J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2014 Oct;56(4):338-343. 10.3340/jkns.2014.56.4.338.
The Effectiveness of Endoscopic Radiofrequency Denervation of Medial Branch for Treatment of Chronic Low Back Pain
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. mddavidkim@gmail.com
- KMID: 2018086
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2014.56.4.338
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The aim of this study is to evaluate the clinical results of endoscopic radiofrequency ablation of medial branch in patients with chronic low back pain originating from facet joints.
METHODS
Between October 2010 and December 2013, 52 consecutive patients had suffering from chronic low back pain had undergone endoscopic radiofrequency denervation of medial branch of dorsal ramus. The clinical outcomes of these 52 patients were reviewed retrospectively. Preoperative and postoperative Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) and Korean version of Oswestry Disability Index (K-ODI), and patients' satisfaction with the procedure were assessed.
RESULTS
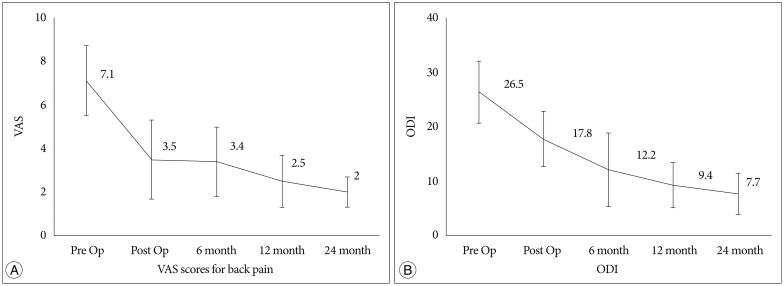
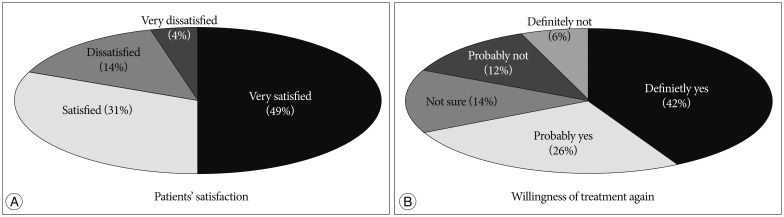
The pain scores on the VAS for back pain had improved significantly from a preoperative mean of 7.1 to a postoperative mean of 2 at the last follow-up (p<0.001). The clinical outcomes based on the K-ODI had also improved significantly from a preoperative mean of 26.5% to postoperative mean of 7.7% at the last follow-up (p<0.001). 80% of patients were satisfied with the procedure. There were no complications associated with the procedure.
CONCLUSION
Our preliminary results demonstrate that endoscopic radiofrequency denervation of medial branch could be an effective alternative treatment modality for chronic back pain originating from facet joints that provides long-term pain relief.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Badgley CE. Pain of spinal origin. J Mich State Med Soc. 1947; 46:812. PMID: 20344349.2. Bogduk N, Wilson AS, Tynan W. The human lumbar dorsal rami. J Anat. 1982; 134(Pt 2):383–397. PMID: 7076562.3. Boswell MV, Colson JD, Sehgal N, Dunbar EE, Epter R. A systematic review of therapeutic facet joint interventions in chronic spinal pain. Pain Physician. 2007; 10:229–253. PMID: 17256032.4. Boswell MV, Trescot AM, Datta S, Schultz DM, Hansen HC, Abdi S, et al. Interventional techniques : evidence-based practice guidelines in the management of chronic spinal pain. Pain Physician. 2007; 10:7–111. PMID: 17256025.5. Carragee EJ, Don AS, Hurwitz EL, Cuellar JM, Carrino JA, Herzog R. 2009 ISSLS Prize Winner : Does discography cause accelerated progression of degeneration changes in the lumbar disc : a ten-year matched cohort study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34:2338–2345. PMID: 19755936.
