Clin Exp Vaccine Res.
2015 Jul;4(2):177-183. 10.7774/cevr.2015.4.2.177.
Production of specific IgY Helicobacter pylori recombinant OipA protein and assessment of its inhibitory effects towards attachment of H. pylori to AGS cell line
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Bacteriology, Faculty of Medical Sciences, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran. mmmobarez@modares.ac.ir
- 2Diagnosis Biotechnology Units, Pasteur Institute of Iran, Alborz, Iran. khabiri@pasteur.ac.ir
- 3Department of Genetic, Faculty of Life Sciences, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran.
- KMID: 1965402
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7774/cevr.2015.4.2.177
Abstract
- PURPOSE
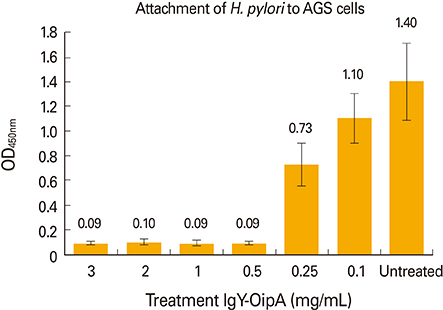
The common triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori is challenged by the increasing cases of antibiotic resistant infections, raising the need to explore alternative therapies. Oral administration of egg yolk immunoglobulin Y (IgY) has been previously reported as a means of passive immunization therapy for H. pylori infections. In this work, we investigated the inhibitory effect of IgY on the attachment of H. pylori to AGS cell line.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
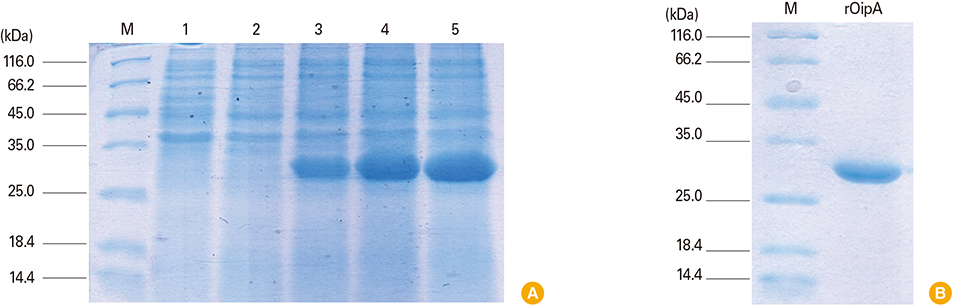
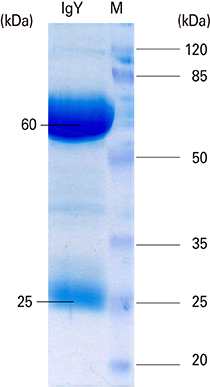
Recombinant OipA was prepared. Hens were immunized with recombinant protein three times. IgY was purified from egg yolks of immunized hens using polyethylene glycol precipitation method. The inhibitory effect of the specific immunoglobulin was evaluated in AGS cell line infected with H. pylori.
RESULTS
The presence of recombinant OipA (30 kD) was confirmed via sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Immunization of hens was confirmed using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The purified IgY from egg yolks were assessed using SDS-PAGE and confirmed by western blot.
CONCLUSION
The results showed that IgY-OipA had inhibitory effect on attachment of H. pylori to AGS cell line and may be utilized as a therapeutic or prophylaxis material.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Administration, Oral
Blotting, Western
Cell Line*
Complementary Therapies
Egg Yolk
Electrophoresis, Polyacrylamide Gel
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Helicobacter pylori*
Helicobacter*
Immunization
Immunization, Passive
Immunoglobulins
Polyethylene Glycols
Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate
Immunoglobulins
Polyethylene Glycols
Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ricci V, Romano M, Boquet P. Molecular cross-talk between Helicobacter pylori and human gastric mucosa. World J Gastroenterol. 2011; 17:1383–1399.
