Prog Med Phys.
2014 Mar;25(1):53-63. 10.14316/pmp.2014.25.1.53.
Study of Variation of Internal Taget Volume between 4DCT and Slow-CT in Respiratory Patterns Using Respiratory Motion Phantom
- Affiliations
-
- 1Radiological Cancer Medicine, University of Science and Technology, Daejeon, Korea. kbkim@kirams.re.kr
- 2Research Center for Radiotherapy, Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiation Oncology, Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Departement of Nuclear Engineering, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Radiation Oncology, SoonChunHyang University Cheonan Hospital, Cheonan, Korea.
- KMID: 1910559
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2014.25.1.53
Abstract
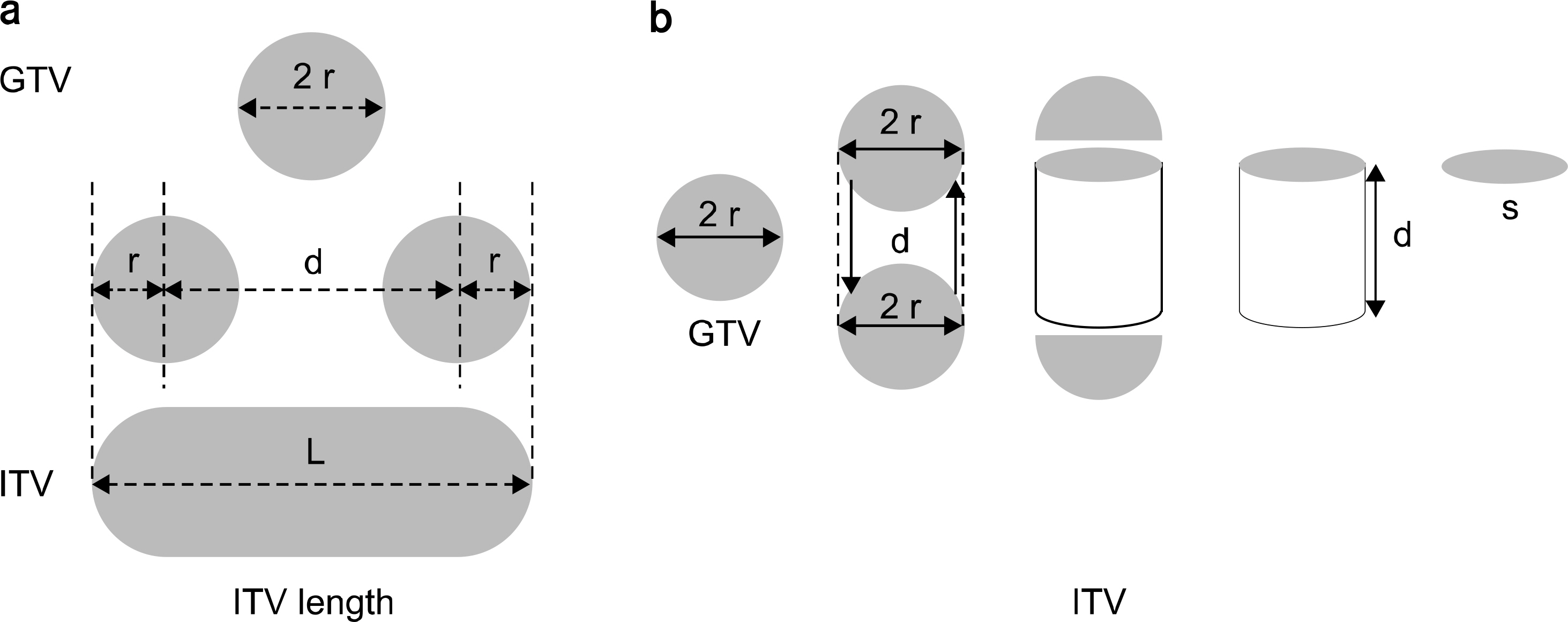
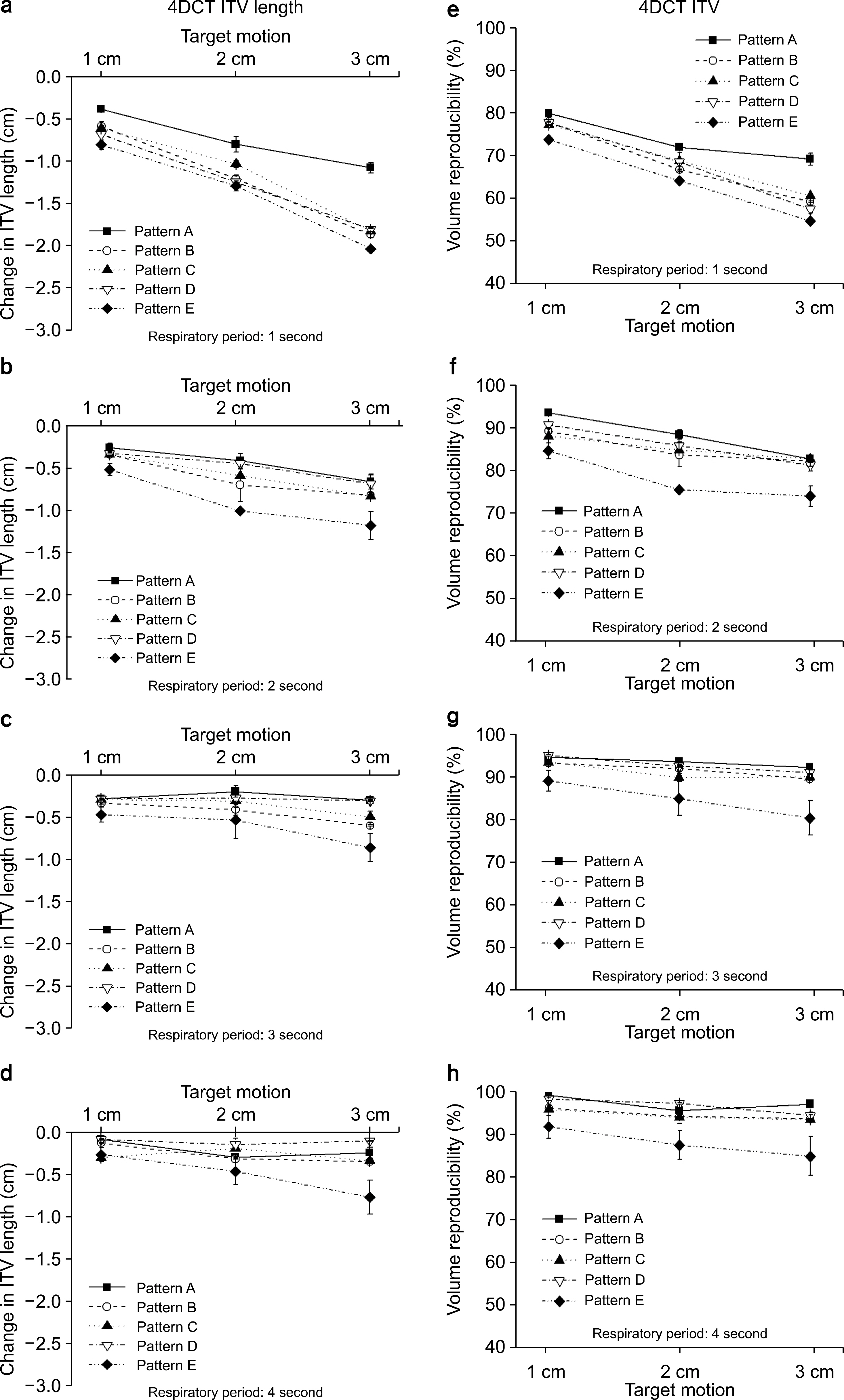
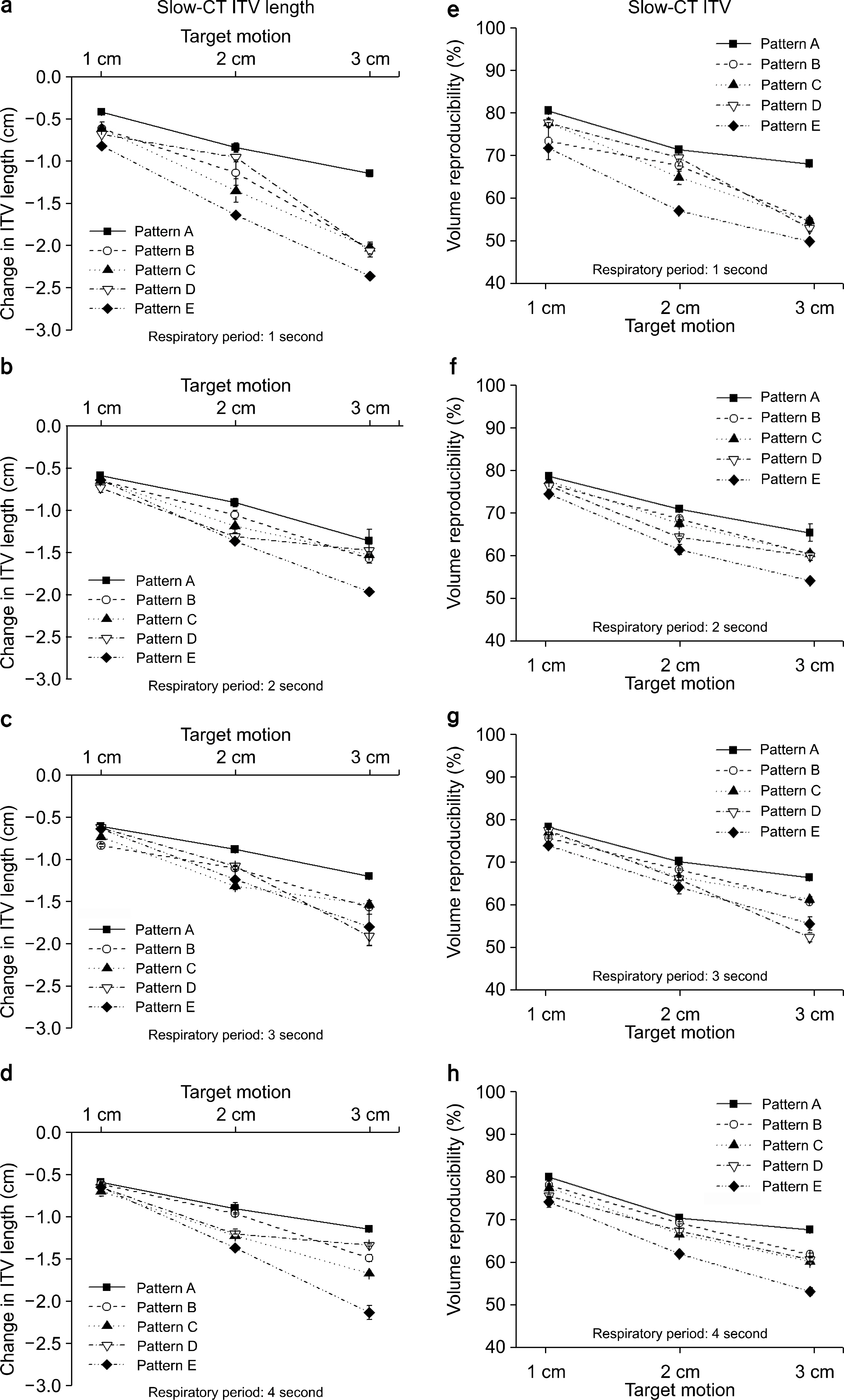
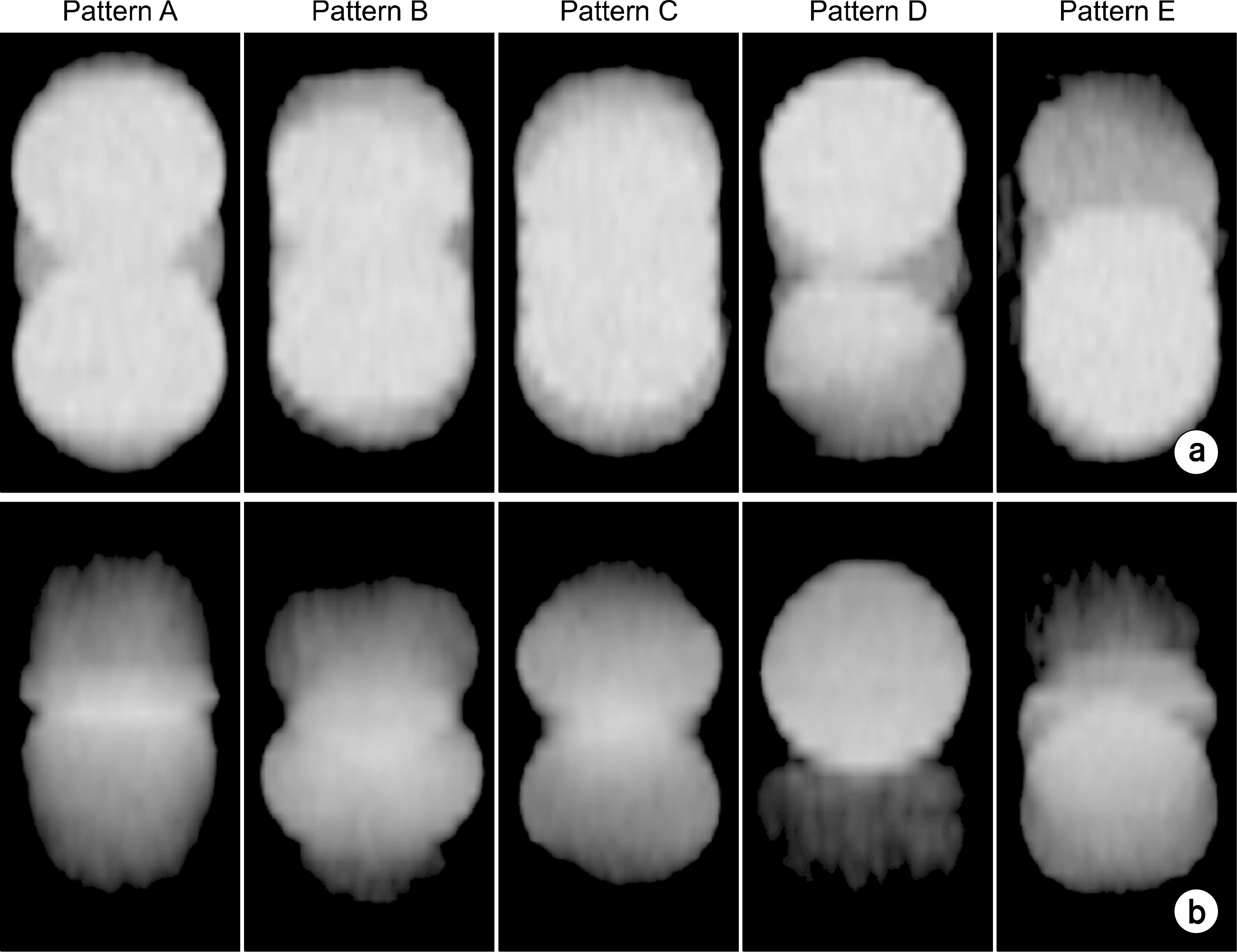
- The objective of this study is to investigate the difference of ITV lengths and ITVs between 4DCT and Slow-CT images according to respiratory patterns using a respiratory motion phantom. The respiratory periods 1~4 s and target motion 1~3 cm were applied on each respiratory pattern. 