J Korean Acad Conserv Dent.
2011 Jul;36(4):313-323. 10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.4.313.
Optimal combination of 3-component photoinitiation system to increase the degree of conversion of resin monomers
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Conservative Dentistry, Dankook University College of Dentistry, Institute of Dental Science, Cheonan, Korea. donyshin@dankook.ac.kr
- KMID: 1986694
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.4.313
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
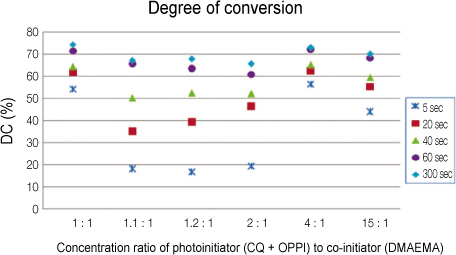
This study investigated the optimal combination of 3-component photoinitiation system, consisting of CQ, p-octyloxy-phenyl-phenyl iodonium hexafluoroantimonate (OPPI), and 2-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate (DMAEMA) to increase the degree of conversion of resin monomers, and analyze the effect of the ratio of the photoinitiator to the co-initiator.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
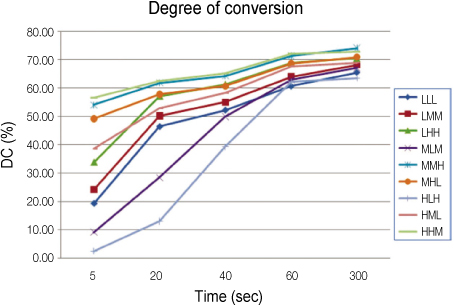
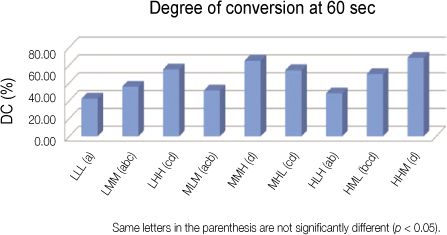
Each photoinitiators (CQ and OPP) and co-initiator (DMAEMA) were mixed in three levels with 0.2 wt.% (low concentration, L), 1.0 wt.% (medium concentration, M), and 2.0 wt.% (high concentration, H). A total of nine groups using the Taguchi method were tested according to the following proportion of components in the photoinitiator system: LLL, LMM, LHH, MLM, MMH, MHL, HLH, HML, HHM. Each monomer was polymerized using a quartz-tungsten-halogen curing unit (Demetron 400, USA) for 5, 20, 40, 60, 300 sec and the degree of conversion (DC) was determined at each exposure time using FTIR.
RESULTS
Significant differences were found for DC values in groups. MMH group and HHM group exhibited greater initial DC than the others. No significant difference was found with the ratio of the photoinitiators (CQ, OPPI) to the co-initiator (DMAEMA). The concentrations of CQ didn't affect the DC values, but those of OPPI did strongly.
CONCLUSIONS
MMH and HHM groups seem to be best ones to get increased DC. MMH group is indicated for bright, translucent color and HHM group is good for dark, opaque colored-resin.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Effect of glycerin on the surface hardness of composites after curing
Hyun-Hee Park, In-Bog Lee
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2011;36(6):483-489. doi: 10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.6.483.Effect of CQ-amine ratio on the degree of conversion in resin monomers with binary and ternary photoinitiation systems
Ho-Jin Moon, Dong-Hoon Shin
Restor Dent Endod. 2012;37(2):96-102. doi: 10.5395/rde.2012.37.2.96.
Reference
-
1. Asmussen E, Peutzfeldt A. Influence of UEDMA, BisGMA and TEGDMA on selected mechanical properties of experimental resin composites. Dent Mater. 1998. 14:51–56.
Article2. Lovell LG, Stansbury JW, Syrpes DC, Bowman CN. Effects of composition and reactivity on the reaction kinetics of dimethacrylate/dimethacrylate copolymerizations. Macromolecules. 1999. 32:3913–3921.
Article3. Sideridou I, Tserki V, Papanastasiou G. Effect of chemical structure on degree of conversion in light-cured dimethacrylate-based dental resins. Biomaterials. 2002. 23:1819–1829.
Article4. Atai M, Watts DC. A new kinetic model for the photopolymerization shrinkage-strain of dental composites and resins. Dent Mater. 2006. 22:785–791.
Article5. Stansbury JW. Curing dental resins and composites by photopolymerization. J Esthet Dent. 2000. 12:300–308.
Article6. Kim JH, Shin DH. Microleakage of the experimental composite resin with three component photoinitiator systems. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2009. 34:333–339.
Article7. Angiolini L, Caretti D, Salatelli E. Synthesis and photoinitiation activity of radical polymeric photoinitiators bearing side-chain camphoroquinone moieties. Macromol Chem Phys. 2000. 201:2646–2653.
Article8. Dart EC, Nemcek J. Photopolymerisable composition. Great Britain Patent Specification No. 1408265 (1971); Japanese Patent No. Toku-Kou-Sho 54-10986 (1979).9. Fujisawa S, Kadoma Y, Masuhara E. Effects of photoinitiators for the visible-light resin system on hemolysis of dog erythrocytes and lipid peroxidation of their components. J Dent Res. 1986. 65:1186–1190.
Article10. Arikawa H, Takahashi H, Kanie T, Ban S. Effect of various visible light photoinitiators on the polymerization and color of light-activated resin. Dent Mater J. 2009. 28:454–460.
Article11. Neumann MG, Schmitt CC, Ferreira GC, Correa IC. The initiating radical yields and the efficiency of polymerization for various dental photoinitiators excited by different light curing units. Dent Mater. 2006. 22:576–584.
