J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2015 Apr;57(4):229-234. 10.3340/jkns.2015.57.4.229.
Pullout Strength after Expandable Polymethylmethacrylate Transpedicular Screw Augmentation for Pedicle Screw Loosening
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Spine Center, Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University Medical Center, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea. nscharisma@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, College of Medicine, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1956419
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.57.4.229
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Pedicle screw fixation for spine arthrodesis is a useful procedure for the treatment of spinal disorders. However, instrument failure often occurs, and pedicle screw loosening is the initial step of a range of complications. The authors recently used a modified transpedicular polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) screw augmentation technique to overcome pedicle screw loosening. Here, they report on the laboratory testing of pedicle screws inserted using this modified technique.
METHODS
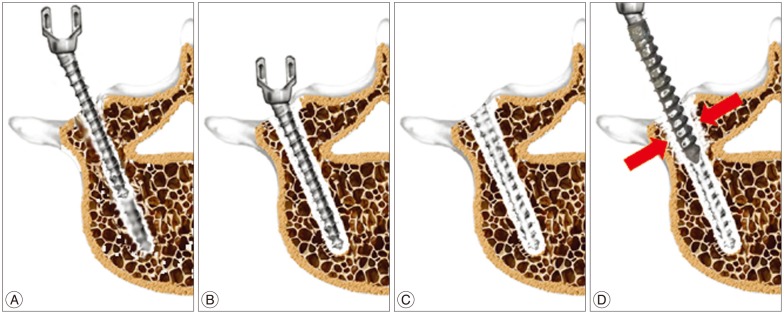
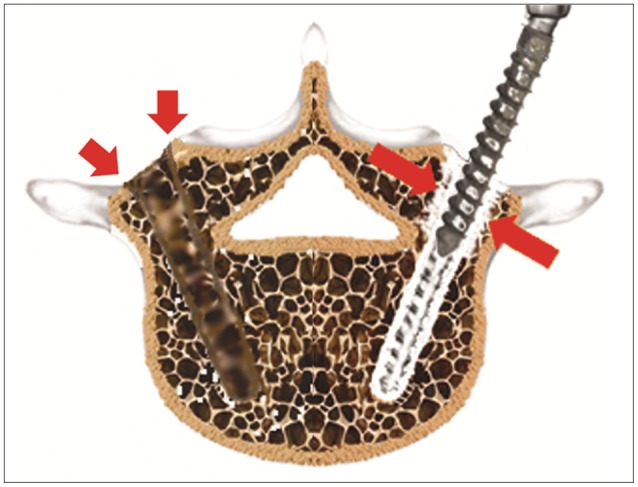
To evaluate pullout strengths three cadaveric spinal columns were used. Three pedicle screw insertion methods were utilized to compare pullout strength; the three methods used were; control (C), traditional transpedicular PMMA augmentation technique (T), and the modified transpedicular augmentation technique (M). After control screws had been pulled out, loosening with instrument was made. Screw augmentations were executed and screw pullout strength was rechecked.
RESULTS
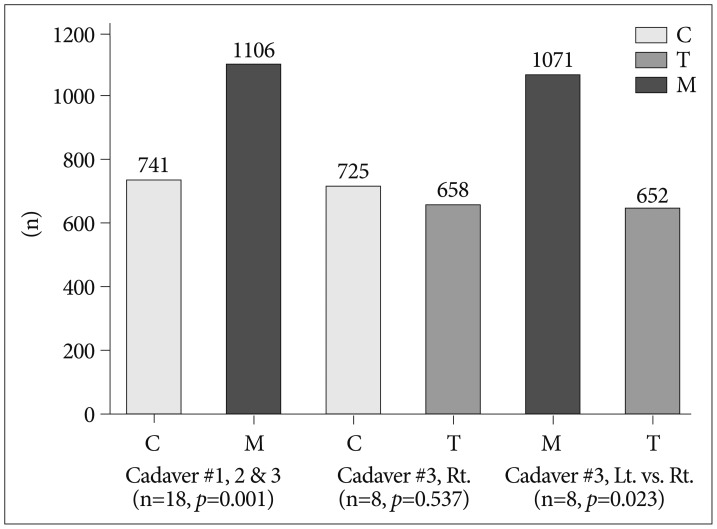
Pedicle screws augmented using the modified technique for pedicle screw loosening had higher pullout strengths than the control (1106.2+/-458.0 N vs. 741.2+/-269.5 N; p=0.001). Traditional transpedicular augmentation achieved a mean pullout strength similar to that of the control group (657.5+/-172.3 N vs. 724.5+/-234.4 N; p=0.537). The modified technique had higher strength than the traditional PMMA augmentation technique (1070.8+/-358.6 N vs. 652.2+/-185.5 N; p=0.023).
CONCLUSION
The modified PMMA transpedicular screw augmentation technique is a straightforward, effective surgical procedure for treating pedicle screw loosening, and exhibits greater pullout strength than traditional PMMA transpedicular augmentation. However, long-term clinical evaluation is required.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bullmann V, Liljenqvist UR, Schmidt C, Schulte TL. [Posterior operative correction of idiopathic scoliosis. Value of pedicle screws versus hooks]. Orthopade. 2009; 38:198–200. 202–204. PMID: 19093095.2. Burval DJ, McLain RF, Milks R, Inceoglu S. Primary pedicle screw augmentation in osteoporotic lumbar vertebrae : biomechanical analysis of pedicle fixation strength. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2007; 32:1077–1083. PMID: 17471088.3. Choma TJ, Frevert WF, Carson WL, Waters NP, Pfeiffer FM. Biomechanical analysis of pedicle screws in osteoporotic bone with bioactive cement augmentation using simulated in vivo multicomponent loading. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2011; 36:454–462. PMID: 20881517.
Article4. Denaro V, Longo UG, Maffulli N, Denaro L. Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab. 2009; 6:125–130. PMID: 22461161.5. Frankel BM, Jones T, Wang C. Segmental polymethylmethacrylate-augmented pedicle screw fixation in patients with bone softening caused by osteoporosis and metastatic tumor involvement : a clinical evaluation. Neurosurgery. 2007; 61:531–537. discussion 537-538. PMID: 17881965.6. Fu TS, Wong CB, Tsai TT, Liang YC, Chen LH, Chen WJ. Pedicle screw insertion : computed tomography versus fluoroscopic image guidance. Int Orthop. 2008; 32:517–521. PMID: 17410363.
Article7. Jang JS, Lee SH, Kim KT, Kim BS, Lee WB. A Biomechanical Study on the Pull-Out Strength of Pedicle Screw Augmented with Polymethylmethacrylate(PMMA)- Cadaveric Study -. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2002; 31:45–49.8. Jo JY, Kang SH, Park SW. Modified polymethylmethacrylate cervical plate and screw augmentation technique for intraoperative screw loosening. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2012; 25:235–239. PMID: 21423049.
Article9. Kang SH, Kim KT, Park SW, Kim YB. A case of pedicle screw loosening treated by modified transpedicular screw augmentation with polymethylmethacrylate. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2011; 49:75–78. PMID: 21494370.
Article10. Ko CC, Tsai HW, Huang WC, Wu JC, Chen YC, Shih YH, et al. Screw loosening in the Dynesys stabilization system : radiographic evidence and effect on outcomes. Neurosurg Focus. 2010; 28:E10. PMID: 20568916.11. Law M, Tencer AF, Anderson PA. Caudo-cephalad loading of pedicle screws : mechanisms of loosening and methods of augmentation. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 1993; 18:2438–2443. PMID: 8303446.12. McLain RF, Fry MF, Moseley TA, Sharkey NA. Lumbar pedicle screw salvage : pullout testing of three different pedicle screw designs. J Spinal Disord. 1995; 8:62–68. PMID: 7711371.13. Moore DC, Maitra RS, Farjo LA, Graziano GP, Goldstein SA. Restoration of pedicle screw fixation with an in situ setting calcium phosphate cement. Spine. 1997; 22:1696–1705. PMID: 9259778.
Article14. Okuyama K, Abe E, Suzuki T, Tamura Y, Chiba M, Sato K. Can insertional torque predict screw loosening and related failures? An in vivo study of pedicle screw fixation augmenting posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2000; 25:858–864. PMID: 10751298.15. Pitzen T, Franta F, Barbier D, Steudel WI. Insertion torque and pullout force of rescue screws for anterior cervical plate fixation in a fatigued initial pilot hole. J Neurosurg Spine. 2004; 1:198–201. PMID: 15347006.
Article16. Ploeg WT, Veldhuizen AG, The B, Sietsma MS. Percutaneous vertebroplasty as a treatment for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures : a systematic review. Eur Spine J. 2006; 15:1749–1758. PMID: 16823557.
Article17. Shen Y, Ren H, Zhang Y, Zhi X, Ding W, Xu J, et al. [Correlative factor analysis of complications resulting from cement leakage after percutaneous kyphoplasty in treatment of osteoporotic vertebral body compression]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2010; 24:27–31. PMID: 20135966.18. Stoll TM, Dubois G, Schwarzenbach O. The dynamic neutralization system for the spine : a multi-center study of a novel non-fusion system. Eur Spine J. 2002; 11(Suppl 2):S170–S178. PMID: 12384741.19. Sugimoto Y, Tanaka M, Konishi H, Takigawa T, Nakanishi K, Misawa H, et al. Posterior spinal fusion using a pedicle nail system with polymethylmethacrylate in a paraplegic patient after vertebral collapse caused by osteoporosis. Spine J. 2009; 9:e5–e8. PMID: 18082464.
Article20. Sun E, Alkalay R, Vader D, Snyder BD. Preventing distal pullout of posterior spine instrumentation in thoracic hyperkyphosis : a biomechanical analysis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2009; 22:270–277. PMID: 19494747.
Article21. Wan S, Lei W, Wu Z, Liu D, Gao M, Fu S. Biomechanical and histological evaluation of an expandable pedicle screw in osteoporotic spine in sheep. Eur Spine J. 2010; 19:2122–2129. PMID: 20577766.
Article22. Wetzel FT, Brustein M, Phillips FM, Trott S. Hardware failure in an unconstrained lumbar pedicle screw system. A 2-year follow-up study. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 1999; 24:1138–1143. PMID: 10361664.23. Wu ZX, Gao MX, Sang HX, Ma ZS, Cui G, Zhang Y, et al. Surgical treatment of osteoporotic thoracolumbar compressive fractures with open vertebral cement augmentation of expandable pedicle screw fixation : a biomechanical study and a 2-year follow-up of 20 patients. J Surg Res. 2012; 173:91–98. PMID: 21067776.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Pedicle Screw Loosening Treated by Modified Transpedicular Screw Augmentation with Polymethylmethacrylate
- Comparison of the Pullout Strength of Different Pedicle Screw Designs and Augmentation Techniques in an Osteoporotic Bone Model
- A Biomechanical Study on the Pull-Out Strength of Pedicle Screw Augmented with Polymethylmethacrylate(PMMA)- Cadaveric Study -
- Clinical Effects and Complications of Pedicle Screw Augmentation with Bone Cement: Comparison of Fenestrated Screw Augmentation and Vertebroplasty Augmentation
- A Biomechanical Study of Two Kinds of Tapered Pedicle Screws in Osteoporotic Lumber Spine