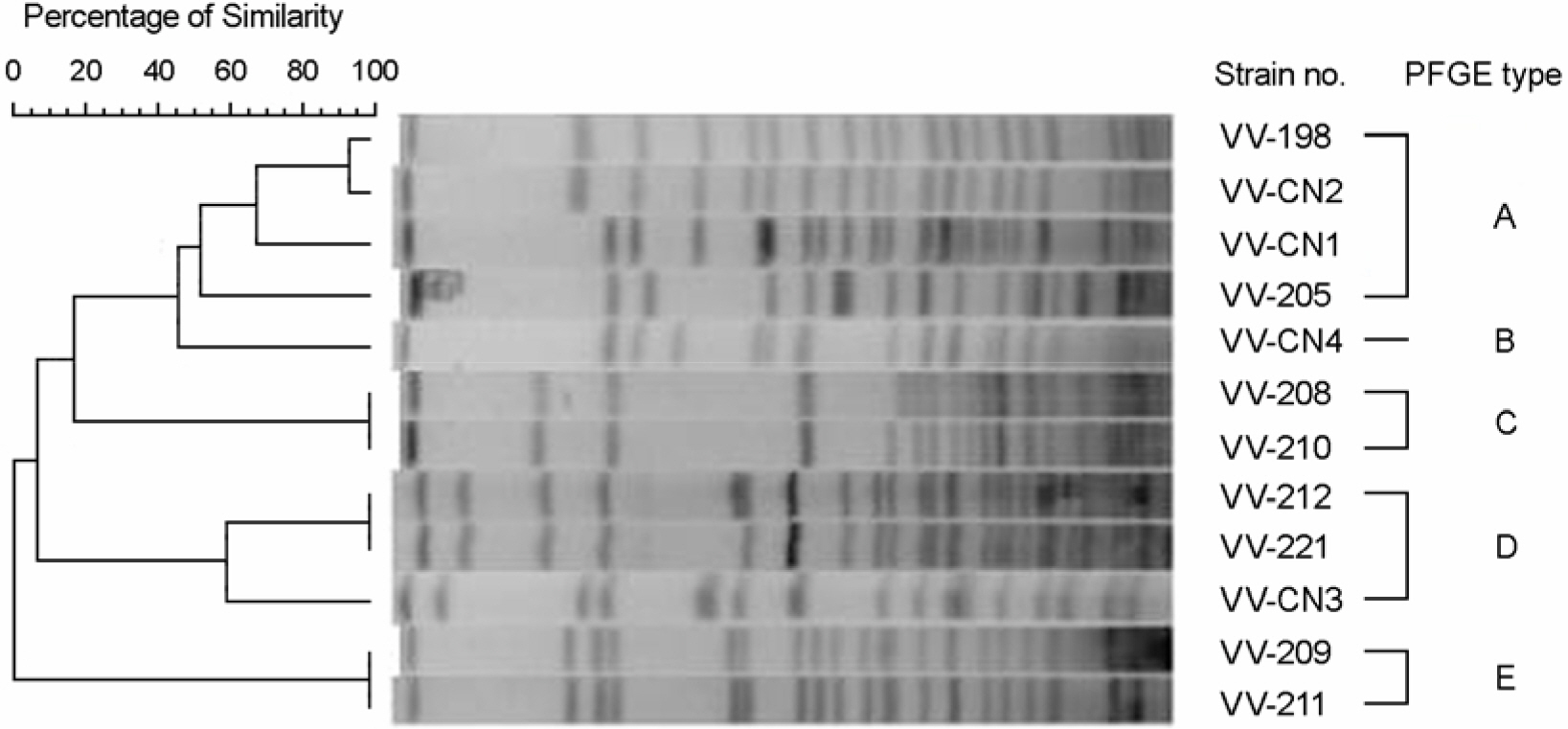
- Twelve strains of V. vulnificus isolated from clinical specimens in 2002~2004 in Jeollado province were determined for their biologic groups, serotypes, presence of vvhA (hemolysin/cytolysin) gene, DNA sequence, and PFGE patterns of NotI-restricted genomic DNA. The following results were obtained. All 12 isolates were biogroup 1, and API 20E profiles were: 5146105 for 5 (41.7%) isolates, and 5148125 for 2 isolates with sucrose fermentation. Ten (83.3%) of the 12 isolates was V. vulnificus serotype O4A, and two sucrose-fermenting isolates belonged to serotype O2. Alleles of cytolysin-hemolysin gene were detected in all 12 isolates. The nucleotide sequences of vvhA genes from strains WKHC 212 and WKHC 221 showed 94~97% similarity compared with those from previously reported 7 strains, YJ016, CMCP6, L-180, CDC B3547, IF Vv10, CIP 75.4T and CNRVC 970121. PFGE of NotI-restricted genomic DNA from the 12 isolates showed approximately 48.5 to 873-kb fragments and they were clustered to five (A to E) patterns. Two sucrose-fermenting isolates belonged to pattern D with 95% similarity with each other. Two strains isolated from two different patients had two identical patterns C and D. It is concluded that sucrose-fermenting strains also exist among clinical isolates of V. vulnificus in Korea, and they can be identified by using API 20E system, and by detecting vvhA gene. DNA sequences and PFGE pattern of NotI-restricted genomic DNA suggested that the two sucrose-fermenting isolates belonged to an identical clone, and two strains each isolated from two different patients belonged to two identical clones.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1). 김신무, 송계민, 김승아, 최수연, 임효빈, 성치남. A Case of Sucrose-Positive Vibrio vulnificus Isolation from Blood Culture. 대한임상검사학회지. 36:69–75. 2004.2). 신종희, 신명근, 양동욱. Vibrio vulnificus 동정에 있어서 ATB32 GN system의 유용성 검토. 대한임상병리학회지. 13:281. 1993.3). 원동일, 이경원, 정윤섭, 권오헌, 김준명. Vibrio vulnificus에 의한 원발성 창상감염 1예. 감염. 26:93–97. 1994.4). CDMR. 2003 년 비브리오패혈증 환자의 역학 및 분리 주의 특성. Communicable disease monthly report. Korea Center for Disease Control. 15(5):93–94. 2004.5). Amaro C, Biosca EG. Vibrio vulnificus Biotype 2, Pathogenic for Eels, Is Also an Opportunistic Pathoigen for Humans. Appl Environ Microbiol. 62(4):1454–1457. 1996.6). Amaro C, Sanjuan E. Protocol for specific isolation virulent strains of Vibrio serovar E (biotype 2) from environmental samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 70(12):7024–7032. 2004.7). Arias CR, Pujalte MJ, Garay E, Aznar R. Genetic relatedness among environmental, clinical, and diseased-eel Vibrio vulnificus isolates from different geographic regions by ribo-typing and randomly amplified polymorphic DNA PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol. 64(9):3403–3410. 1998.8). Arias CR, Verdonck L, Swings J, Garay E, Aznar R. Intraspecific differentiation of Vibrio vulnificus biotypes by amplified fragment length polymorphism and ribotyping. Appl Environ Microbiol. 63:2600–2606. 