Article6. Cavanaugh JM, Lu Y, Chen C, Kallakuri S. Pain generation in lumbar and cervical facet joints. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88(Suppl 2):63–67. PMID: 16595446.
Article7. Datta S, Lee M, Falco FJ, Bryce DA, Hayek SM. Systematic assessment of diagnostic accuracy and therapeutic utility of lumbar facet joint interventions. Pain Physician. 2009; 12:437–460. PMID: 19305489.8. Freburger JK, Holmes GM, Agans RP, Jackman AM, Darter JD, Wallace AS, et al. The rising prevalence of chronic low back pain. Arch Intern Med. 2009; 169:251–258. PMID: 19204216.
Article9. Jhala A, Mistry M. Endoscopic lumbar discectomy : experience of first 100 cases. Indian J Orthop. 2010; 44:184–190. PMID: 20419006.10. Katz JN. Lumbar disc disorders and low-back pain : socioeconomic factors and consequences. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88(Suppl 2):21–24. PMID: 16595438.
Article11. Lakemeier S, Lind M, Schultz W, Fuchs-Winkelmann S, Timmesfeld N, Foelsch C, et al. A comparison of intraarticular lumbar facet joint steroid injections and lumbar facet joint radiofrequency denervation in the treatment of low back pain : a randomized, controlled, double-blind trial. Anesth Analg. 2013; 117:228–235. PMID: 23632051.
Article12. Laslett M, Oberg B, Aprill CN, McDonald B. Zygapophysial joint blocks in chronic low back pain : a test of Revel's model as a screening test. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2004; 5:43. PMID: 15546487.13. Leclaire R, Fortin L, Lambert R, Bergeron YM, Rossignol M. Radiofrequency facet joint denervation in the treatment of low back pain : a placebo-controlled clinical trial to assess efficacy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26:1411–1416. discussion 1417. PMID: 11458140.
Article14. Manchikanti L, Boswell MV, Singh V, Benyamin RM, Fellows B, Abdi S, et al. Comprehensive evidence-based guidelines for interventional techniques in the management of chronic spinal pain. Pain Physician. 2009; 12:699–802. PMID: 19644537.15. Manchikanti L, Pampati V, Fellows B, Bakhit CE. Prevalence of lumbar facet joint pain in chronic low back pain. Pain Physician. 1999; 2:59–64. PMID: 16906217.
Article16. McLain RF, Pickar JG. Mechanoreceptor endings in human thoracic and lumbar facet joints. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998; 23:168–173. PMID: 9474721.
Article17. Poetscher AW, Gentil AF, Lenza M, Ferretti M. Radiofrequency denervation for facet joint low back pain : a systematic review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014; 39:E842–E849. PMID: 24732848.18. Saito T, Steinke H, Miyaki T, Nawa S, Umemoto K, Miyakawa K, et al. Analysis of the posterior ramus of the lumbar spinal nerve : the structure of the posterior ramus of the spinal nerve. Anesthesiology. 2013; 118:88–94. PMID: 23165471.19. Schwarzer AC, Derby R, Aprill CN, Fortin J, Kine G, Bogduk N. Pain from the lumbar zygapophysial joints : a test of two models. J Spinal Disord. 1994; 7:331–336. PMID: 7949701.20. Shealy CN. Facet denervation in the management of back and sciatic pain. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976; (115):157–164. PMID: 130217.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Erratum to "The Effectiveness of Endoscopic Radiofrequency Denervation of Medial Branch for Treatment of Chronic Low Back Pain" by Jeong SY, et al. (J Korean Neurosurg Soc 56 : 338-343, 2014)
- New More Reliable Indicator for Confirmation of the Medial Branch in Radiofrequency Neurotomy
- Comprasion of Effectiveness of CT vs C-arm Guided Percutaneous Radiofrequency Lumbar Facet Rhizotomy
- Radiofrequency Facet Denervation for Low Back Pain after Microscopic Discectomy
- Rercutaneous Radiofrequency Denervation in Lumbago