Electrolyte Blood Press.
2007 Dec;5(2):140-146. 10.5049/EBP.2007.5.2.140.
Long-term Follow up of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Patients with Hyponatremia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Kyunghee University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. bscho@dreamwiz.com
- KMID: 2052298
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5049/EBP.2007.5.2.140
Abstract
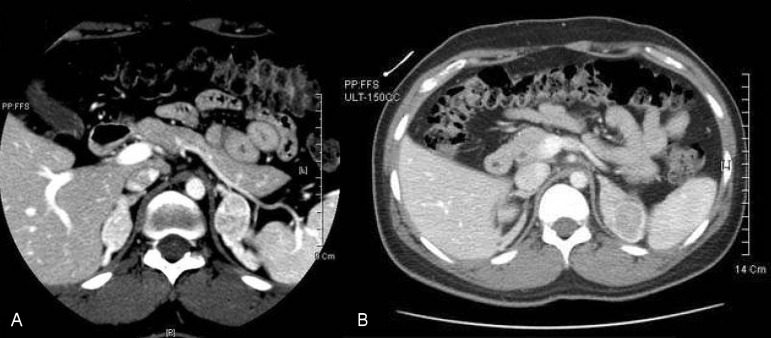
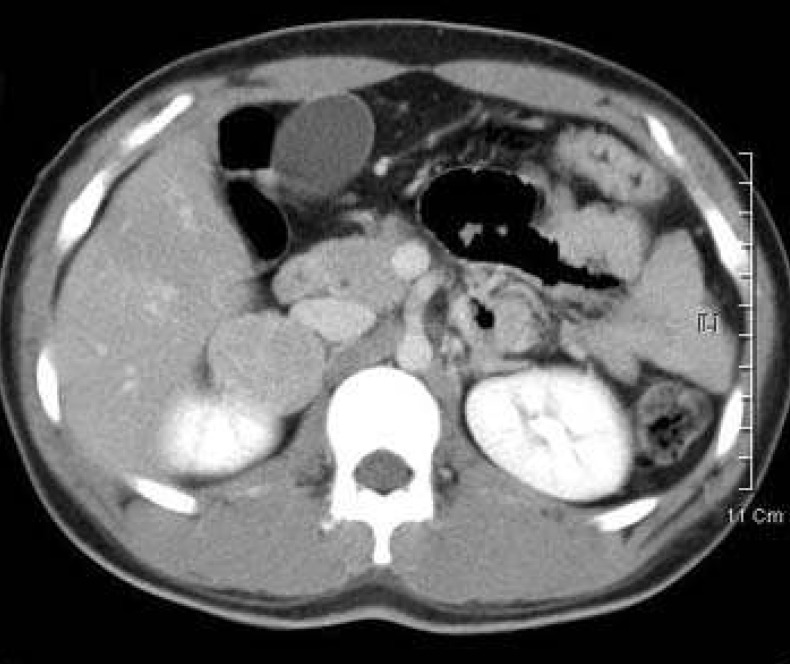
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) caused by 21-hydroxylase deficiency is an autosomal recessive disease, which leads to cortisol and aldosterone deficiency and hyperandrogenism. Typical medical treatment includes oral glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid administration to suppress adrenal androgens and to compensate for adrenal steroid deficiencies. Usually, they have been managed with hydrocortisone (cortisone) and fludrocortisone (florinef). However, some patients stopped taking medicine without the doctor's consent. Among these patients, four cases of CAH patients showing the presence of hyponatremia as an initial electrolyte disorder were found with adrenal adenoma discovered by abdominal computerized tomography scan. Hypersecretion of adrenocorticotrophic hormone may play a role in the development of adrenal tumor and chronic poor compliance to therapy appears to be associated with development of the tumor. Two cases were managed with adrenalectomy because of increasing adrenal tumor size and virilization. Whereas the other two cases did not increase in size and were observed without adrenalectomy. Therefore, it is important that patients with CAH maintain steroid medication to avoid the appearance of adrenal tumor.
MeSH Terms
-
Adenoma
Adrenal Hyperplasia, Congenital*
Adrenalectomy
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone
Aldosterone
Androgens
Compliance
Fludrocortisone
Follow-Up Studies*
Humans
Hydrocortisone
Hyperandrogenism
Hyponatremia*
Steroid 21-Hydroxylase
Virilism
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone
Aldosterone
Androgens
Fludrocortisone
Hydrocortisone
Steroid 21-Hydroxylase
Figure
Reference
-
1. White PC. Congenital adrenal hyperplasias. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001; 15:17–41. PMID: 11469809.
Article2. Wilkins L, Lewis RA, Klein R, Rosemberg E. The suppression of androgen secretion by cortisone in a case of congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1950; 86:249–252. PMID: 15411555.3. Jaresch S, Kornely E, Kley HK, Schlaghecke R. Adrenal incidentaloma and patients with homozygous or heterozygous congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992; 74:685–689. PMID: 1311000.
Article4. Ravichandran R, Lafferty F, McGinniss MJ, Taylor HC. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia presenting as massive adrenal incidentalomas in the sixth decade of life: report of two patients with 21-hydroxylase deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996; 81:1776–1779. PMID: 8626833.