1997.9). Arias CR, Aznar R, Pujalte MJ, Garay E. A comparison of strategies for the detection and recovery of Vibrio vulnificus from marine samples of the western Mediterranean coast. Syst Appl Microbiol. 21(1):128–134. 1998.10). Biosca EG, Amaro C, Larsen JL, Pedersen K. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of Vibrio vulnificus: proposal for the substitution of the subspecific Taxon biotype for serovar. Appl Environ Microbiol. 63(4):1460–1466. 1997.11). Bisharat N, Agmon V, Finkelstein R, Raz R, Ben-Dror G, Lerner L, Soboh S, Colodner R, Cameron DN, Wykstrta L, Swerdlow DL, Farmer JJ 3rd. Clinical, epidemiological, and microbilogical features of Vibrio vulnificus biogroup 3 causing outbreaks of wound infection and bacteremia in Israel. Israel Vibrio Study group. Lancet. 354:1421–1424. 1999.12). Branus LA, Hudson MC, Oliver JD. Use of the polymerase chain reaction in detection of culturable and nonculturable Vibrio vulnificus cells. Appl Environ Microbiol. 57(9):2651–2655. 1991.13). Buchrieser C, Gangar VV, Murphree RL, Tamlin ML, Kaspar CW. Multiple Vibrio vulnificus strains in oysters as demonstrated by clamped homogeneous electric field gel electrophoresis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 61:1163–1168. 1995.14). Cho JH, Ryang DW, Moon YH. Restriction enzyme analysis of chromosomal DNA and serotype of Vibrio vulnificus prevailed in Honam area. Korea J Clin Pathol. 15:240–249. 1995.15). Dalsgaard A, Dalsgaard I, Hoi L, Larsen JL. Comparison of a commercial biochemical kit and an oligonucleotide probe for identification of environmental isolates of Vibrio vulnificus. Lett Appl Microbiol. 22:184–188. 1996.16). Farmer JJ III, Hickman-Brenner FW, Kelly MT. Vibrio. In. Lennette EH, Balows A, Hausler WJ, Shadomy HJ EJ, editors. p. 282–301. Manual of clinical microbiology. 4th ed.ASM press Inc;Washington D. C.: 1985.17). Hill MK, Sanders CV. Localized and systemic infection due to Vibrio species. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1:687. 1987.18). Hill WE, Keasler SP, Trucksess MW, Feng P, Kaysner CA, Lampel KA. Polymerase chain reaction identification of Vibrio vulnificus in artificially contaminated oysters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 57(3):707–711. 1991.19). Hoi L, Dalsgaard A, Larsen JL, Warner JM, Oliver JD. Comparison of ribotyping and randomly amplified polymorphic DNA PCR for characterization of Vibrio vulnificus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 63:1674–1678. 1997.20). Hollis DG, Weaver RE, Baker CN, Thornsberry C. Halophilic Vibrio species isolated from blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 3:425. 1976.21). Janda JM: Powers C, Bryant RG, Abbott SL. Current perspectives on the epidemiology and pathogenesis of clinically significant Vibrio spp. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1:245. 1988.22). Kim SM, Park Y, Chong YS. A study on biological characteristics and serovar of Vibrio vulnificus isolated in Korea. J Korea Soc Microbiol. 26:403–415. 1991.23). Koenig KL, Mueller J, Rose T. Vibrio vulnificus. Hazard on the Half Shell. West J Med. 155:400. 1991.24). Lee CT, Amaro C, Sanjuan Eva, Hor L. Identification of DNA sequence for Vibrio vulnificus biotype2 strains by suppression subtractive hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol. 71(9):5593–5597. 