J Adv Prosthodont.
2009 Jul;1(2):75-84. 10.4047/jap.2009.1.2.75.
Histologic evaluation and removal torque analysis of nano- and microtreated titanium implants in the dogs
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, Graduate school, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea. psw320@chonnam.ac.kr
- KMID: 2045467
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2009.1.2.75
Abstract
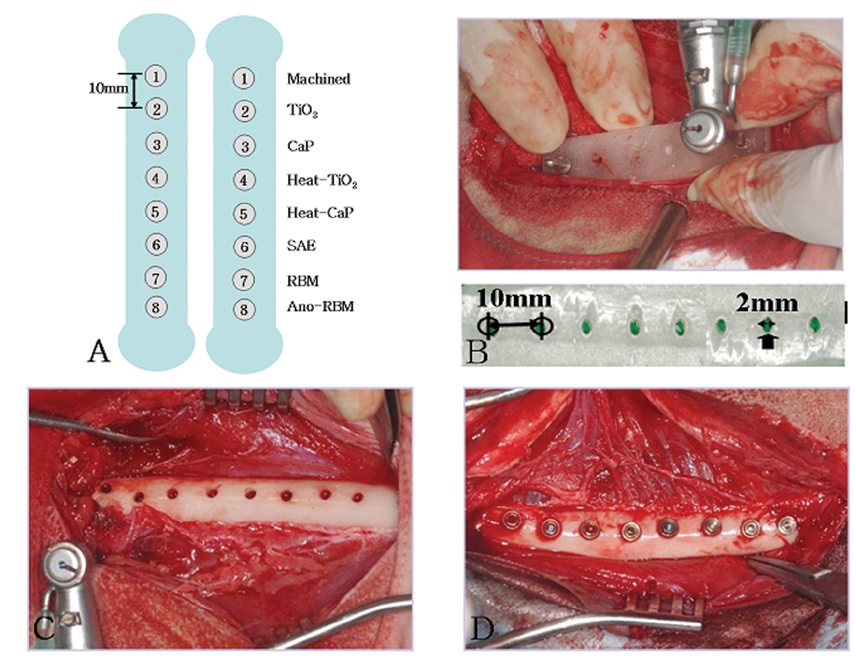
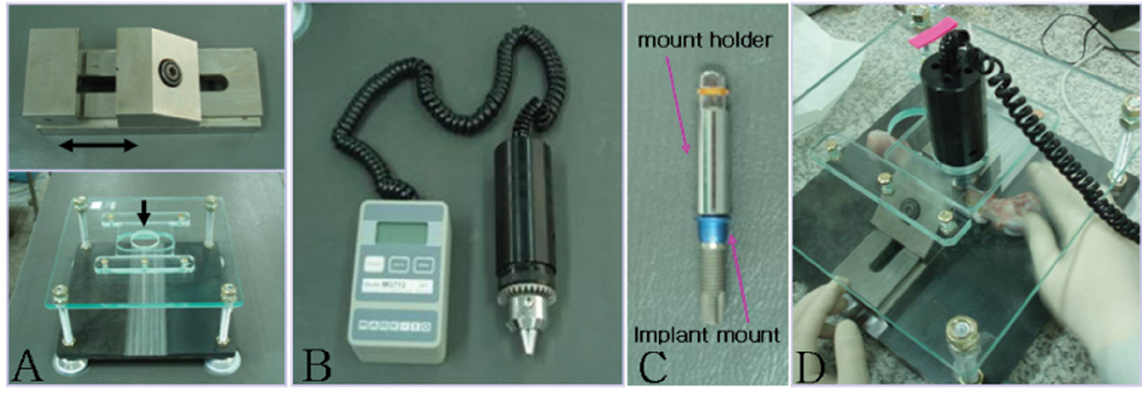
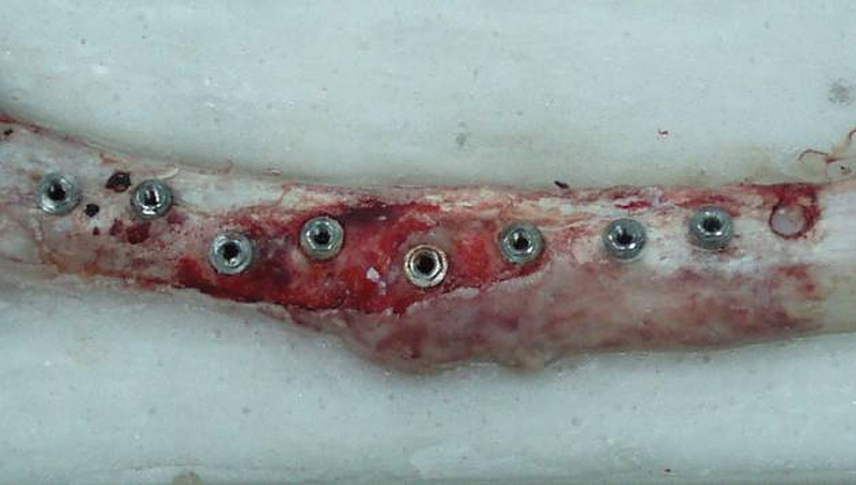
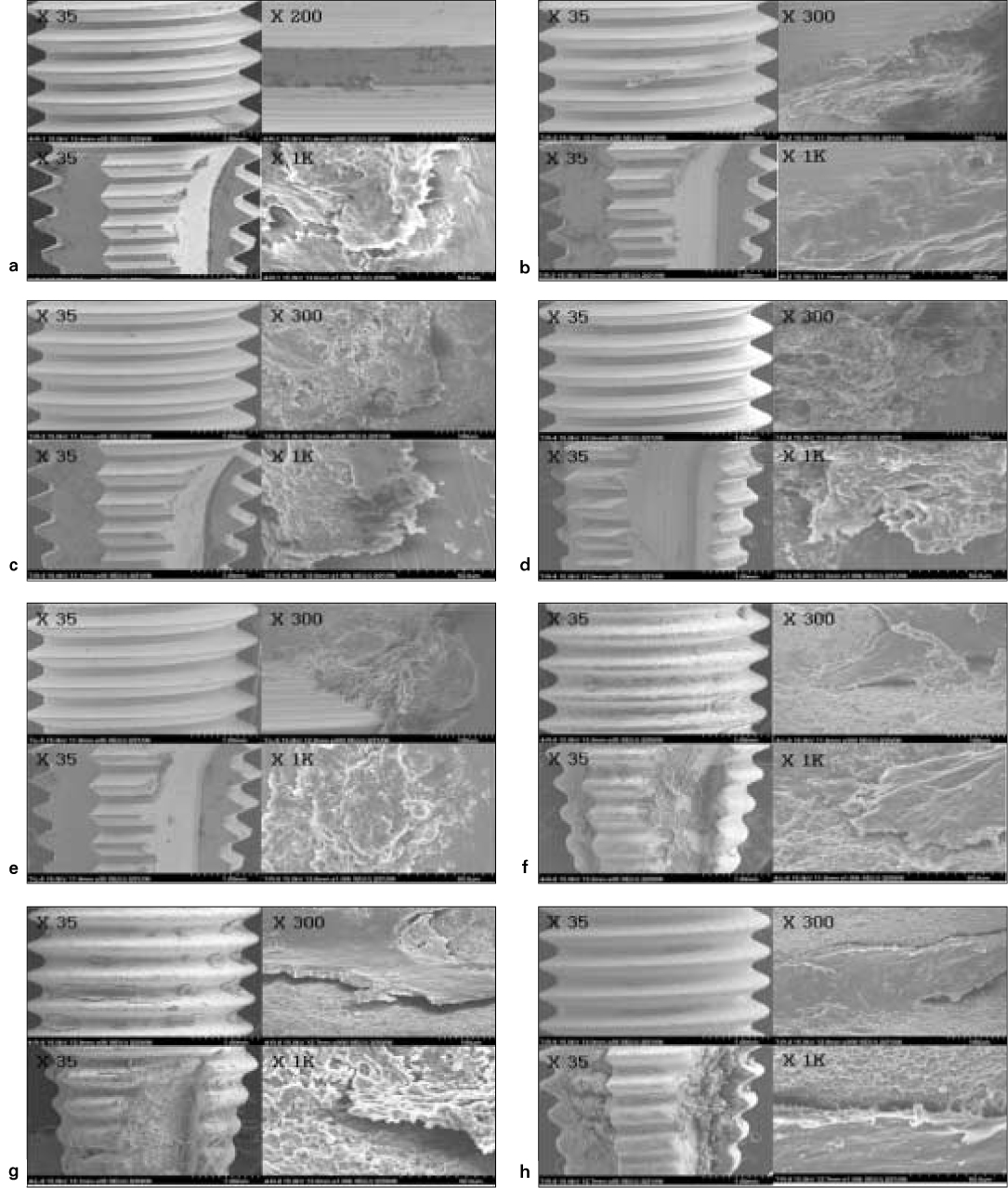
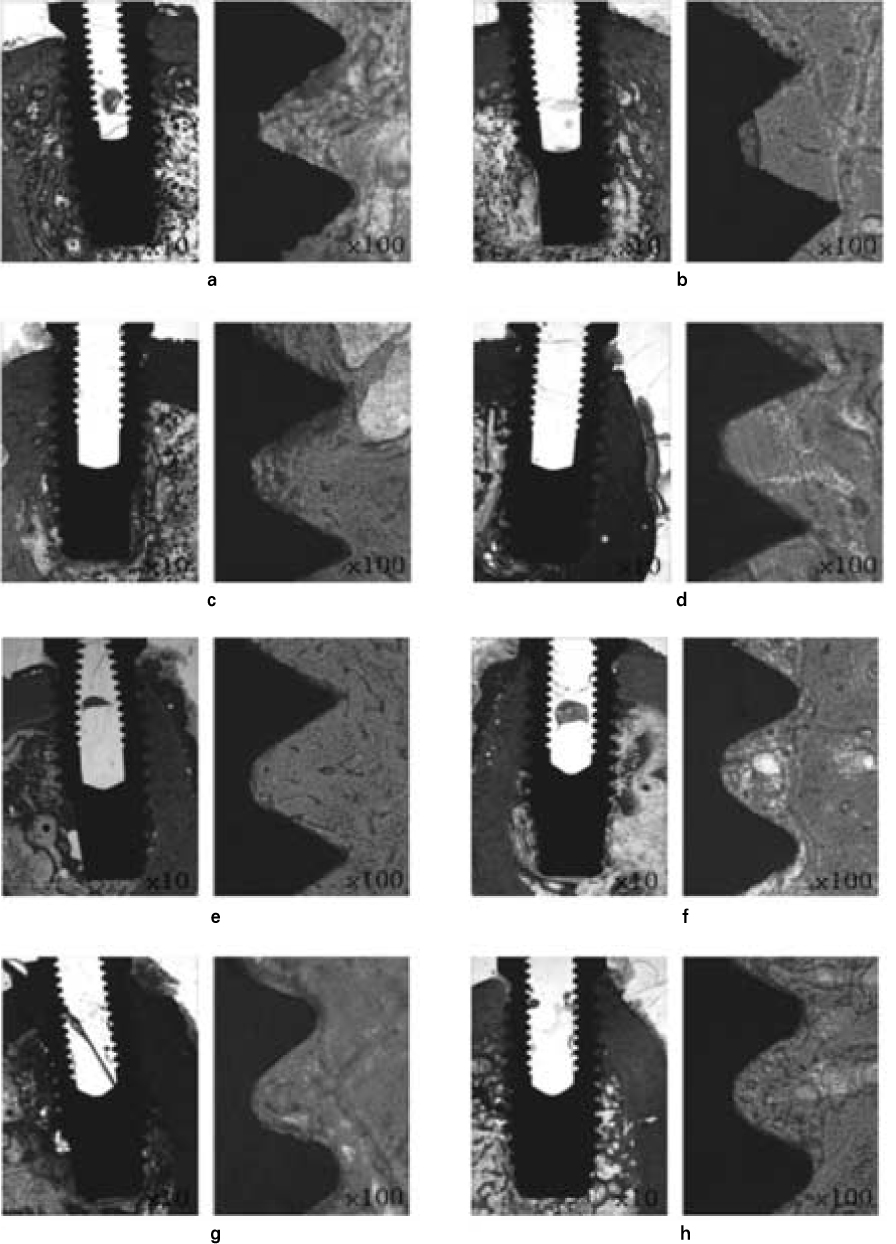
- STATEMENT OF PROBLEM: A number of studies about the nano-treated surfaces of implants have been conducting along with micro-treated surfaces of implants. PURPOSE: The purpose of this study was to get information for the clinical use of nano-treated surfaces compared with micro-treated surfaces by measuring removal torque and analyzing histological characteristics after the placement of various surface-treated implants on femurs of dogs. MATERIAL AND METHODS: Machined surface implants were used as a control group. 4 nano-treated surface implants and 3 micro-treated surface implants [resorbable blast media surface (RBM), sandblast and acid-etched surface (SAE), anodized RBM surface] were used as experimental groups. Removal torque values of implants were measured respectively and the histological analyses were conducted on both 4weeks and 8weeks after implant surgery. The surfaces of removed implants after measuring removal torque values were observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) at 8 weeks. RESULTS: 1. Removal torque values of the nano-treated groups were lower than those of micro-treated groups. 2. Removal torque values were similar in the anodized RBM surface groups. 3. On the histological views, there was much of bone formation at 8 weeks, but there was no difference between 4 and 8 weeks, and between the types of implant surfaces as well. CONCLUSION: It is suggested that implant topography is more effective in removal torque test than surface chemistry. To get better clinical result, further studies should be fulfilled on the combined effect of surface topography and chemistry for the implant surface treatments.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Li DH, Liu BL, Zou JC, Xu KW. Improvement of osseointegration of titanium dental implants by a modified sandblasting surface treatment: an in vivo interfacial biomechanics study. Implant Dent. 1999. 8:289–294.2. Buser D, Schenk RK, Steinemann S, Fiorellini JP, Fox CH, Stich H. Influence of surface characteristics on bone integration of titanium implants. A histomorphometric study in miniature pigs. J Biomed Mater Res. 1991. 25:889–902.3. Bowers KT, Keller JC, Randolph BA, Wick DG, Michaels CM. Optimization of surface micromorphology for enhanced osteoblast responses in vitro. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1992. 7:302–310.4. Brunette DM. The effects of implant surface topography on the behavior of cells. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1988. 3:231–246.5. Mustafa K, Silva Lopez B, Hultenby K, Wennerberg A, Arvidson K. Attachment and proliferation of human oral fibroblasts to titanium surfaces blasted with TiO2 particles. A scanning electron microscopic and histomorphometric analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1998. 9:195–207.6. Johansson C, Albrektsson T. Integration of screw implants in the rabbit: a 1-year follow-up of removal torque of titanium implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1987. 2:69–75.7. Han CH, Johansson CB, Wennerberg A, Albrektsson T. Quantitative and qualitative investigations of surface enlarged titanium and titanium alloy implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1998. 9:1–10.8. Wennerberg A, Albrektsson T, Johansson C, Andersson B. Experimental study of turned and grit-blasted screw-shaped implants with special emphasis on effects of blasting material and surface topography. Biomaterials. 1996. 17:15–22.9. Ericsson I, Johansson CB, Bystedt H, Norton MR. A histomorphometric evaluation of bone-to-implant contact on machine-prepared and roughened titanium dental implants. A pilot study in the dog. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1994. 5:202–206.10. Larsson C, Thomsen P, Aronsson BO, Rodahl M, Lausmaa J, Kasemo B, Ericson LE. Bone response to surface-modified titanium implants: studies on the early tissue response to machined and electropolished implants with different oxide thicknesses. Biomaterials. 1996. 17:605–616.11. Sul YT, Johansson CB, Jeong Y, Wennerberg A, Albrektsson T. Resonance frequency and removal torque analysis of implants with turned and anodized surface oxides. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2002. 13:252–259.12. Letić-Gavrilović A, Scandurra R, Abe K. Genetic potential of interfacial guided osteogenesis in implant devices. Dent Mater J. 2000. 19:99–132.13. Novaes AB Jr, Souza SL, de Oliveira PT, Souza AM. Histomorphometric analysis of the bone-implant contact obtained with 4 different implant surface treatments placed side by side in the dog mandible. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2002. 17:377–383.14. Ivanoff CJ, Hallgren C, Widmark G, Sennerby L, Wennerberg A. Histologic evaluation of the bone integration of TiO(2) blasted and turned titanium microimplants in humans. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2001. 12:128–134.15. Ivanoff CJ, Widmark G, Johansson C, Wennerberg A. Histologic evaluation of bone response to oxidized and turned titanium micro-implants in human jawbone. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2003. 18:341–348.16. Sul YT. The significance of the surface properties of oxidized titanium to the bone response: special emphasis on potential biochemical bonding of oxidized titanium implant. Biomaterials. 2003. 24:3893–3907.17. Thomas KA, Kay JF, Cook SD, Jarcho M. The effect of surface macrotexture and hydroxylapatite coating on the mechanical strengths and histologic profiles of titanium implant materials. J Biomed Mater Res. 1987. 21:1395–1414.18. Carlsson L, Röstlund T, Albrektsson B, Albrektsson T. Removal torques for polished and rough titanium implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1988. 3:21–24.19. Webster TJ, Ergun C, Doremus RH, Siegel RW, Bizios R. Enhanced functions of osteoblasts on nanophase ceramics. Biomaterials. 2000. 21:1803–1810.20. Webster TJ, Schadler LS, Siegel RW, Bizios R. Mechanisms of enhanced osteoblast adhesion on nanophase alumina involve vitronectin. Tissue Eng. 2001. 7:291–301.21. Berglundh T, Abrahamsson I, Lang NP, Lindhe J. De novo alveolar bone formation adjacent to endosseous implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2003. 14:251–262.22. Ericsson I, Johansson CB, Bystedt H, Norton MR. A histomorphometric evaluation of bone-to-implant contact on machine-prepared and roughened titanium dental implants. A pilot study in the dog. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1994. 5:202–206.23. Schatzker J, Horne JG, Sumner-Smith G. The effect of movement on the holding power of screws in bone. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1975. 111:257–262.24. Albrektsson T, Lekholm U. Osseointegration: current state of the art. Dent Clin North Am. 1989. 33:537–554.25. Misch CE. Density of bone: effect on treatment plans, surgical approach, healing, and progressive boen loading. Int J Oral Implantol. 1990. 6:23–31.26. Glauser R, Lundgren AK, Gottlow J, Sennerby L, Portmann M, Ruhstaller P, Hämmerle CH. Immediate occlusal loading of Brånemark TiUnite implants placed predominantly in soft bone: 1-year results of a prospective clinical study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2003. 5:47–56.27. Olsson M, Urde G, Andersen JB, Sennerby L. Early loading of maxillary fixed cross-arch dental prostheses supported by six or eight oxidized titanium implants: results after 1 year of loading, case series. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2003. 5:81–87.28. Oh SH, Finõnes RR, Daraio C, Chen LH, Jin S. Growth of nanoscale hydroxyapatite using chemically treated titanium oxide nanotubes. Biomaterials. 2005. 26:4938–4943.29. Karlsson M, Pålsgård E, Wilshaw PR, Di Silvio L. Initial in vitro interaction of osteoblasts with nano-porous alumina. Biomaterials. 2003. 24:3039–3046.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of removal torque of saline-soaking RBM implants and RBM implants in rabbit tibias
- Comparison of histologic observation and insertional and removal torque values between titanium grade 2 and 4 microimplants
- Healing of the bone around pure titanium implants without primary bone contact
- Quantitative investigations of titanium alloy implants
- On the effect of saline immersion to the removal torque for resorbable blasting media and acid treated implants