4DCT and Slow-CT images were acquired for 3 times. 4DCT and Slow-CT ITVs were measured with contouring the target in the Eclipse RTP system. The measured ITV lenghts and ITVs in 4DCT and Slow-CT images were compared to the known values. For the ITV lengths and ITVs in the 4DCT, the difference of them were reduced as the respiratory period is longer and target motion is shorter. For the Slow-CT, there was same tendency with change in 4DCT ITV lengths and ITVs about target motion. However, the difference of ITV lengths and ITVs for the respiratory periods were the lowest in respiratory period 1 second and different slightly within respiratory period 2-4 seconds. According to the respiratory patterns, pattern A had the highest reproducibility. Pattern B, C and D were showed the difference similar to each other. However, for pattern E, the reproducibility was the lowest compared with other four patterns. The difference of ITV lengths and ITVs between Slow-CT and 4DCT was increased by increasing the respiratory periods and target motion for all respiratory patterns. When the difference of Slow-CT ITV lengths and ITVs were compared with that of 4DCT ITV lengths and ITVs, Slow-CT ITV lengths and ITVs were approximately 22 % smaller than 4DCT, and the representations of target were different in each pattern. In case of pattern A, B and C, length difference was 3 mm at S (superior) and I (inferior) direction, and the length difference of pattern D was 1.45 cm at only "I" direction whereas the length difference of pattern E was 5 mm longer in "S" direction than "I" direction. Therefore, the margin in SI directions should be determined by considering the respiratory patterns when the margin of Slow-CT is compensated for 4DCT ITV lengths. Afterward, we think that the result of this study will be useful to analyze the ITV lengths and ITVs from the CT images on the basis of the patient respiratory signals.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Heck B, Jess-Hempen A, Kreiner HJ, Schopgens H, Mack A. Accuracy and stability of positioning in radiosurgery: Long term results of the Gamma Knife system. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 34:1487–1495. 2007.
