J Korean Acad Conserv Dent.
2003 Sep;28(5):409-418. 10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.5.409.
The effect of substance P on the secretion of interleukin-8 and MCP (Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein)-1 from the Human Dental Pulp Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Conservative Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Kyung Hee University, Korea. consdent94@hanmail.net
- KMID: 1987267
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.5.409
Abstract
- No abstract available.
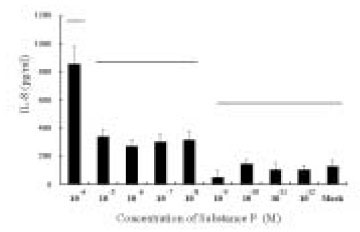
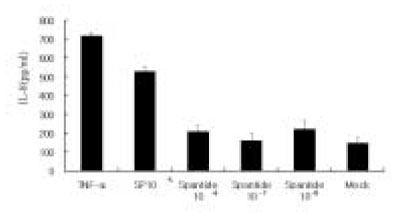
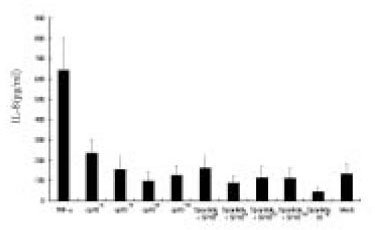
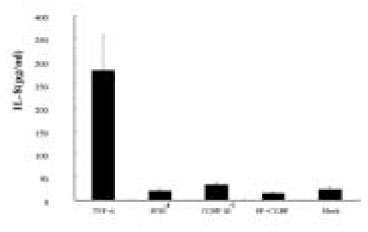
Figure
Reference
-
1. Stanley HR. Importance of the leukocyte to dental health. J Endod. 1977. 3:334–341.2. Bergenholtz G, Lindhe J. Effect of soluble plaque factors on inflammatory reactions in the dental pulp. Scand J Dent Res. 1975. 83:153–158.
Article3. Seltzer S, Bender IB, Ziontz M. The dynamics of pulp inflammation : Correlations between diagnostic data and actual histologic findings in the pulp. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1963. 16:846–871.
Article4. Rauschenberger C, Bailey J, Cootauco C. Detection of human IL-2 in normal and inflamed dental pulps. J Endod. 1997. 23:366–370.
Article5. Baggiolini M, Walz A, Kunkel SL. Neutrophil-activating peptide-1/interleukin 8, a novel cytokine that activates neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1989. 84:1045–1049.
Article6. Larsen CG, Anderson AO, Appella E, Oppenheim JJ, Matsushima K. The neutrophil-activating protein(NAP-1) is also chemotactic for T lymphocytes. Science. 1989. 243:1464–1466.
Article7. Peveri P, Walz A, Dewald B, Baggiolini M. A novel neutrophil activating factor produced by human mononuclear phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1988. 167:1547–1559.
Article8. Detmers PA, Lo SK, Olsen-Egbert E, Walz A, Baggiolini M, Cohn ZA. Neutrophil-activating protein 1/interleukin 8 stimulates the binding activity of the leukocyte adhesion receptor CD11b/CD18 on human neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1990. 171:1155–1162.
Article9. Rot A. Neutrophol attractant/activation protein-1 (interleukin-8) induces in vito neutrophil migration by haptotactic mechanism. Eur J Immunol. 1993. 23:303–306.
Article10. Kim S. Neurovascular interactions in the dental pulp in health and inflammation. J Endod. 1990. 16:48–53.
Article11. Wakisaka S. Neuropeptides in the dental pulp : distribution, origins, and correlation. J Endod. 1990. 16:67–69.12. Grutzner EH, Garry MG, Hargreaves KM. Effect of injury on pulpal levels of immunoreactive substance P and immunoreactive calcitonin gene-related peptide. J Endod. 1992. 18:553–557.
Article13. Buck S, Reese K, Hargreaves KM. Pulpal exposure alters neuropeptide levels in inflamed dental pulp and trigeminel ganglia: evaluation of axonal transport. J Endod. 1999. 25:718–721.