Article2. Matsunari O, Shiota S, Suzuki R, et al. Association between Helicobacter pylori virulence factors and gastroduodenal diseases in Okinawa, Japan. J Clin Microbiol. 2012; 50:876–883.
Article3. Liu YE, Gong YH, Sun LP, Xu Q, Yuan Y. The relationship between H. pylori virulence genotypes and gastric diseases. Pol J Microbiol. 2012; 61:147–150.
Article4. Gisbert JP, Pajares JM. Treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection: the past and the future. Eur J Intern Med. 2010; 21:357–359.
Article5. Gerrits MM, van Vliet AH, Kuipers EJ, Kusters JG. Helicobacter pylori and antimicrobial resistance: molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. Lancet Infect Dis. 2006; 6:699–709.
Article6. Kovacs-Nolan J, Mine Y. Egg yolk antibodies for passive immunity. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol. 2012; 3:163–182.
Article7. Nomura S, Suzuki H, Masaoka T, et al. Effect of dietary anti-urease immunoglobulin Y on Helicobacter pylori infection in Mongolian gerbils. Helicobacter. 2005; 10:43–52.
Article8. Xu Y, Li X, Jin L, et al. Application of chicken egg yolk immunoglobulins in the control of terrestrial and aquatic animal diseases: a review. Biotechnol Adv. 2011; 29:860–868.
Article9. Shin JH, Yang M, Nam SW, et al. Use of egg yolk-derived immunoglobulin as an alternative to antibiotic treatment for control of Helicobacter pylori infection. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2002; 9:1061–1066.
Article10. Malekshahi ZV, Gargari SL, Rasooli I, Ebrahimizadeh W. Treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection in mice with oral administration of egg yolk-driven anti-UreC immunoglobulin. Microb Pathog. 2011; 51:366–372.
Article11. Kudo T, Nurgalieva ZZ, Conner ME, et al. Correlation between Helicobacter pylori OipA protein expression and oipA gene switch status. J Clin Microbiol. 2004; 42:2279–2281.
Article12. Dossumbekova A, Prinz C, Mages J, et al. Helicobacter pylori HopH (OipA) and bacterial pathogenicity: genetic and functional genomic analysis of hopH gene polymorphisms. J Infect Dis. 2006; 194:1346–1355.
Article13. Franco AT, Johnston E, Krishna U, et al. Regulation of gastric carcinogenesis by Helicobacter pylori virulence factors. Cancer Res. 2008; 68:379–387.
Article14. Teymournejad O, Mobarez AM, Hassan ZM, Noori S, Moazzeni SM, Khoramabadi N. Cloning, expression, purification and toxicity evaluation of Helicobacter pylori outer inflammatory protein A. Indian J Microbiol. 2013; 53:391–394.
Article15. Aghababa H, Mohabati Mobarez A, Khoramabadi N, et al. A comparative approach to strategies for cloning, expression, and purification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis mycolyl transferase 85B and evaluation of immune responses in BALB/c mice. Mol Biotechnol. 2014; 56:487–497.
Article16. Khabiri AR, Bagheri F, Alimohammadian MH, Assmar M, Nadaf SR. Leishmanin skin test in guinea pig with a single purified protein of Leishmania major. Exp Parasitol. 2005; 111:239–243.
Article17. Pauly D, Chacana PA, Calzado EG, Brembs B, Schade R. IgY technology: extraction of chicken antibodies from egg yolk by polyethylene glycol (PEG) precipitation. J Vis Exp. 2011; (51):3084.
Article18. Ramezani V, Vatanara A, Najafabadi AR, Shokrgozar MA, Khabiri A, Seyedabadi M. A comparative study on the physicochemical and biological stability of IgG1 and monoclonal antibodies during spray drying process. Daru. 2014; 22:31.
Article19. Laemmli UK. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970; 227:680–685.
Article20. Zhang ZW, Dorrell N, Wren BW, Farthingt MJ. Helicobacter pylori adherence to gastric epithelial cells: a role for non-adhesin virulence genes. J Med Microbiol. 2002; 51:495–502.
Article21. Yu CC, Yang JC, Chang YC, et al. VCP phosphorylation-dependent interaction partners prevent apoptosis in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric epithelial cells. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e55724.
Article22. Kim N, Park WY, Kim JM, et al. Analysis of gene expression profile of AGS cells stimulated by Helicobacter pylori adhesion. Gut Liver. 2007; 1:40–48.
Article23. Schade R, Terzolo HR. IgY-technology: application and trends. EPC 2006. 12th European Poultry Conference; 2006 Sep 10-14; Verona, Italy. Beekbergen: World's Poultry Science Association (WPSA);2006.24. Lee EN, Sunwoo HH, Menninen K, Sim JS. In vitro studies of chicken egg yolk antibody (IgY) against Salmonella enteritidis and Salmonella typhimurium. Poult Sci. 2002; 81:632–641.
Article25. Sarker SA, Casswall TH, Juneja LR, et al. Randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trial of hyperimmunized chicken egg yolk immunoglobulin in children with rotavirus diarrhea. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2001; 32:19–25.
Article26. Schade R, Zhang XY, Terzolo HR. Use of IgY antibodies in human and veterinary medicine. In : Huopalahti R, Lopez-Fandino R, Anton M, Schade R, editors. Bioactive egg compounds. . Berlin: Springer-Verlag;2007. p. 213–222.27. Rahman S, Van Nguyen S, Icatlo FC Jr, Umeda K, Kodama Y. Oral passive IgY-based immunotherapeutics: a novel solution for prevention and treatment of alimentary tract diseases. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013; 9:1039–1048.28. Tini M, Jewell UR, Camenisch G, Chilov D, Gassmann M. Generation and application of chicken egg-yolk antibodies. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2002; 131:569–574.
Article29. Andersen LP. Colonization and infection by Helicobacter pylori in humans. Helicobacter. 2007; 12:Suppl 2. 12–15.
Article30. Suzuki H, Nomura S, Masaoka T, et al. Effect of dietary anti-Helicobacter pylori-urease immunoglobulin Y on Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004; 20:Suppl 1. 185–192.
Article31. Yamaoka Y, Kita M, Kodama T, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection in mice: role of outer membrane proteins in colonization and inflammation. Gastroenterology. 2002; 123:1992–2004.
Article32. Yamaoka Y. Mechanisms of disease: Helicobacter pylori virulence factors. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010; 7:629–641.
Article33. Keates AC, Tummala S, Peek RM Jr, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection stimulates plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 production by gastric epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 2008; 76:3992–3999.
Article34. Akita EM, Nakai S. Comparison of four purification methods for the production of immunoglobulins from eggs laid by hens immunized with an enterotoxigenic E. coli strain. J Immunol Methods. 1993; 160:207–214.
Article35. Ko KY, Ahn DU. Preparation of immunoglobulin Y from egg yolk using ammonium sulfate precipitation and ion exchange chromatography. Poult Sci. 2007; 86:400–407.
Article36. Hodek P, Trefil P, Simunek J, Simunek J, Hudecek J, Stiborova M. Optimized protocol of chicken antibody (IgY) purification providing electrophoretically homogenous preparations. Int J Electrochem Sci. 2013; 8:113–124.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Promising Effect of Egg Yolk Antibody (Immunoglobulin Yolk) on the Treatment of Helicobacter pylori-associated Gastric Diseases
- Secreted Proteins of Helicobacter pylori Identified using Pulse-Chase Analysis
- Effects of Morphologic Conversion of Helicobacter pylori on the Production of Interleukin -8 in Gastric Epithelial Cells
- The Activation of Caspase - 3 and Mitogen - activated Protein Kinases during H . Pylori - induced Apoptosis in Gastric Cancer Cells
- Helicobacter pylori-induced Apoptosis in Gastric Cancer Cell Lines