Anat Cell Biol.
2015 Mar;48(1):62-65. 10.5115/acb.2015.48.1.62.
Variations of the cubital superficial vein investigated by using the intravenous illuminator
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. ijchoi@dsmc.or.kr
- 2Department of Emergency Medicine, Dongsan Medical Center, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2046076
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2015.48.1.62
Abstract
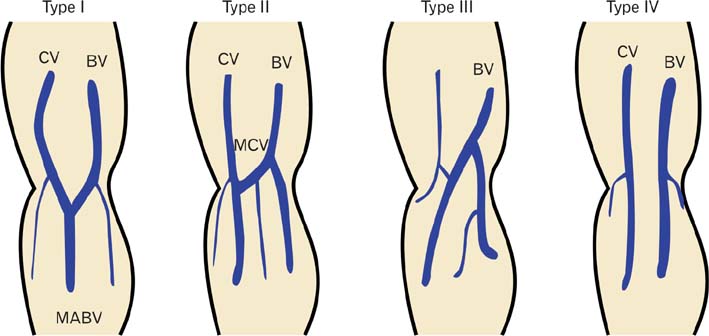
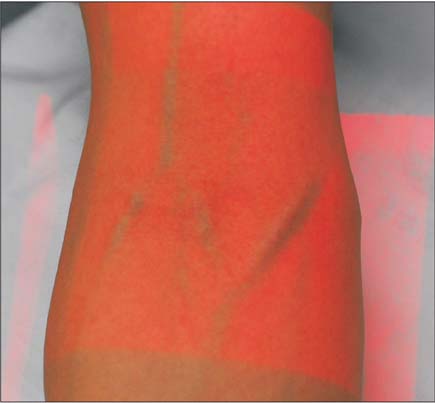
- The purpose of this study was to report variations of the cubital superficial vein patterns in the Korean subjects, which was investigated by using venous illuminator, AccuVein. The 200 Korean subjects were randomly chosen from the patients and staff of the Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center in Daegu, Korea. After excluding the inappropriate cases for detecting venous pattern, we collected 174 cases of right upper limbs and 179 cases of left upper limbs. The superficial veins of the cubital fossa were detected and classified into four types according to the presence of the median cubital vein (MCV) or median antebrachial vein. The type II, presenting the both cephalic and basilic vein connected by the MCV, was most common (177 upper limbs, 50.1%). Although the most common type in male and female was different as type I (108 upper limbs, 49.3%) and type II (75 upper limbs, 56.0%), respectively, statistical significance was not detected (P=0.241). The frequency of the each types between right and left upper limbs was also not different (P=0.973). Among 154 subjects who were observed the venous pattern in the both upper limbs, 76 subjects (49.3%) had the same venous pattern. Using AccuVein to investigate the venous pattern has an advantage of lager scale examination compared to the cadaver study. Our results might be helpful for medical practitioner to be aware of the variation of the superficial cubital superficial vein.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Patterns of superficial veins in the cubital fossa and its clinical implications among southern Ethiopian population
Tesfaye Melaku, Habtamu Wondmagegn, Abinet Gebremickael, Amanuel Tadesse
Anat Cell Biol. 2022;55(2):148-152. doi: 10.5115/acb.21.217.
Reference
-
1. Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AM. Clinically oriented anatomy. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2013.2. Warwick R, Williams PL. Gray's anatomy. Edinburgh: Longman;1973.3. Newman BH, Pichette S, Pichette D, Dzaka E. Adverse effects in blood donors after whole-blood donation: a study of 1000 blood donors interviewed 3 weeks after whole-blood donation. Transfusion. 2003; 43:598–603.4. Newman BH, Waxman DA. Blood donation-related neurologic needle injury: evaluation of 2 years' worth of data from a large blood center. Transfusion. 1996; 36:213–215.5. Dharap AS, Shaharuddin MY. Patterns of superficial veins of the cubital fossa in Malays. Med J Malaysia. 1994; 49:239–241.6. Mikuni Y, Chiba S, Tonosaki Y. Topographical anatomy of superficial veins, cutaneous nerves, and arteries at venipuncture sites in the cubital fossa. Anat Sci Int. 2013; 88:46–57.7. Ukoha UU, Oranusi CK, Okafor JI, Ogugua PC, Obiaduo AO. Patterns of superficial venous arrangement in the cubital fossa of adult Nigerians. Niger J Clin Pract. 2013; 16:104–109.8. Yamada K, Yamada K, Katsuda I, Hida T. Cubital fossa venipuncture sites based on anatomical variations and relationships of cutaneous veins and nerves. Clin Anat. 2008; 21:307–313.9. Wasfi FA, Dabbagh AW, AlAthari FM, Salman SS. Biostatistical study on the arrangement of the superficial veins of the cubital fossa in Iraqis. Acta Anat (Basel). 1986; 126:183–186.10. Hess HA. A biomedical device to improve pediatric vascular access success. Pediatr Nurs. 2010; 36:259–263.11. Kaddoum RN, Anghelescu DL, Parish ME, Wright BB, Trujillo L, Wu J, Wu Y, Burgoyne LL. A randomized controlled trial comparing the AccuVein AV300 device to standard insertion technique for intravenous cannulation of anesthetized children. Paediatr Anaesth. 2012; 22:884–889.12. Kim MJ, Park JM, Rhee N, Je SM, Hong SH, Lee YM, Chung SP, Kim SH. Efficacy of VeinViewer in pediatric peripheral intravenous access: a randomized controlled trial. Eur J Pediatr. 2012; 171:1121–1125.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Patterns of superficial veins in the cubital fossa and its clinical implications among southern Ethiopian population
- Unilateral external jugular vein fenestration with variant anatomy of the retromandibular and facial vein
- Use of the frontal branch of the superficial temporal artery and the postauricular vein to overcome anatomic variations of superficial temporal vessels in scalp reconstruction with free tissue transfer: a case report
- A case of potentially lethal vascular variation in association with palmaris profundus muscle
- Endovascular Treatment of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula via Radial Artery and Median Cubital Vein