J Cardiovasc Ultrasound.
2014 Dec;22(4):196-204. 10.4250/jcu.2014.22.4.196.
Endurance and Strength Athlete's Heart: Analysis of Myocardial Deformation by Speckle Tracking Echocardiography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, University of Siena, Siena, Italy. federico-alvino@hotmail.it
- KMID: 1980423
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jcu.2014.22.4.196
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Intensive training induces two morphological myocardial typologies of athlete's heart. Endurance training (ET) induces eccentric remodeling, bradycardia and better diastolic filling. Strength training (ST) determines concentric chamber remodelling maintaining a normal heart rate (HR). Aim of the study was to compare ET and ST athletes' heart using speckle tracking echocardiography (STE).
METHODS
33 professional ET, 36 ST athletes, and 17 healthy controls (CT) were enrolled. All subjects underwent standard transthoracic echocardiography at rest and STE.
RESULTS
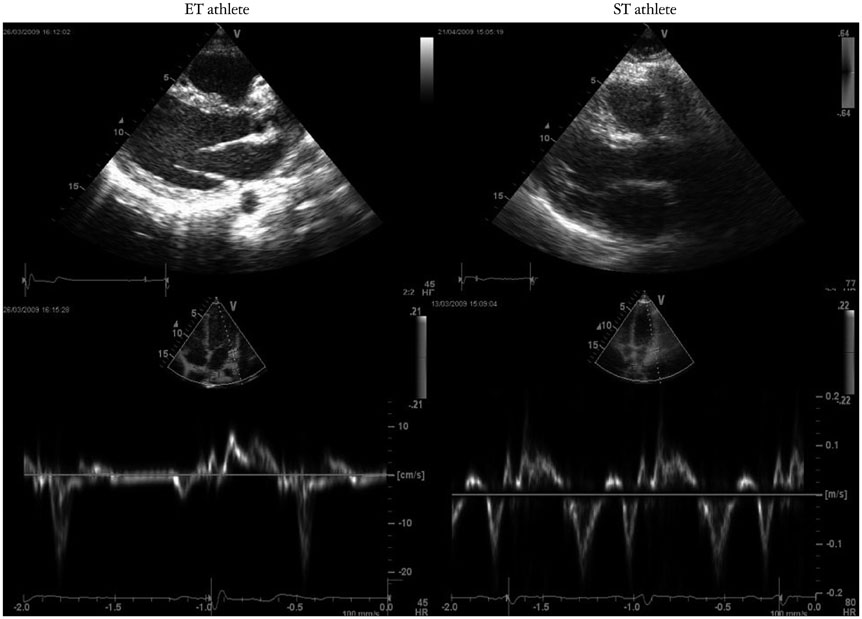
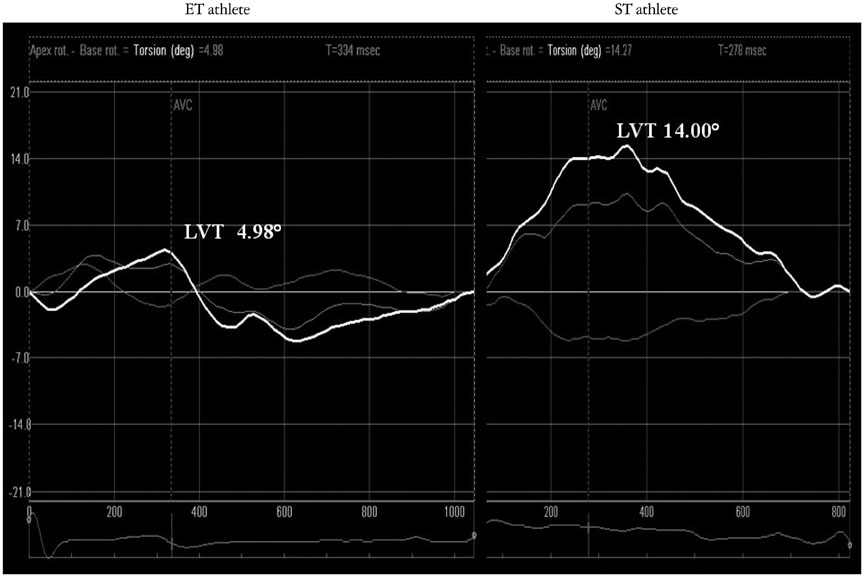
In ET group, HR was lower than ST group and CT group (p < 0.001; p < 0.01). ET group had higher E/A ratio than ST group and CT group (p < 0.01; p < 0.001). The left ventricular apical circumferential strain in ET group was lower than ST group and CT group (-21.6 +/- 4.1% vs. -26.8 +/- 7.7%, p < 0.05; vs. -27.8 +/- 5.6%, p < 0.01). ET group had lower left ventricular twist (LVT) and untwisting (UTW) than ST group (6.2 +/- 0.1degrees vs. 12.0 +/- 0.1degrees, p < 0.01; -67.3 +/- 22.9degrees/s vs. -122.5 +/- 52.8degrees/s, p < 0.01) and CT group (10.0 +/- 0.1degrees, p < 0.01; -103.3 +/- 29.3degrees/s, p < 0.01). The univariate analysis showed significant correlation between E/A ratio and HR (r = -0.54; p < 0.001), LVT (r = -0.45; p < 0.01), UTW (r = 0.24; p < 0.05). At the multivariate analysis only HR was confirmed as independent predictor of diastolic function in all groups (Beta -0.52; p < 0.001).
CONCLUSION
