J Cardiovasc Ultrasound.
2011 Dec;19(4):183-191. 10.4250/jcu.2011.19.4.183.
Evaluation of the Relationship between Circadian Blood Pressure Variation and Left Atrial Function Using Strain Imaging
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. younhj@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 1980380
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jcu.2011.19.4.183
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Non-dippers were reported as showing different left atrial function, compared to dippers, but no study to date investigated the changes in the left atrial function according to the diurnal blood pressure pattern, using tissue Doppler and strain imaging.
METHODS
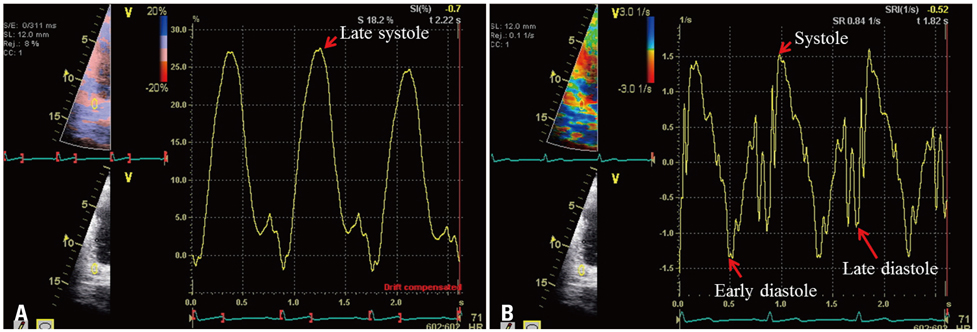
Forty never treated hypertensive patients between 30 and 80 years of age were enrolled in this study. Patients were classified as non-dippers when, during night time, they had a blood pressure decrease of less than 10%. Strain of the left atrium was measured during late systole, and peak strain rates of the left atrium were measured during systole, early and late diastolic periods.
RESULTS
The left atrial expansion index, left atrial active emptying volume and left atrial active emptying fraction were all significantly increased in non-dippers. They also had increased values of mean peak left atrial strain (dippers = 21.26 +/- 4.23% vs. non-dippers = 24.91 +/- 5.20%, p = 0.02), strain rate during reservoir (dippers = 1.29 +/- 0.23 s-1 vs. non-dippers =1.52 +/- 0.27 s-1, p = 0.01) and contractile period (dippers = -1.38 +/- 0.24 s-1 vs. non-dippers = -1.68 +/- 0.32 s-1, p < 0.01).
CONCLUSION
Strain and strain rate acquired from color Doppler tissue imaging demonstrate exaggerated reservoir and booster pump function in never-treated, non-dipper hypertensive patients. These methods are simple and sensitive for the early detection of subtle changes in the left atrial function.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL Jr, Jones DW, Materson BJ, Oparil S, Wright JT Jr, Roccella EJ;. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. National High Blood Pressure Education Program Coordinating Committee. The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA. 2003. 289:2560–2572.
Article2. Verdecchia P, Porcellati C, Schillaci G, Borgioni C, Ciucci A, Battistelli M, Guerrieri M, Gatteschi C, Zampi I, Santucci A, Santuci C, Reboldi G. Ambulatory blood pressure. An independent predictor of prognosis in essential hypertension. Hypertension. 1994. 24:793–801.
Article3. Pickering TG. The clinical significance of diurnal blood pressure variations. Dippers and nondippers. Circulation. 1990. 81:700–702.
Article4. Pickering TG. Blood pressure measurement and detection of hypertension. Lancet. 1994. 344:31–35.
Article5. Cuspidi C, Meani S, Valerio C, Fusi V, Catini E, Sala C, Zanchetti A. Ambulatory blood pressure, target organ damage and left atrial size in never-treated essential hypertensive individuals. J Hypertens. 2005. 23:1589–1595.
