Restor Dent Endod.
2013 Feb;38(1):55-56. 10.5395/rde.2013.38.1.55.
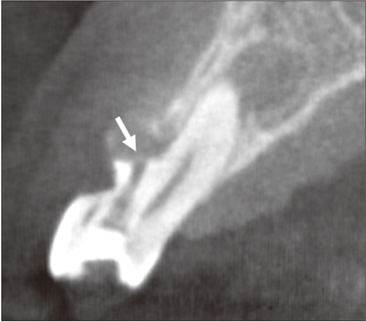
Management of root canal perforation by using cone-beam computed tomography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Chonbuk National University, Korea.
- KMID: 1995479
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.1.55
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tachibana H, Matsumoto K. Applicability of X-ray computerized tomography in endodontics. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1990. 6:16–20.
Article2. Shemesh H, Cristescu RC, Wesselink PR, Wu MK. The use of cone-beam computed tomography and digital periapical radiographs to diagnose root perforation. J Endod. 2011. 37:513–516.
Article3. Lim YJ, Nam SH, Jung SH, Shin DR, Shin SJ, Min KS. Endodontic management of a maxillary lateral incisor with dens invaginatus and external root irregularity using cone-beam computed tomography. Restor Dent Endod. 2012. 37:50–53.
Article4. Patel S, Dawood A, Ford TP, Whaites E. The potential applications of cone beam computed tomography in the management of endodontic problems. Int Endod J. 2007. 40:818–830.
Article5. Song CK, Chang HS, Min KS. Endodontic management of supernumerary tooth fused with maxillary first molar by using cone-beam computed tomography. J Endod. 2010. 36:1901–1904.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Detection of maxillary second molar with two palatal roots using cone beam computed tomography: a case report
- Endodontic management of a maxillary first molar with three roots and seven root canals with the aid of cone-beam computed tomography
- Management of a permanent maxillary first molar with unusual crown and root anatomy: a case report
- A cone-beam computed tomographic study of C-shaped root and root canal in maxillary molars
- Observation of mandibular second molar roots and root canal morphology using dental cone-beam computed tomography