In ET there was a better global systolic and diastolic functional reserve at rest observed with strain analysis and it maybe depended on autonomic modulation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Maron BJ. Structural features of the athlete heart as defined by echocardiography. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1986; 7:190–203.
Article2. Morganroth J, Maron BJ, Henry WL, Epstein SE. Comparative left ventricular dimensions in trained athletes. Ann Intern Med. 1975; 82:521–524.
Article3. D'Andrea A, Limongelli G, Caso P, Sarubbi B, Della Pietra A, Brancaccio P, Cice G, Scherillo M, Limongelli F, Calabrò R. Association between left ventricular structure and cardiac performance during effort in two morphological forms of athletes heart. Int J Cardiol. 2002; 86:177–184.4. D'Andrea A, Riegler L, Cocchia R, Scarafile R, Salerno G, Gravino R, Golia E, Vriz O, Citro R, Limongelli G, Calabrò P, Di Salvo G, Caso P, Russo MG, Bossone E, Calabrò R. Left atrial volume index in highly trained athletes. Am Heart J. 2010; 159:1155–1161.5. Pelliccia A, Culasso F, Di Paolo FM, Maron BJ. Physiologic left ventricular cavity dilatation in elite athletes. Ann Intern Med. 1999; 130:23–31.
Article6. Baggish AL, Wang F, Weiner RB, Elinoff JM, Tournoux F, Boland A, Picard MH, Hutter AM Jr, Wood MJ. Training-specific changes in cardiac structure and function: a prospective and longitudinal assessment of competitive athletes. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2008; 104:1121–1128.
Article7. Kuchynka P, Palecek T, Vilikus Z, Havranek S, Taborska K, Louch WE, Linhart A. Cardiac structural and functional changes in competitive amateur cyclists. Echocardiography. 2010; 27:11–16.
Article8. Teske AJ, Prakken NH, De Boeck BW, Velthuis BK, Martens EP, Doevendans PA, Cramer MJ. Echocardiographic tissue deformation imaging of right ventricular systolic function in endurance athletes. Eur Heart J. 2009; 30:969–977.
Article9. Pluim BM, Zwinderman AH, van der Laarse A, van der Wall EE. The athlete's heart. A meta-analysis of cardiac structure and function. Circulation. 2000; 101:336–344.10. Weiner RB, Hutter AM Jr, Wang F, Kim J, Weyman AE, Wood MJ, Picard MH, Baggish AL. The impact of endurance exercise training on left ventricular torsion. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2010; 3:1001–1009.