Article6. Kim WS, Park SH. Correlation between N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide and Doppler Echocardiographic Parameters of Left Ventricular Filling Pressure in Atrial Fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2011. 19:26–31.
Article7. Wambach G, Bönner G, Stimpel M, Kaufmann W. Relationship between plasma atrial natriuretic peptide and left atrial and left ventricular involvement in essential hypertension. J Hypertens. 1988. 6:573–577.
Article8. Nakatsu T, Shinohata R, Mashima K, Yuki Y, Nishitani A, Toyonaga S, Ogawa H, Hirohata S, Usui S, Kusachi S. Use of plasma Btype natriuretic peptide level to identify asymptomatic hypertensive patients with abnormal diurnal blood pressure variation profiles: nondippers, extreme dippers, and risers. Hypertens Res. 2007. 30:651–658.
Article9. Nyström F, Malmqvist K, Lind L, Kahan T. Nurse-recorded clinic and ambulatory blood pressures correlate equally well with left ventricular mass and carotid intima-media thickness. J Intern Med. 2005. 257:514–522.
Article10. Leung DY, Boyd A, Ng AA, Chi C, Thomas L. Echocardiographic evaluation of left atrial size and function: current understanding, pathophysiologic correlates, and prognostic implications. Am Heart J. 2008. 156:1056–1064.
Article11. Sirbu C, Herbots L, D'hooge J, Claus P, Marciniak A, Langeland T, Bijnens B, Rademakers FE, Sutherland GR. Feasibility of strain and strain rate imaging for the assessment of regional left atrial deformation: a study in normal subjects. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2006. 7:199–208.
Article12. Eshoo S, Boyd AC, Ross DL, Marwick TH, Thomas L. Strain rate evaluation of phasic atrial function in hypertension. Heart. 2009. 95:1184–1191.
Article13. Muranaka A, Yuda S, Tsuchihashi K, Hashimoto A, Nakata T, Miura T, Tsuzuki M, Wakabayashi C, Watanabe N, Shimamoto K. Quantitative assessment of left ventricular and left atrial functions by strain rate imaging in diabetic patients with and without hypertension. Echocardiography. 2009. 26:262–271.
Article14. Di Salvo G, Caso P, Lo Piccolo R, Fusco A, Martiniello AR, Russo MG, D'Onofrio A, Severino S, Calabró P, Pacileo G, Mininni N, Calabró R. Atrial myocardial deformation properties predict maintenance of sinus rhythm after external cardioversion of recent-onset lone atrial fibrillation: a color Doppler myocardial imaging and transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiographic study. Circulation. 2005. 112:387–395.
Article15. Schneider C, Malisius R, Krause K, Lampe F, Bahlmann E, Boczor S, Antz M, Ernst S, Kuck KH. Strain rate imaging for functional quantification of the left atrium: atrial deformation predicts the maintenance of sinus rhythm after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J. 2008. 29:1397–1409.
Article16. Aydin M, Ozeren A, Bilge M, Dursun A, Cam F, Elbey MA. Effects of dipper and non-dipper status of essential hypertension on left atrial mechanical functions. Int J Cardiol. 2004. 96:419–424.
Article17. Lang RM, Bierig M, Devereux RB, Flachskampf FA, Foster E, Pellikka PA, Picard MH, Roman MJ, Seward J, Shanewise JS, Solomon SD, Spencer KT, Sutton MS, Stewart WJ. Chamber Quantification Writing Group. American Society of Echocardiography's Guidelines and Standards Committee. European Association of Echocardiography. Recommendations for chamber quantification: a report from the American Society of Echocardiography's Guidelines and Standards Committee and the Chamber Quantification Writing Group, developed in conjunction with the European Association of Echocardiography, a branch of the European Society of Cardiology. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2005. 18:1440–1463.
Article18. Toutouzas K, Trikas A, Pitsavos C, Barbetseas J, Androulakis A, Stefanadis C, Toutouzas P. Echocardiographic features of left atrium in elite male athletes. Am J Cardiol. 1996. 78:1314–1317.
Article19. Erol MK, Yilmaz M, Acikel M, Karakelleoglu S. Left atrial mechanical function in patients with essential hypertension. Acta Cardiol. 2002. 57:323–327.20. Barbier P, Solomon SB, Schiller NB, Glantz SA. Left atrial relaxation and left ventricular systolic function determine left atrial reservoir function. Circulation. 1999. 100:427–436.
Article21. Matsuda M, Matsuda Y. Mechanism of left atrial enlargement related to ventricular diastolic impairment in hypertension. Clin Cardiol. 1996. 19:954–959.
Article22. Eshoo S, Ross DL, Thomas L. Impact of mild hypertension on left atrial size and function. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2009. 2:93–99.
Article23. Pickering TG, James GD. Ambulatory blood pressure and prognosis. J Hypertens Suppl. 1994. 12:S29–S33.
Article24. Kim BK, Lim YH, Lee HT, Lee JU, Kim KS, Kim SG, Kim JH, Lim HK, Shin J. Non-Dipper Pattern is a Determinant of the Inappropriateness of Left Ventricular Mass in Essential Hypertensive Patients. Korean Circ J. 2011. 41:191–197.
Article25. Seo HS, Kang TS, Park S, Choi EY, Ko YG, Choi D, Ha J, Rim SJ, Chung N. Non-dippers are associated with adverse cardiac remodeling and dysfunction (R1). Int J Cardiol. 2006. 112:171–177.
Article26. Ermis N, Acikgoz N, Cuglan B, Cansel M, Yagmur J, Tasolar H, Barutcu I, Pekdemir H, Ozdemir R. Comparison of atrial electromechanical coupling interval and P-wave dispersion in non-dipper versus dipper hypertensive subjects. Blood Press. 2010. 20:60–66.
Article27. Soylu A, Yazici M, Duzenli MA, Tokac M, Ozdemir K, Gok H. Relation between abnormalities in circadian blood pressure rhythm and target organ damage in normotensives. Circ J. 2009. 73:899–904.
Article28. Hoshide S, Kario K, Hoshide Y, Umeda Y, Hashimoto T, Kunii O, Ojima T, Shimada K. Associations between nondipping of nocturnal blood pressure decrease and cardiovascular target organ damage in strictly selected community-dwelling normotensives. Am J Hypertens. 2003. 16:434–438.
Article29. Saha SK, Anderson PL, Caracciolo G, Kiotsekoglou A, Wilansky S, Govind S, Mori N, Sengupta PP. Global left atrial strain correlates with CHADS2 risk score in patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2011. 24:506–512.
Article30. Vianna-Pinton R, Moreno CA, Baxter CM, Lee KS, Tsang TS, Appleton CP. Two-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography of the left atrium: feasibility and regional contraction and relaxation differences in normal subjects. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2009. 22:299–305.
Article31. Mor-Avi V, Lang RM, Badano LP, Belohlavek M, Cardim NM, Derumeaux G, Galderisi M, Marwick T, Nagueh SF, Sengupta PP, Sicari R, Smiseth OA, Smulevitz B, Takeuchi M, Thomas JD, Vannan M, Voigt JU, Zamorano JL. Current and evolving echocardiographic techniques for the quantitative evaluation of cardiac mechanics: ASE/EAE consensus statement on methodology and indications endorsed by the Japanese Society of Echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2011. 24:277–313.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Relationship between ambulatory blood pressure monitoring and cardiac function
- Blood Pressure Variation and Cardiovascular Risks
- The Relationship between Plasma Level of Immunoreactive Atrial Natriuretic Factor and Hemodynamic Function in Man
- Echocardiographic Measurement of Left Atrial Strain as a Tool for Assessing Left Atrial Function and Geometric Change
- Diurnal Variation of Blood Pressure; the Difference between before and after Removal of Pheochromocytoma: Evaluation by Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring