Relationship between Physical Examinations and Two-Dimensional Computed Tomographic Findings in Children with Intoeing Gait
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Pusan Paik Hospital, Busan 614-735, Korea. ddongsiki@naver.com
- 2Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan 612-030, Korea.
- KMID: 1971714
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2011.35.4.491
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
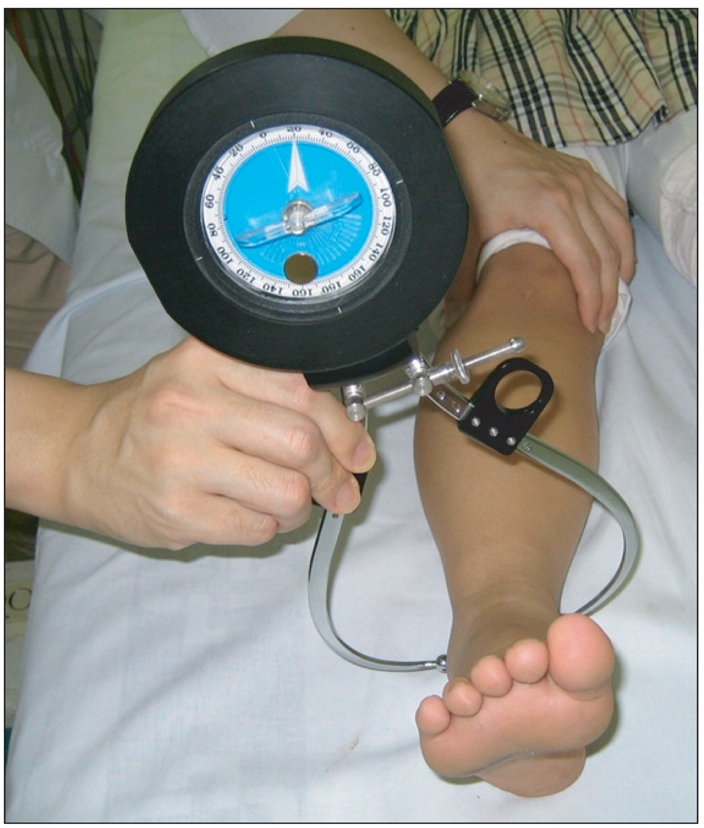
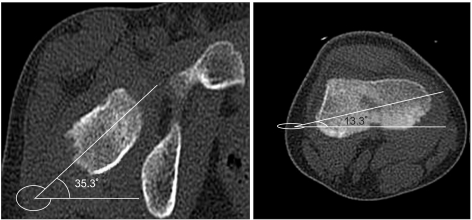
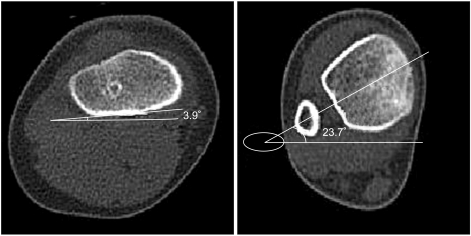
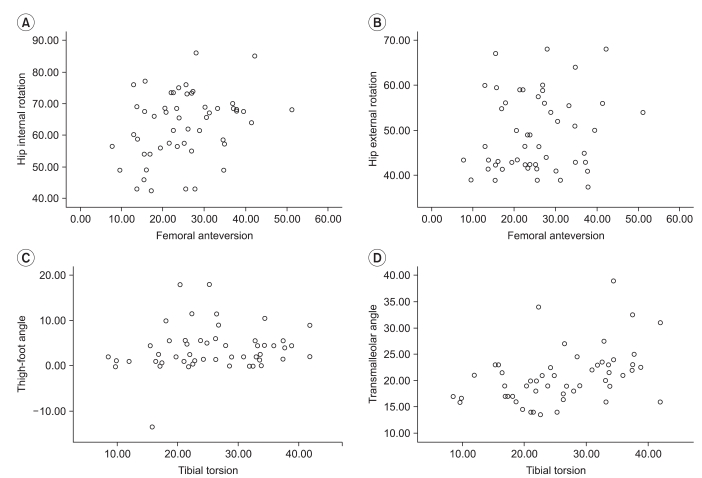
To evaluate the validity of physical examinations by assessment of correlation between physical examinations and CT measurements in children with intoeing gait and the causes of intoeing gait by age using CT measurements. METHOD: Twenty-six children with intoeing gait participated in this study. The internal and external hip rotation, thigh-foot angle and transmalleolar angle were measured. In addition, femoral anteversion and tibial torsion of the subjects were assessed using a CT scan. The measurements of torsional angles were performed twice by two raters. The correlation coefficients between physical examinations and CT measurements were calculated using Pearson correlation. The data was analyzed statistically using SPSS v12.0.
RESULTS
The correlation coefficients between physical examinations and CT measurements were not high. Before 5 years of age, intoeing gait was caused by femoral anteversion in 17.86%, tibial torsion in 32.29% and the combination of causes in 35.71% of cases. After 6 years of age, the contributions changed to 29.17%, 8.33% and 45.83%, respectively.
