J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2012 Jul;50(3):191-197. 10.4047/jkap.2012.50.3.191.
Immediate implant placement into extraction sites with periapical lesions in the esthetic zone: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, College of Dentistry, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea. DONGHOOHAN@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2000208
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2012.50.3.191
Abstract
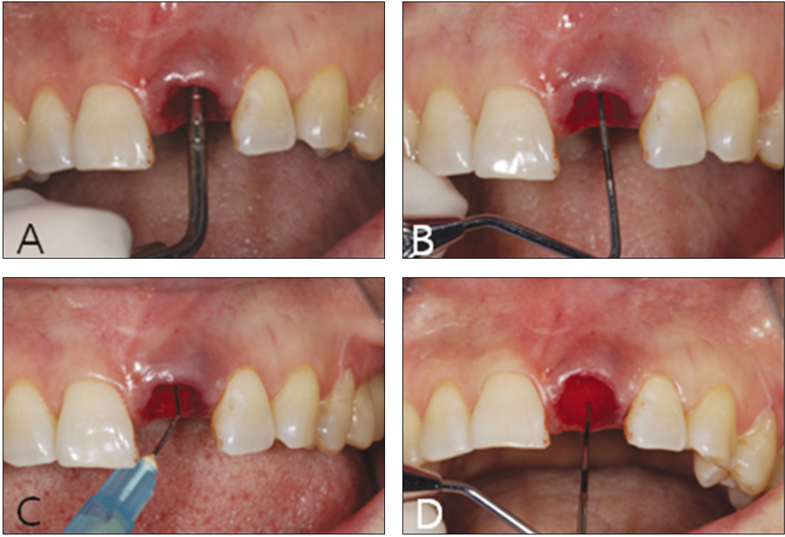
- Esthetics is important in restoring maxillary anterior area. Alveolar bone resorption and loss of interdental papilla may be minimized by immediate implantation. Previous studies showed successful results with the immediate implantation in healthy extraction socket, while many of these studies objected the immediate implantation into extraction sites with periapical lesions. Recent studies, however, reported successful results of the immediate implantation into extraction sites with periapical lesions with careful debridement of extraction sockets and general medication of antibiotics prior to implantation. A 73-year-old female visited the department of Prosthodontics in oo University Dental Hospital with the chief complaint of fallen post-core and crown on left maxillary incisor. Although the incisor was with vertical root fracture and periapical lesion, the immediate implantation following the extraction of tooth was planned. Thorough socket debridement, irrigation with chlorhexidine, and tetracycline soaking were followed by immediate implantation. The general medication of antibiotics (Moxicle Tab.(R), 375 mg) was prescribed before and after the surgery. Immediate provisional restoration was delivered two days after the surgery, and the definitive metal-ceramic restoration was placed about six months later after reproducing the emergence profile from the provisional restoration. This case presents satisfying result esthetically and functionally upto two years after the placement of prosthesis with the harmonious gingival line and no loss of marginal bone.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chen ST, Wilson TG Jr, Ha¨mmerle CH. Immediate or early placement of implants following tooth extraction: review of biologic basis, clinical procedures, and outcomes. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2004. 19:12–25.2. Tan WL, Wong TL, Wong MC, Lang NP. A systematic review of post-extractional alveolar hard and soft tissue dimensional changes in humans. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012. 23:1–21.
Article3. Schwartz-Arad D, Chaushu G. The ways and wherefores of immediate placement of implants into fresh extraction sites: a literature review. J Periodontol. 1997. 68:915–923.
Article4. Novaes AB Jr, Vidigal Ju′nior GM, Novaes AB, Grisi MF, Polloni S, Rosa A. Immediate implants placed into infected sites: a histomorphometric study in dogs. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1998. 13:422–427.5. Peñarrocha M, Uribe R, Balaguer J. Immediate implants after extraction. A review of the current situation. Med Oral. 2004. 9:234–242.6. Quirynen M, Gijbels F, Jacobs R. An infected jawbone site compromising successful osseointegration. Periodontol 2000. 2003. 33:129–144.