Article11. D'Andrea A, Caso P, Scarafile R, Salerno G, De Corato G, Mita C, Di Salvo G, Allocca F, Colonna D, Caprile M, Ascione L, Cuomo S, Calabrò R. Biventricular myocardial adaptation to different training protocols in competitive master athletes. Int J Cardiol. 2007; 115:342–349.12. D'Andrea A, Caso P, Severino S, Galderisi M, Sarubbi B, Limongelli G, Cice G, D'Andrea L, Scherillo M, Mininni N, Calabrò R. Effects of different training protocols on left ventricular myocardial function in competitive athletes: a Doppler tissue imaging study. Ital Heart J. 2002; 3:34–40.13. Spence AL, Naylor LH, Carter HH, Buck CL, Dembo L, Murray CP, Watson P, Oxborough D, George KP, Green DJ. A prospective randomised longitudinal MRI study of left ventricular adaptation to endurance and resistance exercise training in humans. J Physiol. 2011; 589(Pt 22):5443–5452.
Article14. D'Andrea A, Cocchia R, Riegler L, Scarafile R, Salerno G, Gravino R, Golia E, Pezzullo E, Citro R, Limongelli G, Pacileo G, Cuomo S, Caso P, Russo MG, Bossone E, Calabrò R. Left ventricular myocardial velocities and deformation indexes in top-level athletes. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2010; 23:1281–1288.15. Mosteller RD. Simplified calculation of body-surface area. N Engl J Med. 1987; 317:1098.
Article16. O'Brien E, Waeber B, Parati G, Staessen J, Myers MG. Blood pressure measuring devices: recommendations of the European Society of Hypertension. BMJ. 2001; 322:531–536.17. ESH/ESC Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension. 2013 Practice guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and the European Society of Cardiology (ESC): ESH/ESC Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension. J Hypertens. 2013; 31:1925–1938.18. Lang RM, Bierig M, Devereux RB, Flachskampf FA, Foster E, Pellikka PA, Picard MH, Roman MJ, Seward J, Shanewise JS, Solomon SD, Spencer KT, Sutton MS, Stewart WJ. Chamber Quantification Writing Group. American Society of Echocardiography's Guidelines and Standards Committee. European Association of Echocardiography. Recommendations for chamber quantification: a report from the American Society of Echocardiography's Guidelines and Standards Committee and the Chamber Quantification Writing Group, developed in conjunction with the European Association of Echocardiography, a branch of the European Society of Cardiology. J Am Soc Echocardiogr Echocardiography. 2005; 18:1440–1463.
Article19. Sjögren AL. Left ventricular wall thickness determined by ultrasound in 100 subjects without heart disease. Chest. 1971; 60:341–346.
Article20. Nagueh SF, Appleton CP, Gillebert TC, Marino PN, Oh JK, Smiseth OA, Waggoner AD, Flachskampf FA, Pellikka PA, Evangelisa A. Recommendations for the evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function by echocardiography. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2009; 10:165–193.
Article21. Kang SJ, Lim HS, Choi BJ, Choi SY, Hwang GS, Yoon MH, Tahk SJ, Shin JH. Longitudinal strain and torsion assessed by two-dimensional speckle tracking correlate with the serum level of tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1, a marker of myocardial fibrosis, in patients with hypertension. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2008; 21:907–911.
Article22. Park SJ, Miyazaki C, Bruce CJ, Ommen S, Miller FA, Oh JK. Left ventricular torsion by two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography in patients with diastolic dysfunction and normal ejection fraction. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2008; 21:1129–1137.
Article23. Geyer H, Caracciolo G, Abe H, Wilansky S, Carerj S, Gentile F, Nesser HJ, Khandheria B, Narula J, Sengupta PP. Assessment of myocardial mechanics using speckle tracking echocardiography: fundamentals and clinical applications. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2010; 23:351–369. quiz 453-5.
