Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2010 Dec;3(4):194-198. 10.3342/ceo.2010.3.4.194.
Analysis of P1 Latency in Normal Hearing and Profound Sensorineural Hearing Loss
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. junlee@snu.ac.kr
- 2Sensory Organ Research Institute, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2049050
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2010.3.4.194
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
P1 is a robust positivity at a latency of 50-150 msec in the auditory evoked potential of young children. It has been reported that over the first 2-3 years of life, there is a rapid decrease of the latency and the mean P1 latency in adults with normal hearing is approximately 60 msec. This study was designed to evaluate the change of the P1 latency in Koreans with normal hearing according to age and to compare this with the P1 latency of young patients with profound sensorineural hearing loss before and/or after cochlear implantation.
METHODS
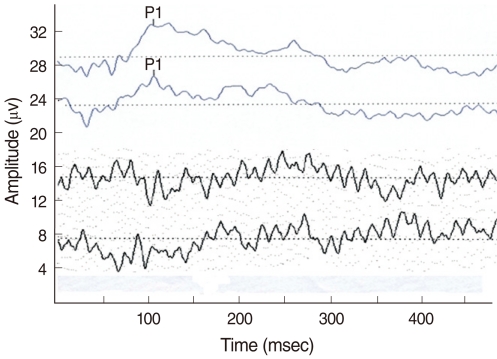
Among the patients who visited the Department of Otorhinolaryngology at Seoul National University Hospital from June 2007 to September 2009, the P1 response was recorded in 53 patients in the normal hearing group, in 13 patients in the pre-cochlear implantation (CI) group and in 10 patients in the post-CI group. A synthesized consonant-vowel syllable /ba/ was used to elicit the evoked responses. The evoked responses were collected using the center of the frontal head. For each subject, an individual grand average waveform was computed by averaging the ten recordings. The P1 latency was visually identified as a robust positivity in the waveform.
RESULTS
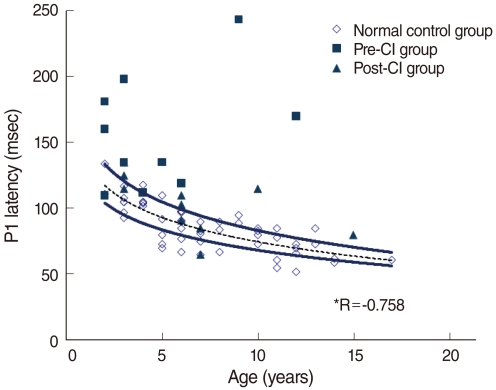
For the normal hearing group, the P1 latency showed the pattern of shortening as the age increased (coefficient, -0.758; P<0.001). For the pre-CI group, 10 cases showed delayed latencies and 3 cases did not show the P1 wave. For the post-CI group, the P1 latencies showed a less delayed tendency than those of the pre-CI group, but this was not statistically different.
CONCLUSION
This report provides the standard value of the P1 latency at each age in Koreans for the first time and the findings support that the maturation of the central auditory pathways could be measured objectively using the P1 latency.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kraus N, Smith DI, Reed NL, Stein LK, Cartee C. Auditory middle latency responses in children: effects of age and diagnostic category. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1985; 9. 62(5):343–351. PMID: 2411516.
Article2. Sharma A, Kraus N, McGee TJ, Nicol TG. Developmental changes in P1 and N1 central auditory responses elicited by consonant-vowel syllables. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1997; 11. 104(6):540–545. PMID: 9402896.
Article3. Ponton CW, Don M, Eggermont JJ, Waring MD, Kwong B, Masuda A. Auditory system plasticity in children after long periods of complete deafness. Neuroreport. 1996; 12. 8(1):61–65. PMID: 9051753.
Article4. Ponton CW, Don M, Eggermont JJ, Waring MD, Masuda A. Maturation of human cortical auditory function: differences between normal-hearing children and children with cochlear implants. Ear Hear. 1996; 10. 17(5):430–437. PMID: 8909891.
Article5. Ceponiene R, Cheour M, Naatanen R. Interstimulus interval and auditory event-related potentials in children: evidence for multiple generators. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1998; 7. 108(4):345–354. PMID: 9714376.6. Cunningham J, Nicol T, Zecker S, Kraus N. Speech-evoked neurophysiologic responses in children with learning problems: development and behavioral correlates of perception. Ear Hear. 2000; 12. 21(6):554–568. PMID: 11132782.
Article7. Ponton CW, Eggermont JJ, Kwong B, Don M. Maturation of human central auditory system activity: evidence from multi-channel evoked potentials. Clin Neurophysiol. 2000; 2. 111(2):220–236. PMID: 10680557.
Article8. Sharma A, Dorman M, Spahr A, Todd NW. Early cochlear implantation in children allows normal development of central auditory pathways. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl. 2002; 5. 189:38–41. PMID: 12018346.
Article9. Sharma A, Dorman MF, Spahr AJ. Rapid development of cortical auditory evoked potentials after early cochlear implantation. Neuroreport. 2002; 7. 19. 13(10):1365–1368. PMID: 12151804.
Article10. Sharma A, Dorman MF. Central auditory development in children with cochlear implants: clinical implications. Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 2006; 64:66–88. PMID: 16891837.11. Kaas JH, Hackett TA, Tramo MJ. Auditory processing in primate cerebral cortex. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1999; 4. 9(2):164–170. PMID: 10322185.
Article12. Dorman MF, Sharma A, Gilley P, Martin K, Roland P. Central auditory development: evidence from CAEP measurements in children fit with cochlear implants. J Commun Disord. 2007; Jul–Aug. 40(4):284–294. PMID: 17433357.
Article13. Sharma A, Dorman MF, Spahr AJ. A sensitive period for the development of the central auditory system in children with cochlear implants: implications for age of implantation. Ear Hear. 2002; 12. 23(6):532–539. PMID: 12476090.
Article14. Lee DS, Lee JS, Oh SH, Kim SK, Kim JW, Chung JK, et al. Cross-modal plasticity and cochlear implants. Nature. 2001; 1. 11. 409(6817):149–150. PMID: 11196628.
Article15. Lee HJ, Kang E, Oh SH, Kang H, Lee DS, Lee MC, et al. Preoperative differences of cerebral metabolism relate to the outcome of cochlear implants in congenitally deaf children. Hear Res. 2005; 5. 203(1-2):2–9. PMID: 15855024.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Rehabilitation of Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Hearing Aid
- Analysis of the Latency of Auditory Brainstem Response Wave V in Infants According to Age, Hearing Threshold and Stimulus Intensity
- A Case of Bilateral Cochlear Implants in Bilateral Profound Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss After COVID-19 Infection
- The Characteristics and the Changes of Tinnitus according to the Recovery of Hearing Loss in the Patients with Sudden Hearing Loss
- A Case of Idiopathic Sequential Profound Bilateral Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss Occurring 37 Days After Unilateral Presentation