CONCLUSION
Before 5 years of age, the common cause of an intoeing gait was tibial torsion, whereas after 6 years of age it was femoral anteversion. Regardless of age, the most common cause of intoeing gait was a combination of causes. This study shows poor correlation between physical examinations and CT. Therefore, it is limiting to use physical examination only for evaluating the cause of intoeing gait in clinical practice.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
The Availability of Radiological Measurement of Femoral Anteversion Angle: Three-Dimensional Computed Tomography Reconstruction
Ha Young Byun, Heesuk Shin, Eun Shin Lee, Min Sik Kong, Seung Hun Lee, Chang Hee Lee
Ann Rehabil Med. 2016;40(2):237-243. doi: 10.5535/arm.2016.40.2.237.Therapeutic Effect of Microcurrent Therapy in Children With In-toeing Gait Caused by Increased Femoral Anteversion: A Pilot Study
Jae Ki Ahn, Dong Rak Kwon, Gi-Young Park, Ki-Hoon Lee, Jae Hwal Rim, Won Bin Jung, Dae Gil Kwon
Ann Rehabil Med. 2017;41(1):104-112. doi: 10.5535/arm.2017.41.1.104.A New Instrument for Measuring Tibial Torsion in Pediatric Patients
Ji Hyun Jeon, Yong-Soon Yoon, Kwang Jae Lee, Ki Pi Yu, Jong Hoo Lee, Tae Yong Seog, EunJi Son
Ann Rehabil Med. 2017;41(3):441-449. doi: 10.5535/arm.2017.41.3.441.Change of Femoral Anteversion Angle in Children With Intoeing Gait Measured by Three-Dimensional Computed Tomography Reconstruction: One-Year Follow-Up Study
Minsik Kong, Hongsik Jo, Chang Han Lee, Se-Woong Chun, Chulho Yoon, Heesuk Shin
Ann Rehabil Med. 2018;42(1):137-144. doi: 10.5535/arm.2018.42.1.137.
Reference
-
1. Li YH, Leong JC. Intoeing gait in children. Hong Kong Med J. 1999; 5:360–366. PMID: 10870163.2. Inan M, Altintas F, Duru I. The evaluation and management of rotational deformity in cerebral palsy. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2009; 43:106–112. PMID: 19448350.
Article3. Butler-Manuel PA, Guy RL, Heatley FW. Measurement of tibial torsion--a new technique applicable to ultrasound and computed tomography. Br J Radiol. 1992; 65:119–126. PMID: 1540801.
Article4. Clementz BG, Magnusson A. Assessment of tibial torsion employing fluoroscopy, computed tomography and the cryosectioning technique. Acta Radiol. 1989; 30:75–80. PMID: 2914121.
Article5. Jakob RP, Haertel M, Stussi E. Tibial torsion calculated by computerised tomography and compared to other methods of measurement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1980; 62-B:238–242. PMID: 7364840.
Article6. Jend HH, Heller M, Dallek M, Schoettle H. Measurement of tibial torsion by computer tomography. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh). 1981; 22:271–276. PMID: 7315504.
Article7. Lee SH, Chung CY, Park MS, Choi IH, Cho TJ. Tibial torsion in cerebral palsy: validity and reliability of measurement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009; 467:2098–2104. PMID: 19159112.
Article8. Weiner DS, Cook AJ, Hoyt WA Jr, Oravec CE. Computed tomography in the measurement of femoral anteversion. Orthopedics. 1978; 1:299–306. PMID: 733194.
Article9. King HA, Staheli LT. Torsional problems in cerebral palsy. Foot Ankle. 1984; 4:180–184. PMID: 6714858.
Article10. Song DH, Eun BL, Park SH, Lee JY, Tockgo YC. Tibial torsion in children of the Jeju area. Korean J Pediatr. 2005; 48:75–80.11. Jang SH, Woo BS, Park SB, Lee SG. Relationship between femoral anteversion and tibial torsion in intoeing gait. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 1999; 23:390–396.12. LaGasse DJ, Staheli LT. The measurement of femoral anteversion. A comparison of the fluoroscopic and biplane roentgenographic methods of measurement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1972; 86:13–15. PMID: 5047779.13. Mahboubi S, Horstmann H. Femoral torsion: CT measurement. Radiology. 1986; 160:843–844. PMID: 3737928.
Article14. Billing L. Roentgen examination of the proximal femur end in children and adolescents; a standardized technique also suitable for determination of the collum-, anteversion-, and epiphyseal angles; a study of slipped epiphysis and coxa plana. Acta Radiol Suppl. 1954; 110:1–80. PMID: 13158141.15. Rethlefsen SA, Healy BS, Wren TA, Skaggs DL, Kay RM. Causes of intoeing gait in children with cerebral palsy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88:2175–2180. PMID: 17015594.
Article16. Sass P, Hassan G. Lower extremity abnormalities in children. Am Fam Physician. 2003; 68:461–468. PMID: 12924829.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Relationship between Femoral Anteversion and Tibial Torsion in Intoeing Gait
- Change of Femoral Anteversion Angle in Children With Intoeing Gait Measured by Three-Dimensional Computed Tomography Reconstruction: 3-Year Follow-Up Study
- Change of Femoral Anteversion Angle in Children With Intoeing Gait Measured by Three-Dimensional Computed Tomography Reconstruction: One-Year Follow-Up Study
- The Availability of Radiological Measurement of Tibial Torsion: Three-Dimensional Computed Tomography Reconstruction
- Anthropologic Study of Korean Mandible Using Three--dimensional Computed Tomography--Evaluation of the Accuracy of a Three--dimensional Image