Article24. Vinereanu D, Florescu N, Sculthorpe N, Tweddel AC, Stephens MR, Fraser AG. Left ventricular long-axis diastolic function is augmented in the hearts of endurance-trained compared with strength-trained athletes. Clin Sci (Lond). 2002; 103:249–257.
Article25. Störk T, Möckel M, Müller R, Eichstädt H, Hochrein H. Left ventricular filling behaviour in ultra endurance and amateur athletes: a stress Doppler-echo study. Int J Sports Med. 1992; 13:600–604.
Article26. Ekblom B, Hermansen L. Cardiac output in athletes. J Appl Physiol. 1968; 25:619–625.
Article27. Ballo P, Mondillo S, Guerrini F, Barbati R, Picchi A, Focardi M. Midwall mechanics in physiologic and hypertensive concentric hypertrophy. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2004; 17:418–427.
Article28. Santoro A, Caputo M, Antonelli G, Lisi M, Padeletti M, D'Ascenzi F, Cameli M, Giacomin E, Mondillo S. Left ventricular twisting as determinant of diastolic function: a speckle tracking study in patients with cardiac hypertrophy. Echocardiography. 2011; 28:892–898.
Article29. Roy A, Doyon M, Dumesnil JG, Jobin J, Landry F. Endurance vs. strength training: comparison of cardiac structures using normal predicted values. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1988; 64:2552–2557.
Article30. Doucende G, Schuster I, Rupp T, Startun A, Dauzat M, Obert P, Nottin S. Kinetics of left ventricular strains and torsion during incremental exercise in healthy subjects: the key role of torsional mechanics for systolic-diastolic coupling. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2010; 3:586–594.
Article31. Esch BT, Scott JM, Warburton DE, Thompson R, Taylor D, Cheng Baron J, Paterson I, Haykowsky MJ. Left ventricular torsion and untwisting during exercise in heart transplant recipients. J Physiol. 2009; 587(Pt 10):2375–2386.
Article32. Caso P, D'Andrea A, Galderisi M, Liccardo B, Severino S, De Simone L, Izzo A, D'Andrea L, Mininni N. Pulsed Doppler tissue imaging in endurance athletes: relation between left ventricular preload and myocardial regional diastolic function. Am J Cardiol. 2000; 85:1131–1136.
Article33. Nottin S, Doucende G, Schuster-Beck I, Dauzat M, Obert P. Alteration in left ventricular normal and shear strains evaluated by 2D-strain echocardiography in the athlete's heart. J Physiol. 2008; 586(Pt 19):4721–4733.
Article34. Akagawa E, Murata K, Tanaka N, Yamada H, Miura T, Kunichika H, Wada Y, Hadano Y, Tanaka T, Nose Y, Yasumoto K, Kono M, Matsuzaki M. Augmentation of left ventricular apical endocardial rotation with inotropic stimulation contributes to increased left ventricular torsion and radial strain in normal subjects: quantitative assessment utilizing a novel automated tissue tracking technique. Circ J. 2007; 71:661–668.
Article35. Baldesberger S, Bauersfeld U, Candinas R, Seifert B, Zuber M, Ritter M, Jenni R, Oechslin E, Luthi P, Scharf C, Marti B, Attenhofer Jost CH. Sinus node disease and arrhythmias in the long-term follow-up of former professional cyclists. Eur Heart J. 2008; 29:71–78.
Article36. Monte IP, Mangiafico S, Buccheri S, Bottari VE, Lavanco V, Arcidiacono AA, Leggio S, Deste W, Tamburino C. Myocardial deformational adaptations to different forms of training: a real-time three-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiographic study. Heart Vessels. 2014; [Epub ahead of print].
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current Status of 3-Dimensional Speckle Tracking Echocardiography: A Review from Our Experiences
- Functional Assessment for Congenital Heart Disease
- Speckle-tracking analysis of myocardial deformation in correlation to age in healthy horses
- Speckle tracking ultrasonography as a new tool to assess diaphragmatic function: a feasibility study
- Characteristics of Myocardial Deformation and Rotation in Subjects With Diastolic Dysfunction Without Diastolic Heart Failure