Article14. Rodd HD, Boissonade FM. Comparative immunohistochemical analysis of the peptidergic innervation of human primary and permanent tooth pulp. Arch Oral Biol. 2002. 47:375–385.
Article15. Olgart LM, Edwall B, Gazelius B. Neurogenic mediators in control of pulpal blood flow. J Endod. 1989. 15:409–412.
Article16. Muller WA, Randolph GJ. Migration of leukocytes across endothelium and beyond : molecules involved in the transmigration and fate of monocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 1999. 66:698–704.
Article17. Huang GTJ, Chugal N, Potente AP, Zhang X. Constitutive Expression of Interleukin-8 and Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 in Human Dental Pulps. Int J Oral Biol. 1999. 24:163–168.18. Tran MT, Ritchie MH, Lausch RN, Oakes JE. Calcitonin gene-related peptide induces IL-8 synthesis in human corneal epithelial cells. J Immunol. 2000. 164:4307–4312.
Article19. Tran MT, Lausch RN, Oakes JE. Substance P differentiall stimulates IL-8 synthesis in human corneal epithelialcells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000. 41:3871–3877.20. Veronesi B, Carter JD, Devlin RB, Simon SA, Oortgiesen M. Neuropeptides and capsaicin stimulate the release of inlfammatory cytokines in a human broncheal epithelial cell line. Neuropeptides. 1999. 33:447–456.
Article21. Kiss M, Kemény L, Gyulai R, Michel G, Husz S, Kovács R, Dobozy A, Ruzicka T. Effects of the neuropeptides substance P, calcitonin gene-related peptide and alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone on the IL-8/IL-receptor system in a cultured human keratinocyte cell line and dermal fibroblasts. Inflammation. 1999. 23:557–567.22. Raap T, Justen HP, Miller LE, Cutolo M, Scholmerich J, Straub RH. Neurotransmitter modulation of interleukin 6 (IL-6) and IL-8 secretion of synovial fibroblasts in patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared to osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 2000. 27:2558–2565.23. Byers MR, Närhi MV. Dental injury models; experimental tools for understanding neuroinflammatory interactions and polymodal nociceptor functions. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1999. 10:4–39.
Article24. Huang GT, Potente AP, Kim JW, Chugal N, Zhang X. Increased interleukin-8 espression in inflamed human dental pulps. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1999. 88:214–220.25. Stashenko P, Teles R, D'Souza R. Periapical inflammatory responses and their modulation. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1998. 9:498–521.
Article26. Awawdeh L, Lundy FT, Shaw C, Lamey PJ, Linden GJ, Kennedy JG. Quantitative analysis of substance P, neurokinin A and calcitonin gene-related peptide in pulp tissue from painful and healthy human teeth. Int Endod J. 2002. 35:30–36.
Article27. Rot A, Hub E, Middleton J, Pons F, Rabeck C, Thierer K, Wintle J, Wolff B, Zsak M, Dukor P. Some aspects of IL-8 pathophysiology. III: Chemokine interaction with endothelial cells. J Leukocyte Biol. 1996. 59:39–44.
Article28. Middleton J, Neil S, Wintle J, Clark-Lewis I, Moore H, Lam C, Auer M, Hub E, Rot A. Transcytosis and surface presentaion of IL-8 by venular endothelial cells. Cell. 1997. 91:385–395.
Article29. Wolff B, Burns AR, Middleton J, Rot A. Endothelial cell "memory" of inflammatory stimulation: human venular endothelial cells store interleukin 8 in Weibel-Palade bodies. J Exp Med. 1998. 188:1757–1762.
Article30. Huang GT, Kim D, Lee JK, Juramitsu HK, Haake SK. Interleukin-8 and intercellular adhesion molecule 1 regulation in oral epithelial cells by selected periodontal bacteria: multiple effects of Porphyromonas gingivalis via antagonistic mechanisms. Infect Immun. 2001. 69:1364–1372.
Article31. Adamus MA, Dabrowski ZJ. Effect of the Neuropeptide Substance P on the rat bone marrow-derived osteogenic cells in vitro. J Cell Biochem. 2001. 81:499–506.
