Korean J Orthod.
2010 Aug;40(4):239-249. 10.4041/kjod.2010.40.4.239.
Expression of nitric oxide synthases in the mandibular condyle of anterior repositioned rat mandibles
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthodontics, School of Dentistry, Wonkwang University, Korea. sangkim@wku.ac.kr
- KMID: 1975604
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4041/kjod.2010.40.4.239
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
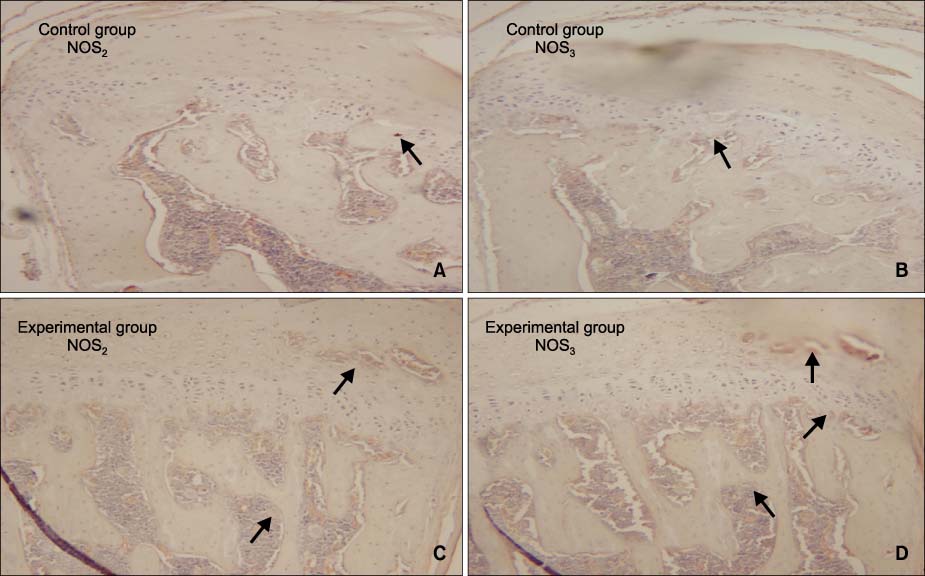
The aim of this study was to identify the expression of nitric oxide synthases (NOS) in the mandibular condyle during mandible advancement by functional appliance and to correlate it with the histologic changes and bone remodeling.
METHODS
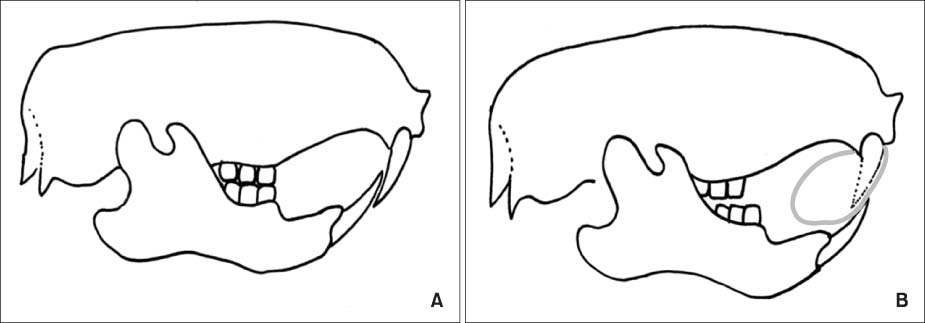
Twenty-four female, 35-day-old Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into 3 experimental groups. In all experimental groups, the mandibles of the rats were kept in a continuous forward position with a fixed bite jumping appliance. The rats were sacrificed on the 3rd, 14th, and 30th days of experiment. More than 2 rats in each group were used for staining.
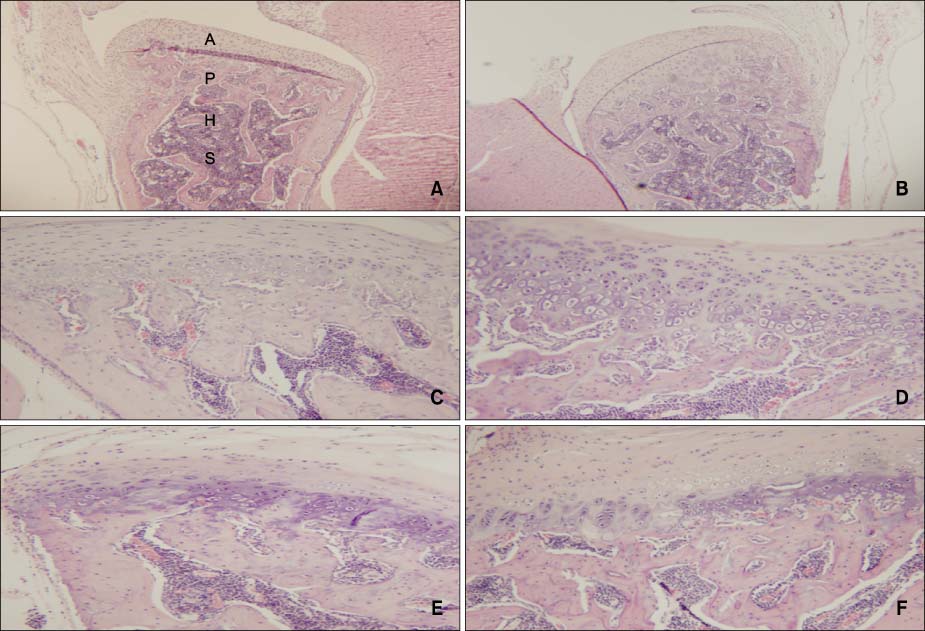
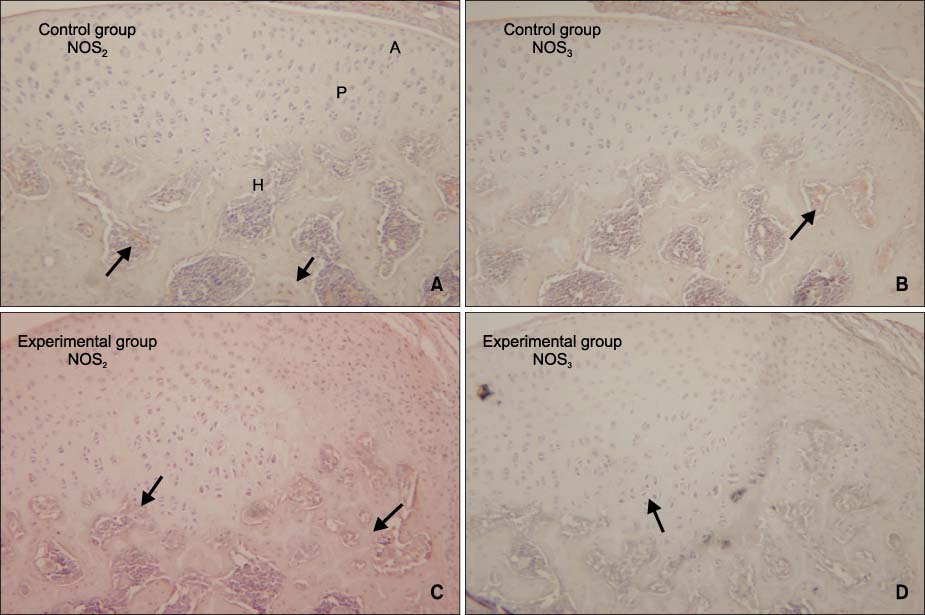
RESULTS
There were no remarkable histologic changes and NOS expression differences in the control group. The most prominent histologic changes occurred in the 14th day experimental group. NOS decreased in the 30th day experimental group. There was increased expression of NOS2 and NOS3 in all experimental groups, comparative to the control group. In all the experimental groups and control group, the expression of NOS2 was greater than that of NOS3.
CONCLUSIONS
It is postulated that NOS2 and NOS3 in the mandibular condyle might play an important role in bone remodelling of the mandibular condyle.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ruf S, Pancherz H. Temporomandibular joint remodeling in adolescents and young adults during Herbst treatment: A prospective longitudinal magnetic resonance imaging and cephalometric radiographic investigation. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1999. 115:607–618.
Article2. McNamara JA Jr. Neuromuscular and skeletal adaptations to altered function in the orofacial region. Am J Orthod. 1973. 64:578–606.
Article3. Pancherz H. The Herbst appliance--its biologic effects and clinical use. Am J Orthod. 1985. 87:1–20.
Article4. Rabie AB, Zhao Z, Shen G, Hägg EU, Dr O, Robinson W. Osteogenesis in the glenoid fossa in response to mandibular advancement. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2001. 119:390–400.
Article5. McNamara JA Jr, Carlson DS. Quantitative analysis of temporomandibular joint adaptations to protrusive function. Am J Orthod. 1979. 76:593–611.
Article6. McNamara JA Jr, Bryan FA. Long-term mandibular adaptations to protrusive function: an experimental study in Macaca mulatta. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1987. 92:98–108.
Article7. Zaman G, Pitsillides AA, Rawlinson SC, Suswillo RF, Mosley JR, Cheng MZ, et al. Mechanical strain stimulates nitric oxide production by rapid activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in osteocytes. J Bone Miner Res. 1999. 14:1123–1131.
Article8. Binderman I, Shimshoni Z, Somjen D. Biochemical pathways involved in the translation of physical stimulus into biological message. Calcif Tissue Int. 1984. 36:suppl 1. S82–S85.
Article9. Yeh CK, Rodan GA. Tensile forces enhance prostaglandin E synthesis in osteoblastic cells grown on collagen ribbons. Calif Tissue Int. 1984. 36:suppl 1. S67–S71.
Article10. Frangos JA, Eskin SG, McIntire LV, Ives CL. Flow effects on prostacyclin production by cultured human endothelial cells. Science. 1985. 227:1477–1479.
Article11. Reich KM, Mcallister TN, Gudi S, Frangos JA. Activation of G proteins mediates flow-induced prostaglandin E2 production in osteoblasts. Endocrinology. 1997. 138:1014–1018.
Article12. Kuchan MJ, Frangos JA. Role of calcium and calmodulin in flow-induced nitric oxide production in endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1994. 266:C628–C636.
Article13. Snyder SH, Bredt DS. Biological roles of nitric oxide. Sci Am. 1992. 266:68–71. 74-7.
Article14. Morgan L. Nitric oxide: a challenge to chiropractic. J Can Chiropr Assoc. 2000. 44:40–48.15. Fox SW, Chambers TJ, Chow JW. Nitric oxide is an early mediator of the increase in bone formation by mechanical stimulation. Am J Physiol. 1996. 270:E955–E960.
Article16. Turner CH, Takano Y, Owan I, Murrell GA. Nitric oxide inhibitor L-NAME suppresses mechanically induced bone formation in rats. Am J Physiol. 1996. 270:E634–E639.
Article17. Lamas S, Marsden PA, Li GK, Tempst P, Michel T. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase: molecular cloning and characterization of a distinct constitutive enzyme isoform. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992. 89:6348–6352.
Article18. Xie QW, Cho HJ, Calaycay J, Mumford RA, Swiderek KM, Lee TD, et al. Cloning and characterization of inducible nitric oxide synthase from mouse macrophages. Science. 1992. 256:225–228.
Article19. Ignarro LJ, Buga GM, Wood KS, Byrns RE, Chaudhuri G. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor produced and released from artery and vein is nitric oxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987. 84:9265–9269.
Article20. Palmer RM, Ferrige AG, Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987. 327:524–526.
Article21. Villars F, Bordenave L, Bareille R, Amédée J. Effect of human endothelial cells on human bone marrow stromal cell phenotype: role of VEGF? J cell Biochem. 2000. 79:672–685.
Article22. Ferrara N. Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in the regulation of angiogenesis. Kidney Int. 1999. 56:794–814.
Article23. Shum L, Rabie AB, Hägg U. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression and bone formation in posterior glenoid fossa during stepwise mandibular advancement. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2004. 125:185–190.
Article24. Rabie AB, Wong L, Hägg U. Correlation of replicating cells and osteogenesis in the glenoid fossa during stepwise advancement. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2003. 123:521–526.
Article25. Griffith OW, Stuehr DJ. Nitric oxide synthases: properties and catalytic mechanism. Annu Rev Physiol. 1995. 57:707–736.
Article26. Reif DW, McCreedy SA. N-nitro-L-arginine and N-monomethyl-L-arginine exhibit a different pattern of inactivation toward the three nitric oxide synthases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1995. 320:170–176.
Article27. Pitsillides AA, Rawlinson SC, Suswillo RF, Bourrin S, Zaman G, Lanyon LE. Mechanical strain-induced NO production by bone cells: a possible role in adaptive bone (re)modeling? FASEB J. 1995. 9:1614–1622.
Article28. Woodside DG, Metaxas A, Altuna G. The influence of functional appliance therapy on glenoid fossa remodelling. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1987. 92:181–198.
Article29. Vargervik K, Harvold EP. Response to activator treatment in Class II malocclusions. Am J Orthod. 1985. 88:242–251.
Article30. Graber TM, Vanasdall RL Jr. Orthodontics, current principles and techniques. 2000. 3rd ed. St Louis: Mosby;473–520.31. Hukkanen M, Hughes FJ, Buttery LD, Gross SS, Evans TJ, Seddon S, et al. Cytokine-stimulated expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase by mouse, rat, and human osteoblast-like cells and its functional role in osteoblast metabolic activity. Endocrinology. 1995. 136:5445–5453.
Article32. Marletta MA. Nitric oxide synthase: aspects concerning structure and catalysis. Cell. 1994. 78:927–930.
Article33. Govers R, Rabelink TJ. Cellular regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2001. 280:F193–F206.
Article34. Fukumura D, Gohongi T, Kadambi A, Izumi Y, Ang J, Yun CO, et al. Predominant role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis and vascular permeability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. 98:2604–2609.
Article35. Duda DG, Fukumura D, Jain RK. Role of eNOS in neovascularization: NO for endothelial progenitor cells. Trends Mol Med. 2004. 10:143–145.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Expression of Constitutive Nitric Oxide Synthase by Gastrointestinal Epithelial Cells
- Alteration of Nitric Oxide Synthase Subtype Expression in Contralateral Testis of Rat in Response to Unilateral Testicular Torsion Followed by Detorsion
- Involvement of Fibronectin in the Migration of Macrophage and Expression of Nitric Oxide Synthase in the BCG induced Inflammatory Sites in Rat Bladder
- Effects of Repetitive Ischemic Preconditioning on the Expression of Nitric Oxide Synthase in Tibialis Anterior and Soleus Muscles of the Rat
- Altered renal nitric oxide system in experimental hypertensive rats