Clin Endosc.
2014 Mar;47(2):155-161. 10.5946/ce.2014.47.2.155.
Predictors of Esophageal Stricture Formation Post Endoscopic Mucosal Resection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Mayo Clinic Florida, Jacksonville, FL, USA. wolfsen.herbert@mayo.edu
- 2Mercy Gilbert Medical Center, Chandler, AZ, USA.
- 3Department of Family Medicine, The Pennsylvania State University Medical Center, Hershey, PA, USA.
- 4Community Internal Medicine at Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL, USA.
- KMID: 2049003
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2014.47.2.155
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
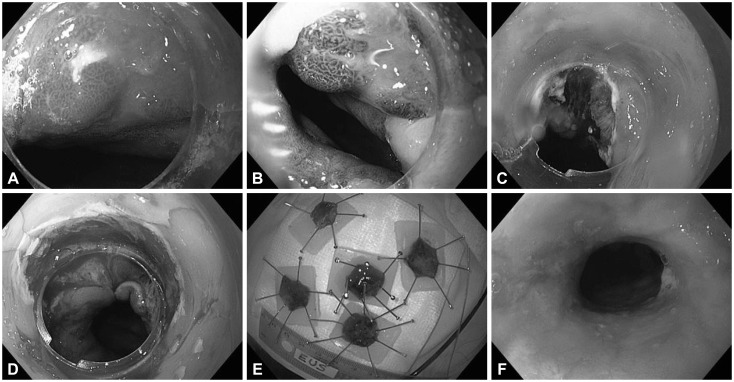
Stricture formation is a common complication after endoscopic mucosal resection. Predictors of stricture formation have not been well studied.
METHODS
We conducted a retrospective, observational, descriptive study by using a prospective endoscopic mucosal resection database in a tertiary referral center. For each patient, we extracted the age, sex, lesion size, use of ablative therapy, and detection of esophageal strictures. The primary outcome was the presence of esophageal stricture at follow-up. Multivariate logistic regression was used to analyze the association between the primary outcome and predictors.
RESULTS
Of 136 patients, 27% (n=37) had esophageal strictures. Thirty-two percent (n=44) needed endoscopic dilation to relieve dysphagia (median, 2; range, 1 to 8). Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that the size of the lesion excised is associated with increased odds of having a stricture (odds ratio, 1.6; 95% confidence interval, 1.1 to 2.3; p=0.01), when controlling for age, sex, and ablative modalities. Similarly, the number of lesions removed in the index procedure was associated with increased odds of developing a stricture (odds ratio, 2.3; 95% confidence interval, 1.3 to 4.2; p=0.007).
CONCLUSIONS
Stricture formation after esophageal endoscopic mucosal resection is common. Risk factors for stricture formation include large mucosal resections and the resection of multiple lesions on the initial procedure.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
When Is Pre-Emptive Treatment Necessary after Endoscopic Mucosal Resection of Early Esophageal Neoplasm?
Hyung Gil Kim
Clin Endosc. 2014;47(2):124-126. doi: 10.5946/ce.2014.47.2.124.
Reference
-
1. Brown LM, Devesa SS. Epidemiologic trends in esophageal and gastric cancer in the United States. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2002; 11:235–256. PMID: 12424848.
Article2. Vizcaino AP, Moreno V, Lambert R, Parkin DM. Time trends incidence of both major histologic types of esophageal carcinomas in selected countries, 1973-1995. Int J Cancer. 2002; 99:860–868. PMID: 12115489.
Article3. Clark GW, DeMeester TR. Surgical management of Barrett's esophagus. Ann Chir Gynaecol. 1995; 84:139–144. PMID: 7574371.4. Hölscher AH, Bollschweiler E, Schneider PM, Siewert JR. Early adenocarcinoma in Barrett's oesophagus. Br J Surg. 1997; 84:1470–1473. PMID: 9361616.
Article5. Pera M, Trastek VF, Carpenter HA, Allen MS, Deschamps C, Pairolero PC. Barrett's esophagus with high-grade dysplasia: an indication for esophagectomy? Ann Thorac Surg. 1992; 54:199–204. PMID: 1637206.
Article6. Pacifico RJ, Wang KK, Wongkeesong LM, Buttar NS, Lutzke LS. Combined endoscopic mucosal resection and photodynamic therapy versus esophagectomy for management of early adenocarcinoma in Barrett's esophagus. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003; 1:252–257. PMID: 15017665.
Article7. Ell C, May A, Pech O, et al. Curative endoscopic resection of early esophageal adenocarcinomas (Barrett's cancer). Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 65:3–10. PMID: 17185072.
Article8. Sampliner RE. Endoscopic therapy for Barrett's esophagus. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 7:716–720. PMID: 19306943.
Article9. Ganz RA, Overholt BF, Sharma VK, et al. Circumferential ablation of Barrett's esophagus that contains high-grade dysplasia: a U.S. Multicenter Registry. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 68:35–40. PMID: 18355819.10. Shaheen NJ, Overholt BF, Sampliner RE, et al. Durability of radiofrequency ablation in Barrett's esophagus with dysplasia. Gastroenterology. 2011; 141:460–468. PMID: 21679712.11. Soehendra N, Seewald S, Groth S, et al. Use of modified multiband ligator facilitates circumferential EMR in Barrett's esophagus (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 63:847–852. PMID: 16650552.
Article12. Lewis JJ, Rubenstein JH, Singal AG, Elmunzer BJ, Kwon RS, Piraka CR. Factors associated with esophageal stricture formation after endoscopic mucosal resection for neoplastic Barrett's esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 74:753–760. PMID: 21820109.
Article13. Wolfsen HC. Endoluminal therapy for esophageal disease: an introduction. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2010; 20:1–10. PMID: 19951790.
Article14. Greenwald BD, Dumot JA, Abrams JA, et al. Endoscopic spray cryotherapy for esophageal cancer: safety and efficacy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 71:686–693. PMID: 20363410.
Article15. Gross SA, Wolfsen HC. The role of photodynamic therapy in the esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2010; 20:35–53. PMID: 19951793.
Article16. Panossian AM, Raimondo M, Wolfsen HC. State of the art in the endoscopic imaging and ablation of Barrett's esophagus. Dig Liver Dis. 2011; 43:365–373. PMID: 21330224.
Article17. Wolfsen HC. Endoscopic ablation therapy: imaging and advanced technology in action. Gastroenterology. 2009; 137:1225–1228. PMID: 19703456.
Article18. Wolfsen HC, Hemminger LL, Wallace MB, Devault KR. Clinical experience of patients undergoing photodynamic therapy for Barrett's dysplasia or cancer. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004; 20:1125–1131. PMID: 15569115.
Article19. Shaheen NJ, Sharma P, Overholt BF, et al. Radiofrequency ablation in Barrett's esophagus with dysplasia. N Engl J Med. 2009; 360:2277–2288. PMID: 19474425.20. Schlemper RJ, Riddell RH, Kato Y, et al. The Vienna classification of gastrointestinal epithelial neoplasia. Gut. 2000; 47:251–255. PMID: 10896917.
Article21. Pech O, Behrens A, May A, et al. Long-term results and risk factor analysis for recurrence after curative endoscopic therapy in 349 patients with high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia and mucosal adenocarcinoma in Barrett's oesophagus. Gut. 2008; 57:1200–1206. PMID: 18460553.
Article22. Pouw RE, Seewald S, Gondrie JJ, et al. Stepwise radical endoscopic resection for eradication of Barrett's oesophagus with early neoplasia in a cohort of 169 patients. Gut. 2010; 59:1169–1177. PMID: 20525701.
Article23. Prasad GA, Wu TT, Wigle DA, et al. Endoscopic and surgical treatment of mucosal (T1a) esophageal adenocarcinoma in Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2009; 137:815–823. PMID: 19524578.
Article24. Seewald S, Ang TL, Gotoda T, Soehendra N. Total endoscopic resection of Barrett esophagus. Endoscopy. 2008; 40:1016–1020. PMID: 19065485.
Article25. Prasad GA, Wang KK, Buttar NS, Wongkeesong LM, Lutzke LS, Borkenhagen LS. Predictors of stricture formation after photodynamic therapy for high-grade dysplasia in Barrett's esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 65:60–66. PMID: 17185080.
Article26. Chung A, Bourke MJ, Hourigan LF, et al. Complete Barrett's excision by stepwise endoscopic resection in short-segment disease: long term outcomes and predictors of stricture. Endoscopy. 2011; 43:1025–1032. PMID: 22068701.
Article27. Katada C, Muto M, Manabe T, Boku N, Ohtsu A, Yoshida S. Esophageal stenosis after endoscopic mucosal resection of superficial esophageal lesions. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 57:165–169. PMID: 12556777.
Article28. Peters FP, Kara MA, Rosmolen WD, et al. Stepwise radical endoscopic resection is effective for complete removal of Barrett's esophagus with early neoplasia: a prospective study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006; 101:1449–1457. PMID: 16863545.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Complications of endoscopic resection in the upper gastrointestinal tract
- Mucosal Resection in the Corrosive Esophageal Stricture: A new technique
- Endoscopic Resection for the Treatment of Superficial Esophageal Neoplasms
- Successful Endoscopic Mucosal Resection of a Low Esophageal Carcinoid Tumor
- Endoscopic Treatment for Esophageal Cancer