Article32. Hargreaves KM, Walter RB, Garry MG. An in vitro method to evaluated regulation of neuropeptide release from dental pulp. J Endod. 1992. 18:597–600.
Article33. Cuesta MC, Quintero H, Pons H, Suarez-Roca . Substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide increase IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α secretion from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Neurochem Int. 2002. 40:301–306.
Article34. Ansel JC, Armstrong CA, Song I, Quinlan KL, Olerud JE, Caughman SW, Bunnett NW. Interaction of the skin and nervous system. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 1997. 2:23–26.35. Taylor PE, Byers MR. An immunocytochemical study of the morphological reaction of nerves containing calcitonin gene-related peptide to microabscess formation and healing in rat molars. Arch Oral Biol. 1990. 35:629–638.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
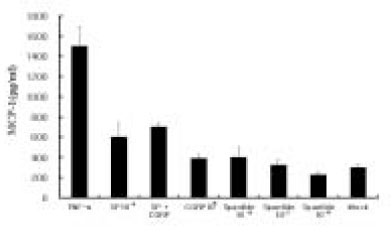
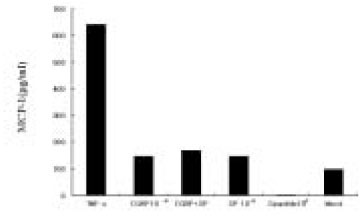
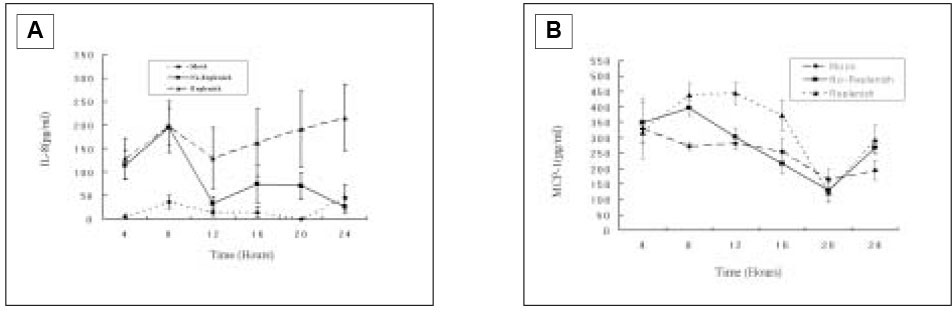
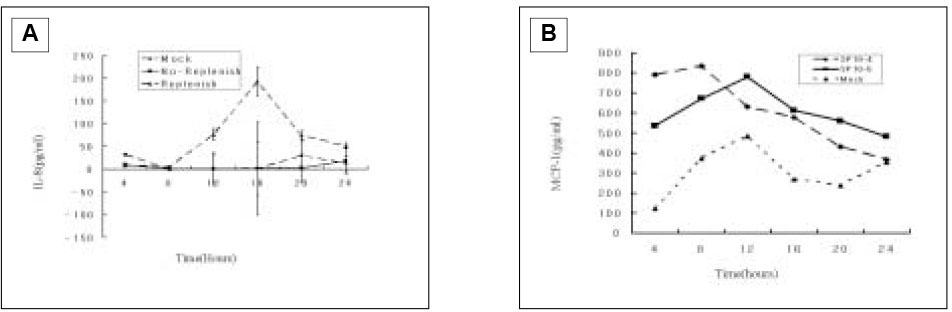
- Interleukin-8 and MCP(Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein)-1 expression by the Human Dental Pulps in cultures stimulated with Substance P
- Activated platelets induce secretion of interleukin-1beta, monocyte chemotactic protein-1, and macrophage inflammatory protein-1alpha and surface expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 on cultured endothelial cells
- Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 Upregulates Fibronectin Secretion by Human Peritoneal Fibroblasts
- Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Strongly Stimulates Endothelial Cells to Produce Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 and Interleukin-8
- Endothelin-1, Endothelin-2 and Endothelin-3 Induced Expression of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 in Rat Mesangial Cells