Article12. Brackett MG, Brackett WW, Browning WD, Rueggeberg FA. The effect of light curing source on the residual yellowing of resin composites. Oper Dent. 2007. 32:443–450.
Article13. Bowen RL, Cobb EN, Rapson JE. Adhesive bonding of various materials to hard tooth tissues: Improvement in bond strength to dentin. J Dent Res. 1982. 61:1070–1076.
Article14. Tay FR, King NM, Suh BI, Pashley DH. Effect of delayed activation of light-curing resin composites on bonding of all in-one adhesives. J Adhes Dent. 2001. 3:207–225.15. Imazato S, Tarumi H, Kobayashi K, Hiraguri H, Oda K, Tsuchitani Y. Relationship between the degree of conversion and internal discoloration of light-activated composite. Dent Mater J. 1995. 14:23–30.
Article16. Park YJ, Chae KH, Rawls HR. Development of a new photoinitiation system for dental light-cure composite resins. Dent Mater. 1999. 15:120–127.
Article17. Guo X, Wang Y, Spencer P, Ye Q, Yao X. Effects of water content and initiator composition on photopolymerization of a model BisGMA/HEMA resin. Dent Mater. 2008. 24:824–831.
Article18. Shin DH, Rawls RL. Degree of conversion and color stability of the light curing resin with new photoinitiator systems. Dent Mater. 2009. 25:1030–1038.
Article19. Brandt WC, Schneider LF, Frollini E, Correr-Sobrinho L, Sinhoreti MA. Effect of different photo-initiators and light curing units on degree of conversion of composites. Braz Oral Res. 2010. 24:263–270.
Article20. Yoshida K, Greener EH. Effect of photoinitiator on degree of conversion of unfilled light-cured resin. J Dent. 1994. 22:296–299.
Article21. Schneider LF, Consani S, Sakaguchi RL, Ferracane JL. Alternative photoinitiator system reduces the rate of stress development without compromising the final properties of the dental composite. Dent Mater. 2009. 25:566–572.
Article22. Lin CL, Chang WJ, Lin YS, Chang YH, Lin YF. Evaluation of the relative contributions of multi-factors in an adhesive MOD restoration using FEA and the Taguchi method. Dent Mater. 2009. 25:1073–1081.
Article23. Park HJ, Son SA, Hur B, Kim HC, Kwon YH, Park JK. Effect of the difference in spectral outputs of the single and dual-peak LEDs on the microhardness and the color stability of resin composites. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2011. 36:108–113.
Article24. Peutzfeldt A, Asmussen E. In vitro wear, hardness, and conversion of diacetyl-containing and propanalcontaining resin materials. Dent Mater. 1996. 12:103–108.
Article25. Brandt WC, de Moraes RR, Correr-Sobrinho L, Sinhoreti MA, Consani S. Effect of different photo-activation methods on push out force, hardness and crosslink density of resin composite restorations. Dent Mater. 2008. 24:846–850.
Article26. Carmichael AJ, Gibson JJ, Walls AW. Allergic contact dermatitis to bisphenol-A-glycidyldimethacrylate (Bis-GMA) dental resin associated with sensitivity to epoxy resin. Br Dent J. 1997. 183:297–298.
Article27. Ferracane JL, Greener EH. Fourier transform infrared analysis of degree of polymerization in unfilled resins-methods comparison. J Dent Res. 1984. 63:1093–1095.
Article28. Alvim HH, Alecio AC, Vasconcellos WA, Furlan M, de Oliveira JE, Saad JRC. Analysis of camphoroquinone in composite resins as a function of shade. Dent Mater. 2007. 23:1245–1249.29. De Raaff AM, Marino TL, Neckers DC. Optimized cure efficiency using a fluorone visible light photoinitiator and a novel charge transfer: complex initiating system. RAI/TECH Conference. 1996.30. He JH, Mendoza VS. Synthesis and study of a novel hybrid UV photoinitiator: p-benzoyldiphenyliodonium hexafluorophosphate (PhCOPhl + PhPF). J Polym Sci A Polym Chem. 1996. 34:2809–2816.
Article31. Schneider LF, Cavalcante LM, Consani S, Ferracane JL. Effect of co-initoator ratio on the polymer properties of experimental resin composites formulated with camphoroquinone and phenyl-propanedione. Dent Mater. 2009. 25:369–375.
Article32. Musanje L, Ferracane JL, Sakaguchi RL. Determination of the optimal photoinitiator cencentraction in dental composites based on essential material properties. Dent Mater. 2009. 25:994–1000.
Article33. Neumann MG, Miranda WG Jr, Schmitt CC, Rueggeberg FA, Correa IC. Molar extinction coefficients and the photon absorption efficiency of dental photoinitiators and light curing units. J Dent. 2005. 33:525–532.
Article34. Dewaele M, Truffier-Boutry D, Leloup G, Devaux J. Volume contraction in photocured dental resins: the shrinkage-conversion relationship revised. Dent Mater. 2006. 22:359–365.
Article35. Silikas N, Eliades G, Watts DC. Light intensity effects on resin-composite degree of conversion and shrinkage strain. Dent Mater. 2000. 16:292–296.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of CQ-amine ratio on the degree of conversion in resin monomers with binary and ternary photoinitiation systems
- Effect of resin matrix on degree of conversion and fracture toughness of dental composites
- The effect of thickness and translucency of polymer-infiltrated ceramic-network material on degree of conversion of resin cements
- Effect of pre-heating on some physical properties of composite resin
- Degree of conversion of resin composite cured by light through a translucent fiber posts