2005.25). Lee SE, Kim SY, Kim SJ, Kim HS, Shin JH, Choi SH, Chung SS, Rhee JH. Direct identification of Vibrio vulnificus in clinical specimens by Nested PCR. J Clin Microbiol. 36:2887–2892. 1998.26). Martinez-Urtaza J, Iozano-Leon A, Depaola A. Ishibashi M, Shimada K, Nishibuchi M, and Liebana E. Charaterization of pathogenic Vibrio parahemolyticus isolates from clinical sources in Spain and comparision with Asian and North American pandemic isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 42:4672–4678. 2004.27). Mehtar S, Bangham L, Kalmatovitch D, Wren M. Adult epiglottitis due to Vibrio vulnificus. Br Med J. 296:827. 1988.28). Reichelt JL, Baumann P, Baumann L. Study of genetic relationships among marine species of the genera Beneckea and Photobacterium by means of in vitro DNA/DNA hybridization. Arch Microbiolo. 110(1):101–120. 1976.
Article29). Ryang DW, Cho SW, Shin MG, Shin JH, Suh SP. Molecular typing of Vibrio vulnificus isolates by random amplified polymorphic DNA(RAPD) analysis. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 50:113–121. 1997.30). Ryang DW, Koo SB, Shin MG, Shin JH, Suh SP. Molecular typing of Vibrio vulnificus isolated from clinical specimens by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 52:38–41. 1999.31). Shimada T, Sakazaki R. On the serology of Vibrio vulnificus. Japanese K Med Sci Biol. 37:241–246. 1984.32). Shin MG, Shin JH, Ryang DW. Clinical characteristics of Vibrio vulnificus infection. Korea J Clin Pathol. 13:287–293. 1993.33). Shin MG, Shin JH, Suh SP, Ryang DW, Bae KS. Cellular fatty acid profiles of ninety-five strains of Vibrio vulnificus isolated from clinical specimens in Korea. J Gen Appl Microbiol. 43:317–324. 1997.33). Tamplin M, Rodrick GE, Blake NJ, Cuba T. Isolation and characterization of Vibrio vulnificus from two Florida estuaries. Appl Environ Microbiol. 44:1466–1470. 1982.34). Woo ML, Patrick WGD, Simon MTP, French GL. Necrotising fasciitis caused by Vibrio vulnificus. J Clin Pathol. 37:1301. 1984.35). Wright AC, Miceli GA, Landry WL, Christy JB, Watkins WD, Morris JG. Rapid identification of Vibrio vulnificus on nonselective media with an alkaline phosphatase-labeled oligonucleotide probe. Appl Environ Microbiol. 59:541–546. 1993.36). Yamamoto K, Wright AC, Kaper JC, Morris Jr JG. The cytolysin gene of Vibrio vulnificus sequence and relationship to the Vibrio cholerae El Tor hemolysin gene. Infec Immun. 58:2706–2709. 1990.37). Yang DO, Kim HS, Kim HW, Shin DH, Kim SJ. Clinical characteristics in fifty-eight cases of micro-biologically confirmed Vibrio vulnificus septicemia. Korea J Int Med. 41:383–391. 1991.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Virulence Characteristics of Sucrose-fermenting Vibrio vulnificus Strains
- Biological characteristics and serovars of vibrio vulnificus
- Characteristics of protease produced by vibrio vulnificus and its effect on the activity of hemolysin
- Cultural Characteristics of Vibrio vulnificus on Various Media
- Vibrio vulnificus Septicemia: Report of Four Cases