Article2. Ryu SI, Chang SD, Kim DH, Murphy MJ, Le QT, Martin DP, et al. Image-guided hypo-fractionated stereotactic radiosurgery to spinal lesions. Neurosurgery. 49(4):838–846. 2001.
Article3. Teh BS, Paulino AC, Lu HH, et al. Versatility of the Novalis System to deliver Image-Guided Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy(SBRT) for Various Anatomical Sites. Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment. 6(4):347–354. 2007.4. Keall PJ, Mageras GS, Balter JM, et al. The management of respiratory motion in radiation oncology: report of AAPM Task Group 76. 2006.5. Keall PJ, Starkschall G, Shukla H, et al. Acquiring 4D thoracic CT scans using a multislice helical method. Phys Med Biol. 49(10):2053–2067. 2004.
Article6. Lagerwaard F, John R, Koste Van Sornsen De, et al. Multiple “Slow” CT Scans for Incorporating Lung Tumor Mobility in Radiotherapy Planning. Int J Radiation Oncology Biol Phys. 51(4):932–937. 2001.7. 김수산, 하성환, 최은경, 이병용. 전산화단층촬영 주사시간 (Scan Time)이 폐종양운동의 재현성에 미치는 영향 분석. 대한 방사선종양학회지. 22(1):55–63. 2004.8. Nakamura M, Narita Y, Matsuo Y, et al. Geometrical differences in target volumes between Slow-CT and 4D CT imaging in stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung tumors in the upper and middle lobe. Med Phys. 35(9):4142–4128. 2008.9. Clements N, Kron T, Franich R, et al. The effect of irregular breathing patterns on internal target volumes in four-dimensional CT and cone-beam CT images in the context of stereotactic lung radiotherapy. Med Phys. 40(2):): 021904;. 1–10. 2013.
Article10. Benedict SH, Yenice KM, Followill D, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy: The report of AAPM Task Group 101. Med Phys. 37(8):4078–4101. 2010.
Article11. Dalah EZ, Nisbet A, Bradley D. Effect of window level on target volume delineation in treatment planning. Appl Radiat Isotopes p1-3. 2009.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Theoretical Model for the Analysis of Residual Motion Artifacts in 4D CT Scans
- Analysis of Respiratory Motional Effect on the Cone-beam CT Image
- Analysis of Respiratory Motion Artifacts in PET Imaging Using Respiratory Gated PET Combined with 4D-CT
- Impact of the Respiratory Motion and Longitudinal Profile on Helical Tomotherapy
- Development of New 4D Phantom Model in Respiratory Gated Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy for Lung SBRT