J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2015 Aug;50(4):313-319. 10.4055/jkoa.2015.50.4.313.
A Comparative Study of Subcutaneous versus Intra-Articular Indwelling Closed Suction Drainage after Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Gangneung Asan Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung, Korea. hyunil@gnah.co.kr
- KMID: 2035868
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2015.50.4.313
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to compare the drainage amount, total blood loss, and clinical results between two different positions of suction drainage after total knee arthroplasty.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
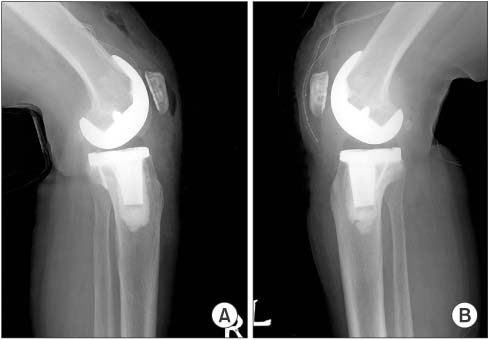
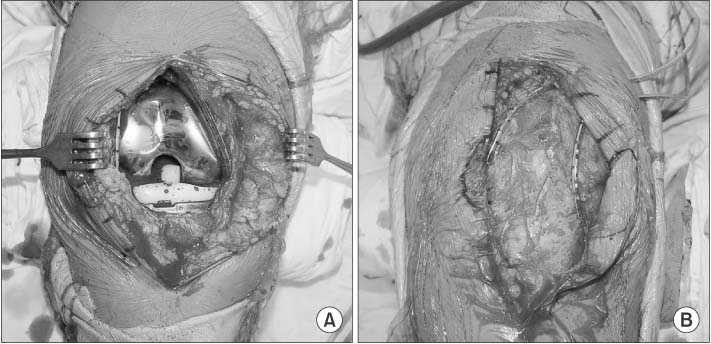
A total of 100 patients who underwent one stage bilateral total knee arthroplasty were enrolled. In experiment 1 with 50 patients, we compared the drainage amount, pain, range of motion, and complications of the leg whose suction drain was inserted into the joint cavity with those of the contralateral leg whose suction drain was inserted in subcutaneous tissue. Another 50 patients of experiment 2 had suction drainage in the joint cavity of both legs and the total blood loss (sum of drainage output, exudates, and hematoma of subcutaneous tissue and joint) was calculated and compared with that of experiment 1.
RESULTS
In experiment 1, the drainage amount was less in the leg with suction drainage in subcutaneous tissue compared with the contralateral leg with suction drainage in the joint cavity (p<0.001). However, the postoperative joint pain was significantly different only on post-operative day 2 between two legs. In experiment 2, there was no significant difference in the total blood loss between the two groups.
CONCLUSION
Although the drainage amount was less in the leg whose suction drain was kept in subcutaneous tissue compared with the contralateral leg whose suction drain was in the joint cavity, the total blood loss and the clinical results were not significantly different according to the position of the suction drain. Therefore, we can conclude that the subcutaneous position of the suction drain did not yield superior results.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim YH, Cho SH, Kim RS. Drainage versus nondrainage in simultaneous bilateral total knee arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998; 347:188–193.
Article2. Ovadia D, Luger E, Bickels J, Menachem A, Dekel S. Efficacy of closed wound drainage after total joint arthroplasty. A prospective randomized study. J Arthroplasty. 1997; 12:317–321.3. Niskanen RO, Korkala OL, Haapala J, Kuokkanen HO, Kaukonen JP, Salo SA. Drainage is of no use in primary uncomplicated cemented hip and knee arthroplasty for osteoarthritis: a prospective randomized study. J Arthroplasty. 2000; 15:567–569.4. Parker MJ, Roberts CP, Hay D. Closed suction drainage for hip and knee arthroplasty. A meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004; 86:1146–1152.5. Seo ES, Yoon SW, Koh IJ, Chang CB, Kim TK. Subcutaneous versus intraarticular indwelling closed suction drainage after TKA: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010; 468:2168–2176.
Article6. Mercuriali F, Inghilleri G. Proposal of an algorithm to help the choice of the best transfusion strategy. Curr Med Res Opin. 1996; 13:465–478.
Article7. Charrois O, Kahwaji A, Vastel L, Rosencher N, Courpied JP. Blood loss in total hip arthroplasty for rapidly destructive coxarthrosis. Int Orthop. 2001; 25:22–24.
Article8. Irisson E, Hémon Y, Pauly V, Parratte S, Argenson JN, Kerbaul F. Tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and financial cost in primary total hip and knee replacement surgery. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012; 98:477–483.
Article9. Reina N, Geiss L, Pailhé R, Maubisson L, Laffosse JM, Chiron P. Traumax screw plate vs Gamma nail. Blood loss in pertrochanteric fractures treated by minimally invasive osteosynthesis. Hip Int. 2014; 24:200–205.
Article10. Ritter MA, Keating EM, Faris PM. Closed wound drainage in total hip or total knee replacement. A prospective, randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994; 76:35–38.
Article11. Jenny JY, Boeri C, Lafare S. No drainage does not increase complication risk after total knee prosthesis implantation: a prospective, comparative, randomized study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2001; 9:299–301.
Article12. Reilly TJ, Gradisar IA Jr, Pakan W, Reilly M. The use of postoperative suction drainage in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986; 208:238–242.
Article13. Crevoisier XM, Reber P, Noesberger B. Is suction drainage necessary after total joint arthroplasty? A prospective study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1998; 117:121–124.14. Kumar S, Penematsa S, Parekh S. Are drains required following a routine primary total joint arthroplasty? Int Orthop. 2007; 31:593–596.
Article15. Farrar JT, Young JP Jr, LaMoreaux L, Werth JL, Poole RM. Clinical importance of changes in chronic pain intensity measured on an 11-point numerical pain rating scale. Pain. 2001; 94:149–158.
Article16. Holm B, Kristensen MT, Bencke J, Husted H, Kehlet H, Bandholm T. Loss of knee-extension strength is related to knee swelling after total knee arthroplasty. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2010; 91:1770–1776.
Article17. Mizner RL, Snyder-Mackler L. Altered loading during walking and sit-to-stand is affected by quadriceps weakness after total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Res. 2005; 23:1083–1090.
Article18. Beer KJ, Lombardi AV Jr, Mallory TH, Vaughn BK. The efficacy of suction drains after routine total joint arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991; 73:584–587.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Closed-Suction Drainage After Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Is Suction Drainage Necessary after Total Knee Arthroplasty?
- Role of Suction Drain after Knee Arthroplasty in the Tranexamic Acid Era: A Randomized Controlled Study
- A Multivariate Analysis on the Effect of No Closed Suction Drain on the Length of Hospital Stay in Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Monitoring Method for Deep Infection after TKA: Significance of Intraoperative Synovial Fluid Culture and Postoperative Suction Drainage Tip Culture