J Clin Neurol.
2009 Sep;5(3):149-150. 10.3988/jcn.2009.5.3.149.
Common Carotid Artery Agenesis: Duplex Ultrasonographic Findings
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. swhan@paik.ac.kr
- KMID: 2045422
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2009.5.3.149
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
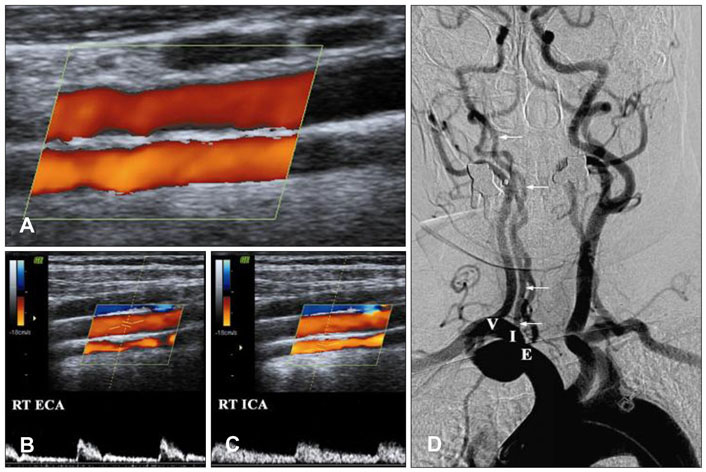
Agenesis of the common carotid artery (CCA) resulting in separation of the origin of the external carotid artery (ECA) and internal carotid artery (ICA) from the aortic arch is rare. Fewer than 25 cases have been reported, and correlative ultrasound data were available for only 1 of them. CASE REPORT: A 52-year-old woman visited the hospital with a 3-day history of vertigo and headache. Color-coded duplex ultrasonography performed to evaluate the carotid and vertebral arteries revealed a normal configuration on the left side. However, the right CCA could not be found; instead, there were two vessels of approximately equal size in close proximity to each other. The cerebral angiographic findings were consistent with the ultrasonographic findings. The ECA and ICA originated directly from the brachiocephalic trunk, and the ECA arose proximal to the ICA. CONCLUSIONS: The ultrasonographic findings revealed absence of the CCA, the ECA and ICA originating separately from the aortic arch. Color-coded duplex ultrasonography appears to be an effective and sensitive method for detecting absence of the CCA. These findings should help to further our understanding of the embryologic development of the carotid arteries.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Right and left common carotid arteries arising from the branchiocephalic, a rare variation of the aortic arch
Eleni Panagouli, Gregory Tsoucalas, Theodoros Papaioannou, Aliki Fiska, Dionysios Venieratos, Panagiotis Skandalakis
Anat Cell Biol. 2018;51(3):215-217. doi: 10.5115/acb.2018.51.3.215.
Reference
-
1. Woodruff WW 3rd, Strunsky VP, Brown NJ. Separate origins of the left internal and external carotid arteries directly from the aortic arch: duplex sonographic findings. J Ultrasound Med. 1995. 14:867–869.
Article2. Maybody M, Uszynski M, Morton E, Vitek JJ. Absence of common carotid artery: a rare vascular anomaly. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003. 24:711–713.3. Simons D, Patetsios P, Moglia R, Dietz P. A case of congenital absence of the right common carotid artery: a rare embryologic anomaly. Journal for Vascular Ultrasound. 2003. 27:106–109.
Article4. Purkayastha S, Gupta AK, Varma DR, Bodhey NK, Vattoth S. Absence of the left common carotid artery with cervical origin of the right subclavian artery. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006. 27:708–711.5. Lie TA. Congenital anomalies of the carotid arteries. 1968. Amsterdam: Excepta Medica Foundation.6. Beach KW, Strandness DE Jr. Carotid artery velocity waveform ansVascular Disease. 1985. St. Louis: Mosby;410–413.7. Faggioli GL, Testi G, Ferri M, Rossi C, Stella A. Common carotid agenesis and internal carotid stenting. Int Angiol. 2007. 26:290–291.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Unique Ultrasonographic Finding of Carotid Thrombus in a Patient with Acute Cardiogenic Cerebral Infarction
- Hypoplasia of the Internal Carotid Artery: Duplex Ultrasonographic Findings
- Bilateral Agenesis of the Internal Carotid Artery: Case Report
- Carotid duplex ultrasound: interpretations and clinical applications
- Overestimation of Carotid Artery Stenosis by Carotid Duplex Ultrasonography Due to Contralateral Occlusion