Korean Diabetes J.
2008 Aug;32(4):366-376. 10.4093/kdj.2008.32.4.366.
An Analysis of Medical Costs of Diabetic Patients in a University Hospital (1996~2005)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Preventive Medicine and Public Health, Ajou University School of Medicine, Korea.
- 2Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Ajou University School of Medicine, Korea.
- 3Division of Social Welfare, Baekseok University, Korea.
- KMID: 2029823
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2008.32.4.366
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: The aim of this research was to find out the costs of diabetes, as research in a prospective cohort study looking into the development of diabetic complications followed by treatment intervention by a medical institution. The research compared the changes in medical costs by following-up on the treatment details of diagnosed diabetes for the last 10 years in a university hospital.
METHODS
The research used data of outpatient, inpatient, pharmaceutical and total medical costs, from 1996 to 2005, of individual patients who were diagnosed with diabetic patients, to analyze the outpatient and inpatient total medical cost changes over the years.
RESULTS
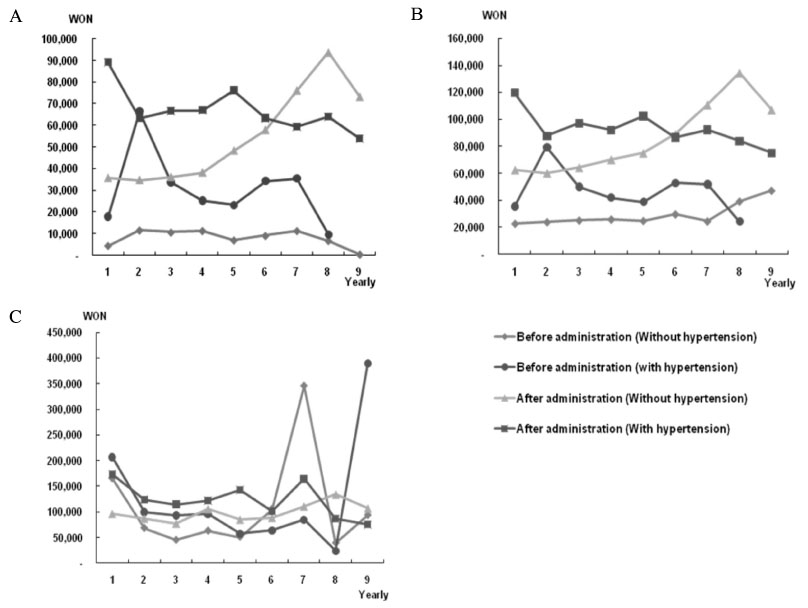
After antidiabetic drug, in the case of outpatient treatment, pharmaceutical costs increased on average by about 25,000 won a month for diabetic patients without complications and by 35,000 won for diabetic patients with microvascular complications. Outpatient medical costs were affected after drug treatment by as much of an increase as created by the pharmaceutical costs. The total medical costs, that is the sum of inpatient and outpatient costs, decreased by 30~40% compared to that before drug treatment. In the case of total medical cost, MI or ESRD cost 2~3 times more in pharmaceutical costs than before the development of complications. The total medical costs of diabetic patients with CVA, MI and ESRD complications increased in the first year after development of the complication, and this was followed by a decrease in the next year, showing a tendency to remain constant with no increase or decrease over subsequent years. This means that the total medical costs of patients with complications remain continuously large throughout the life of the diagnosed patient.
CONCLUSION
For diabetic patients, pharmaceutical costs are the most important factor in determining outpatient medical costs.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Outcome Research in Diabetes
Kwan Woo Lee
J Korean Diabetes. 2011;12(1):2-5. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2011.12.1.2.
Reference
-
1. International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes Atlas. 2003. 2nd ed.2. Stratton IM, Adler AI, Neil HA, Matthews DR, Manley SE, Cull CA, Hadden D, Turner RC, Holman RR. Association of glycaemia with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 35): prospective observational study. BMJ. 2000. 321:405–412.3. Gilmer TP, O'Connor PJ, Rush WA, Crain AL, Whitebird RR, Hanson AM, Solberg LI. Predictors of health care costs in adults with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2005. 28:59–64.6. The DCCT Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin -dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993. 329:977–986.7. U.K. Prospective Diabetes Study Group. U.K. Prospective Diabetes Study 16: Overview of 6 years therapy of type II diabetes: a progressive disease. Diabetes. 1995. 44:1249–1258.8. David CK, Daniel MS. An Economic Analysis of Interventions for Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2000. 23:390–404.9. Marcia AT, Donald CS. Health Economic Benefits and Quality of Life During Improved Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. JAMA. 1998. 280:1490–1496.10. U.K. Prospective Diabetes Study Group. Cost effectiveness of an intensive blood glucose control policy in patients with type 2 diabetes: economic analysis alongside randomized controlled trial (UKPDS 41). BMJ. 2000. 320:1373–1378.11. Zhang P, Engelgau MM, Noris SL, Gregg EW, Venkat Narayan KM. Application of Economic Analysis to Diabetes and Diabetes Care. Ann Intern Med. 2004. 140:972–977.12. American diabetes association. Economic costs of diabetes in the U.S. in 2002. Diabetes care. 2003. 26:917–932.13. Dawson KG, Gomes D, Gerstein H, Blanchard JF, Kahler KD. The Economic Cost of Diabetes in Canada, 1998. Diabetes Care. 2002. 25:1303–1307.17. O'Brien JA, Shomphe LA, Kavanagh PL, Raggio G, Caro JJ. Direct Medical costs of complications resulting from type 2 diabetes in the U.S. Diabetes Care. 1998. 21:1122–1128.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Direct Medical Costs of Type 2 Diabetic Patients in the Tertiary Hospital
- Cost-effectiveness Analysis of Home Care Services for Patients with Diabetic Foot
- Costs of Diabetes Mellitus in Korea
- Clinical Characteristics and Direct Medical Costs of Type 2 Diabetic Patients
- Urgent Reimbursement Need for Diabetes Supplies in Blood Glucose Management of Diabetic Patients