J Korean Soc Radiol.
2014 Apr;70(4):261-268. 10.3348/jksr.2014.70.4.261.
Impact of the New International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer Staging System in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: With Comparison to the Union for International Cancer Control 6th Tumor, Node, Metastasis Edition
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Mokdong Hospital, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sinisim@ewha.ac.kr
- 2Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Mokdong Hospital, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2041936
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2014.70.4.261
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To investigate the impact of the proposed International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC) tumor, node, metastasis (TNM) system on staging and outcome of non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
With a total of 501 NSCLC patients with staging according to Union for International Cancer Control (UICC), 6th TNM (TNM-6) were reclassified according to the IASLC proposed TNM staging (TNM-7). The impact of TNM-7 in comparison with TNM-6 was evaluated at three levels: change in substage, staging, and outcome. The outcome measure was to compare the stage-specific overall survival of NSCLC between the two groups of patients.
RESULTS
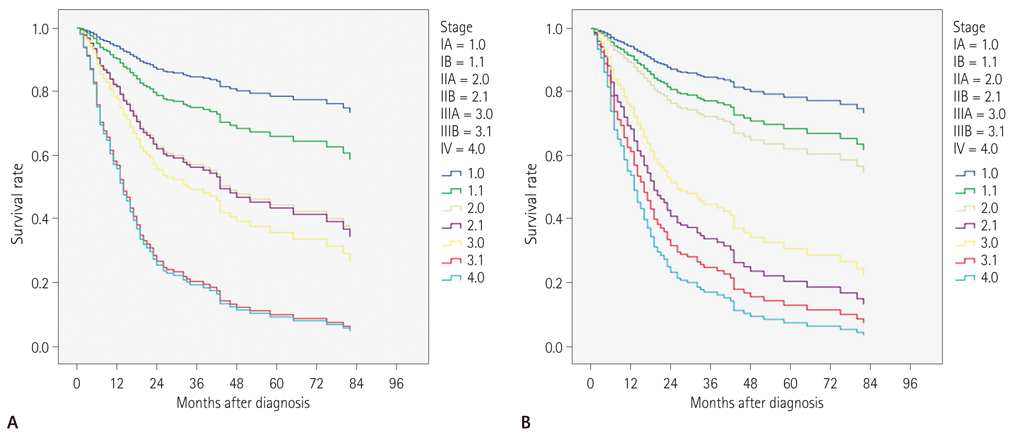
A total of 214 (42.7%) patients had changed TNM staging, and 101 (20.2%) patients had changed stage groupings in TNM-7 compared to TNM-6. Among 100 patients showing changed stage grouping, 72 (14.4%) showed upstage and 29 (5.8%) demonstrated downstage. The TNM-7 system resulted in better separation of survival curves among stage-specific NSCLC than TNM-6 system, especially in separation of stage IIA vs. IIB (p = 0.023) and stage IIIB vs. IV (p < 0.001).
CONCLUSION
TNM-7 for lung cancer appears to be superior in defining stage-specific survival groups than TNM-6, especially between stage IIA vs. stage IIB and stage IIIB vs. stage IV.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jung KW, Park S, Won YJ, Kong HJ, Lee JY, Seo HG, et al. Prediction of cancer incidence and mortality in Korea, 2012. Cancer Res Treat. 2012; 44:25–31.2. Rami-Porta R, Crowley JJ, Goldstraw P. The revised TNM staging system for lung cancer. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2009; 15:4–9.3. Kim ES, Bosquée L. The importance of accurate lymph node staging in early and locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer: an update on available techniques. J Thorac Oncol. 2007; 2:Suppl 2. S59–S67.4. Mountain CF, Carr DT, Anderson WA. A system for the clinical staging of lung cancer. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1974; 120:130–138.5. Rami-Porta R, Ball D, Crowley J, Giroux DJ, Jett J, Travis WD, et al. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: proposals for the revision of the T descriptors in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the TNM classification for lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2007; 2:593–602.6. Fukui T, Mori S, Hatooka S, Shinoda M, Mitsudomi T. Prognostic evaluation based on a new TNM staging system proposed by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer for resected non-small cell lung cancers. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008; 136:1343–1348.7. Kameyama K, Takahashi M, Ohata K, Igai H, Yamashina A, Matsuoka T, et al. Evaluation of the new TNM staging system proposed by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer at a single institution. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2009; 137:1180–1184.8. Chien CR, Yang ST, Chen CY, Fang HY, Tu CY, Tseng GC, et al. Impact of the new lung cancer staging system for a predominantly advanced-disease patient population. J Thorac Oncol. 2010; 5:340–343.9. Ruffini E, Filosso PL, Bruna MC, Coni F, Cristofori RC, Mossetti C, et al. Recommended changes for T and N descriptors proposed by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer - Lung Cancer Staging Project: a validation study from a single-centre experience. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2009; 36:1037–1044.10. Ou SH, Zell JA. Validation study of the proposed IASLC staging revisions of the T4 and M non-small cell lung cancer descriptors using data from 23,583 patients in the California Cancer Registry. J Thorac Oncol. 2008; 3:216–227.11. Ou SH, Zell JA, Ziogas A, Anton-Culver H. Prognostic factors for survival of stage I nonsmall cell lung cancer patients: a population-based analysis of 19,702 stage I patients in the California Cancer Registry from 1989 to 2003. Cancer. 2007; 110:1532–1541.12. Port JL, Kent MS, Korst RJ, Libby D, Pasmantier M, Altorki NK. Tumor size predicts survival within stage IA non-small cell lung cancer. Chest. 2003; 124:1828–1833.13. Rena O, Massera F, Robustellini M, Papalia E, Delfanti R, Lisi E, et al. Use of the proposals of the international association for the study of lung cancer in the forthcoming edition of lung cancer staging system to predict long-term prognosis of operated patients. Cancer J. 2010; 16:176–181.14. Zell JA, Ignatius Ou SH, Ziogas A, Anton-Culver H. Validation of the proposed International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer non-small cell lung cancer staging system revisions for advanced bronchioloalveolar carcinoma using data from the California Cancer Registry. J Thorac Oncol. 2007; 2:1078–1085.15. Baltayiannis N, Chandrinos M, Anagnostopoulos D, Zarogoulidis P, Tsakiridis K, Mpakas A, et al. Lung cancer surgery: an up to date. J Thorac Dis. 2013; 5:Suppl 4. S425–S439.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer Lymph Node Map: A Radiologic Atlas and Review
- Tumor Size Evaluation according to the T Component of the Seventh Edition of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer's TNM Classification: Interobserver Agreement between Radiologists and Computer-Aided Diagnosis System in Patients with Lung Cancer
- Newly Revised Lung Cancer Staging System and Survival in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients
- Staging of Lung Cancer
- The Comparison between 6th and 7th International Union Against Cancer/American Joint Committee on Cancer Classification for Survival Prognosis of Gastric Cancer