Article5. Lightner ES, Levine LS. The adrenal incidentaloma. A pediatric perspective. Am J Dis Child. 1993; 147:1274–1276. PMID: 8249939.6. Merke DP, Bornstein SR. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Lancet. 2005; 365:2125–2136. PMID: 15964450.
Article7. Bachelot A, Plu-Bureau G, Thibaud E, Laborde K, Pinto G, Samara D, Nihoul-Fékété C, Kuttenn F, Polak M, Touraine P. Long-term outcome of patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Horm Res. 2007; 67:268–276. PMID: 17170529.
Article8. Therrell BL. Newborn screening for congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2001; 30:15–30. PMID: 11344933.
Article9. Levine LS, Zachmann M, New MI, Prader A, Pollack MS, O'Neill GJ, Yang SY, Oberfield SE, Dupont B. Genetic mapping of the 21-hydroxylase-deficiency gene within the HLA linkage group. N Engl J Med. 1978; 299:911–915. PMID: 692595.
Article10. White PC, Tusie-Luna MT, New MI, Speiser PW. Mutations in steroid 21-hydroxylase (CYP21). Hum Mutat. 1994; 3:373–378. PMID: 8081391.
Article11. Merke DP, Chrousos GP, Eisenhofer G, Weise M, Keil MF, Rogol AD, Van Wyk JJ, Bornstein SR. Adrenomedullary dysplasia and hypofunction in patients with classic 21-hydroxylase deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2000; 343:1362–1368. PMID: 11070100.
Article12. Pang S, Shook MK. Current status of neonatal screening for congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Curr Opin Pediatr. 1997; 9:419–423. PMID: 9300201.
Article13. Lebovitz RM, Pauli RM, Laxova R. Delayed diagnosis in congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Need for newborn screening. Am J Dis Child. 1984; 138:571–573. PMID: 6609631.
Article14. Chrousos GP, Loriaux DL, Mann D, Cutler GB Jr. Late-onset 21-hydroxylase deficiency is an allelic variant of congenital adrenal hyperplasia characterized by attenuated clinical expression and different HLA haplotype associations. Horm Res. 1982; 16:193–200. PMID: 6290362.
Article15. Kerrigan JR, Veldhuis JD, Leyo SA, Iranmanesh A, Rogol AD. Estimation of daily cortisol production and clearance rates in normal pubertal males by deconvolution analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993; 76:1505–1510. PMID: 8501158.
Article16. Linder BL, Esteban NV, Yergey AL, Winterer JC, Loriaux DL, Cassorla F. Cortisol production rate in childhood and adolescence. J Pediatr. 1990; 117:892–896. PMID: 2104527.
Article17. Metzger DL, Wright NM, Veldhuis JD, Rogol AD, Kerrigan JR. Characterization of pulsatile secretion and clearance of plasma cortisol in premature and term neonates using deconvolution analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993; 77:458–463. PMID: 8345052.
Article18. Clayton PE, Miller WL, Oberfield SE, Ritzén EM, Sippell WG, Speiser PW. ESPE/LWPES CAH Working Group. Consensus statement on 21-hydroxylase deficiency from the European Society for Paediatric Endocrinology and the Lawson Wilkins Pediatric Endocrine Society. Horm Res. 2002; 58:188–195. PMID: 12324718.19. Riepe FG, Krone N, Viemann M, Partsch CJ, Sippell WG. Management of congenital adrenal hyperplasia: results of the ESPE questionnaire. Horm Res. 2002; 58:196–205. PMID: 12324719.
Article20. Azziz R, Dewailly D, Owerbach D. Clinical review 56: Nonclassic adrenal hyperplasia: current concepts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994; 78:810–815. PMID: 8157702.
Article21. Blum RW. Transition to adult health care: setting the stage. J Adolesc Health. 1995; 17:3–5. PMID: 7578159.
Article22. Watson AR. Non-compliance and transfer from paediatric to adult transplant unit. Pediatr Nephrol. 2000; 14:469–472. PMID: 10872185.
Article23. Kruse B, Riepe FG, Krone N, Bosinski HA, Kloehn S, Partsch CJ, Sippell WG, Mönig H. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia - how to improve the transition from adolescence to adult life. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2004; 112:343–355. PMID: 15239019.
Article24. Hughes IA. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia: transitional care. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2004; 14(Suppl A):S60–S66. PMID: 15135780.
Article25. Ravichandran R, Lafferty F, McGinniss MJ, Taylor HC. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia presenting as massive adrenal incidentalomas in the sixth decade of life: report of two patients with 21-hydroxylase deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996; 81:1776–1779. PMID: 8626833.
Article26. Wang J, Bissada MA, Williamson HO, Yakout H, Bissada NK. Adrenal tumors associated with inadequately treated congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Can J Urol. 2002; 9:1563–1564. PMID: 12121582.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of adrenocortical adenoma following long-term treatment in a patient with congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- A Case of Congenital Lipoid Adrenal Hyperplasia: Early Diagnosis by Using Computed Tomography
- Long-Term Outcomes of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
- Ultrasound Follow-Up of Testicular Adrenal Rest Tumors with Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: Report of Three Cases
- Management of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia