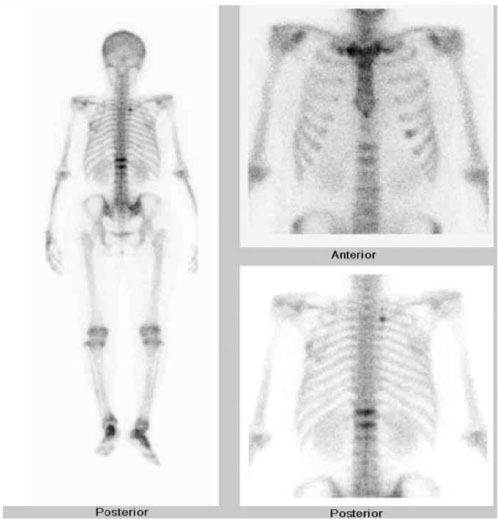
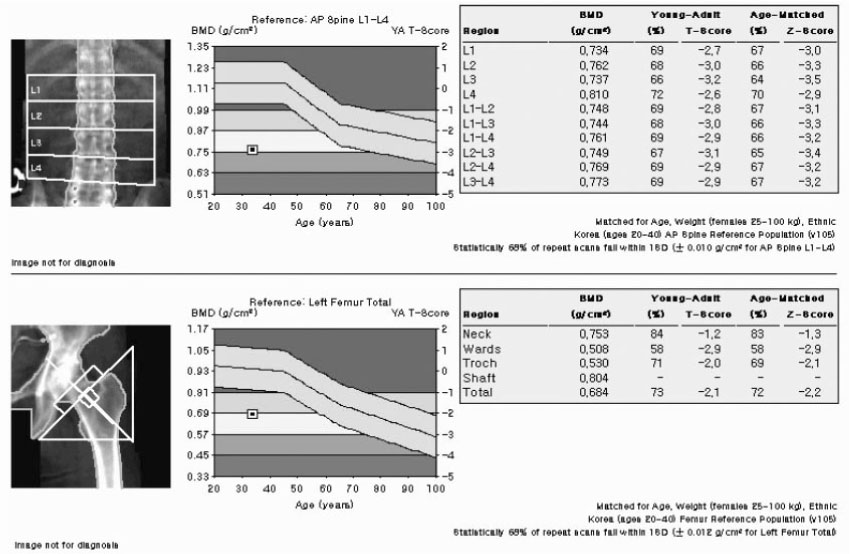
J Korean Endocr Soc.
2007 Dec;22(6):446-452. 10.3803/jkes.2007.22.6.446.
A Case of Type I Osteogenesis Imperfecta Differentially Diagnosed as a Cause of a Spinal Compression Fracture
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Korea.
- 2Research Institute of Endocrinology, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Korea.
- KMID: 1958910
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2007.22.6.446
Abstract
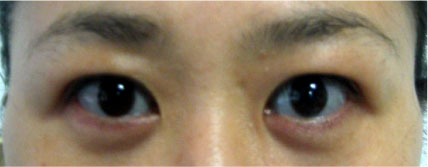
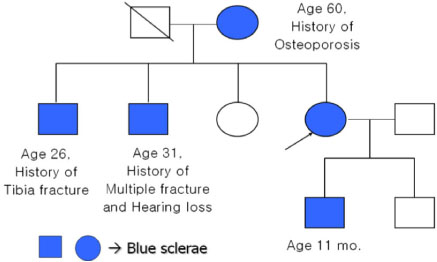
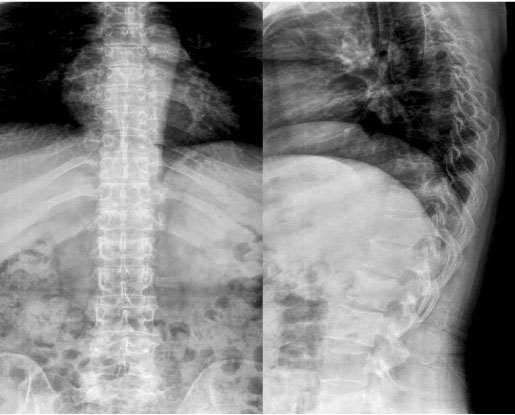
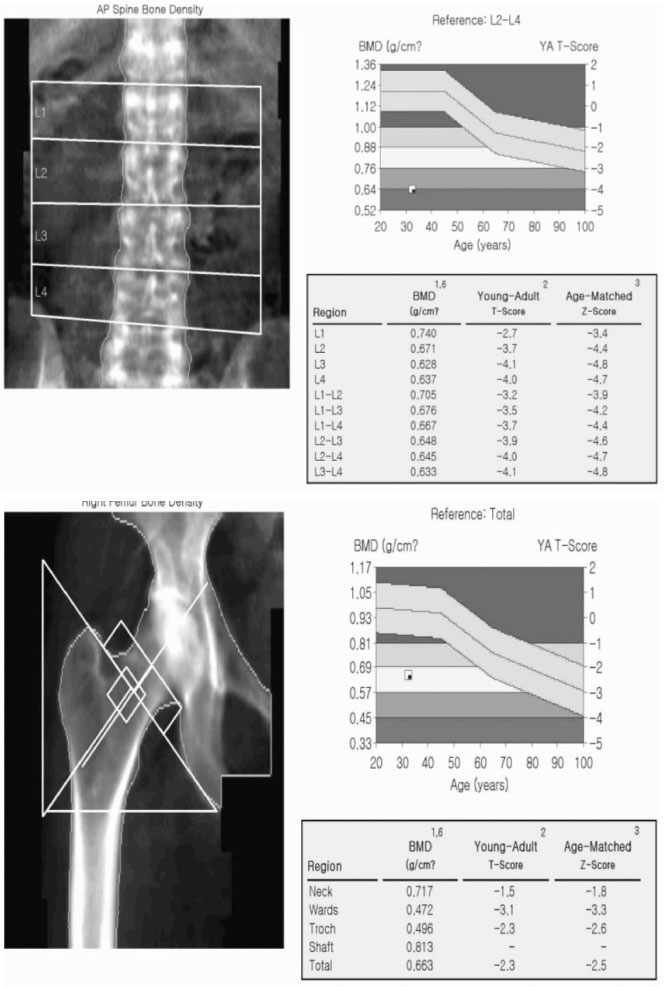
- Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is a genetic disease that is caused by a synthetic anomaly of type I collagen. It is characterized by such features as low bone density, multiple fractures, bone deformities and chronic bone pain. According to the hereditary pattern and degree of phenotypical expression, it also has various extraskeletal manifestations such as blue sclera, hearing deformities and dentinogenesis imperfecta. Recently, an expanded seven subgroup classification of OI has been suggested by means of its clinical severity and mutational characteristics. However, most of the OI cases reported in Korea have been classified as type II or III that can be diagnosed easily and present with severe clinical manifestations. Only rare type I OI cases have been currently reported in Korea. Herein, we report a case of type I OI that was differentially diagnosed as a cause of a spinal compression fracture.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shapiro JR, Stover ML, Burn VE, McKinstry MB, Burshell AL, Chipman SD, Rowe DW. An osteopenic nonfracture syndrome with features of mild osteogenesis imperfecta associated with the substitution of a cysteine for glycine at triple helix position 43 in the pro alpha 1(I) chain of type I collagen. J Clin Invest. 1992. 89:567–573.2. Raisz LG, Kream BE, Lorenzo JA. Larsen PR, Kronenberg HM, Melmed S, Polonsky KS, editors. Osteogenesis Imperfecta. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 2003. 10th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;1399–1400.3. Wenstrup RJ, Willing MC, Starman BJ, Byers PH. Distinct biochemical phenotypes predict clinical severity in nonlethal variants of osteogenesis imperfecta. Am J Hum Genet. 1990. 46:975–982.4. Sillence DO, Senn A, Danks DM. Genetic heterogeneity in osteogenesis imperfecta. J Med Genet. 1979. 16:101–116.5. Rauch F, Glorieux FH. Osteogenesis imperfecta. Lancet. 2004. 363:1377–1385.6. Jang SL, Cho YS, Kim BW, Hong SR, Park JY, Park YJ, Lee JH. A Case of Perinatal Lethal Osteogenesis Imperfecta. Korean J Perinatol. 1997. 8:55–59.7. Kim JS, Kang JB, Huh JS, Kim HB, Lee KY, Kang SW, Park KJ. A Case of Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Diagnosed in Uterus by Ultrasonogram. Korean J Obstet Gynecol. 1997. 40:198–202.8. Hong SB, Ko SM, Park YK, Park YJ, Oh YJ, Kim YW, Kim SK, Nam MS, Kim YS. Histomorphometry of Osteogenesis Imperfecta I. J Kor Soc Endocrinol. 2002. 17:117–123.9. Lee HS, Kim HJ, Cho JH, Lee SW, Kim HA, Choi JH, Song YJ, Kim DJ, Lee KW, Chung YS. Clinical Characteristics of 10 cases of Korean Osteogenesis Imperfecta. J Kor Soc Endocrinol. 2003. 18:496–503.10. Gertner JM, Root L. Osteogenesis imperfecta. Orthop Clin North Am. 1990. 21:151–162.11. Marini JC. Osteogenesis imperfecta: comprehensive management. Adv Pediatr. 1988. 35:391–426.12. Petersen K, Wetzel WE. Recent findings in classification of osteogenesis imperfecta by means of existing dental symptoms. ASDC J Dent Child. 1998. 65:305–309. 35413. Lee SW, Kim HJ, Cho JH, Lee HS, Jung YM, Kim DJ, Lee KW, Chung YS. Effects of Pamidronate Treatment on Osteogenesis Imperfecta. J Kor Soc Endocrinol. 2004. 19:485–491.14. Bischoff H, Freitag P, Jundt G, Steinmann B, Tyndall A, Theiler R. Type I osteogenesis imperfecta: diagnostic difficulties. Clin Rheumatol. 1999. 18:48–51.15. Nishi Y, Hamamoto K, Kajiyama M, Ono H, Kihara M, Jinno K. Effect of long-term calcitonin therapy by injection and nasal spray on the incidence of fractures in osteogenesis imperfecta. J Pediatr. 1992. 121:477–480.16. Noda H, Onishi H, Saitoh K, Nakajima H. Growth hormone therapy may increase fracture risk in a pubertal patient with osteogenesis imperfecta. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2002. 15:217–218.17. Rauch F, Travers R, Plotkin H, Glorieux FH. The effects of intravenous pamidronate on the bone tissue of children and adolescents with osteogenesis imperfecta. J Clin Invest. 2002. 110:1293–1299.18. Zeitlin L, Rauch F, Plotkin H, Glorieux FH. Height and weight development during four years of therapy with cyclical intravenous pamidronate in children and adolescents with osteogenesis imperfecta types I, III, and IV. Pediatrics. 2003. 111:1030–1036.19. Maasalu K, Haviko T, Martson A. Treatment of children with Osteogenesis imperfecta in Estonia. Acta Paediatr. 2003. 92:452–455.20. Sun L, Davies TF, Blair HC, Abe E, Zaidi M. TSH and bone loss. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006. 1068:309–318.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Diagnosed in Uterus by Ultrasonogram
- A Case of Perinatal Lethal Osteogeenesis Imperfecta
- Spinal anesthesia during cesarean section in a patient with severe osteogenesis imperfecta: A case report
- A Case of Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Diagnosis in Uterus by Ultrasonogram
- A Case of Osteogenesis Imperfecta Type II