Article7. Quirynen M, Vogels R, Alsaadi G, Naert I, Jacobs R, van Steenberghe D. Predisposing conditions for retrograde periimplantitis, and treatment suggestions. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2005. 16:599–608.
Article8. Villa R, Rangert B. Early loading of interforaminal implants immediately installed after extraction of teeth presenting endodontic and periodontal lesions. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2005. 7:S28–S35.
Article9. Bell CL, Diehl D, Bell BM, Bell RE. The immediate placement of dental implants into extraction sites with periapical lesions: a retrospective chart review. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011. 69:1623–1627.
Article10. Fugazzotto P. A retrospective analysis of immediately placed implants in 418 sites exhibiting periapical pathology: results and clinical considerations. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2012. 27:194–202.11. Siegenthaler DW, Jung RE, Holderegger C, Roos M, Ha¨mmerle CH. Replacement of teeth exhibiting periapical pathology by immediate implants: a prospective, controlled clinical trial. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2007. 18:727–737.
Article12. Del Fabbro M, Boggian C, Taschieri S. Immediate implant placement into fresh extraction sites with chronic periapical pathologic features combined with plasma rich in growth factors: preliminary results of single-cohort study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009. 67:2476–2484.
Article13. Casap N, Zeltser C, Wexler A, Tarazi E, Zeltser R. Immediate placement of dental implants into debrided infected dentoalveolar sockets. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007. 65:384–392.
Article14. Evans CD, Chen ST. Esthetic outcomes of immediate implant placements. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2008. 19:73–80.
Article15. Waasdorp JA, Evian CI, Mandracchia M. Immediate placement of implants into infected sites: a systematic review of the literature. J Periodontol. 2010. 81:801–808.
Article16. Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Talati M, Coulthard P, Oliver R, Worthington HV. Interventions for replacing missing teeth: antibiotics at dental implant placement to prevent complications. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. (3):CD004152.
Article17. Mazzocchi A, Passi L, Moretti R. Retrospective analysis of 736 implants inserted without antibiotic therapy. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007. 65:2321–2323.
Article18. Becker BE, Becker W, Ricci A, Geurs N. A prospective clinical trial of endosseous screw-shaped implants placed at the time of tooth extraction without augmentation. J Periodontol. 1998. 69:920–926.
Article19. Botticelli D, Berglundh T, Lindhe J. Hard-tissue alterations following immediate implant placement in extraction sites. J Clin Periodontol. 2004. 31:820–828.
Article20. Botticelli D, Berglundh T, Lindhe J. Resolution of bone defects of varying dimension and configuration in the marginal portion of the peri-implant bone. An experimental study in the dog. J Clin Periodontol. 2004. 31:309–317.
Article21. Covani U, Cornelini R, Barone A. Bucco-lingual bone remodeling around implants placed into immediate extraction sockets: a case series. J Periodontol. 2003. 74:268–273.
Article22. Degidi M, Piattelli A. Immediate functional and non-functional loading of dental implants: a 2- to 60-month follow-up study of 646 titanium implants. J Periodontol. 2003. 74:225–241.
Article23. De Rouck T, Collys K, Cosyn J. Single-tooth replacement in the anterior maxilla by means of immediate implantation and provisionalization: a review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2008. 23:897–904.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Esthetic restoration in continuous maxillary anterior area using immediate implant placement: A case report
- Outcome Evaluation of an Immediately Placed Maxillary Anterior Single-Tooth Implant Using Objective Esthetic Criteria: Case Report
- Clinical Evaluation about the Immediate Implant Replacement after Tooth Extraction
- Immediate implant placement in areas of aesthetic priority
- Simultaneous Hard Tissue and Soft Tissue Graft with Dental Implant Placement and Provisionalization: A Case Report