Anat Cell Biol.
2014 Dec;47(4):271-273. 10.5115/acb.2014.47.4.271.
Unusual morphology of the superior belly of omohyoid muscle
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, Melaka Manipal Medical College (Manipal Campus), Manipal University, Manipal, Karnataka, India. seenaih.anat@gmail.com
- KMID: 1882607
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2014.47.4.271
Abstract
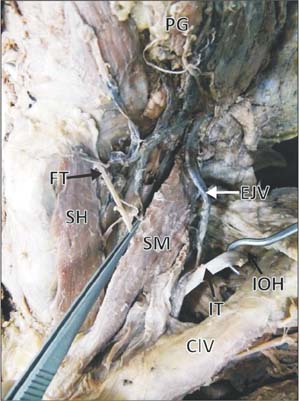
- Though anomalies of the superior belly of the omohyoid have been described in medical literature, absence of superior belly of omohyoid is rarely reported. Herein, we report a rare case of unilateral absence of muscular part of superior belly of omohyoid. During laboratory dissections for medical undergraduate students, unusual morphology of the superior belly of the omohyoid muscle has been observed in formalin embalmed male cadaver of South Indian origin. The muscular part of the superior belly of the omohyoid was completely absent. The inferior belly originated normally from the upper border of scapula, and continued with a fibrous tendon which ran vertically lateral to sternohyoid muscle and finally attached to the lower border of the body of hyoid bone. The fibrous tendon was about 1 mm thick and received a nerve supply form the superior root of the ansa cervicalis. As omohyoid mucle is used to achieve the reconstruction of the laryngeal muscles and bowed vocal folds, the knowledge of the possible anomalies of the omohyoid muscle is important during neck surgeries.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Standring S. Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. 39th ed. Edinburgh: Churchill and Livingstone;2005. p. 538–539.2. Sukekawa R, Itoh I. Anatomical study of the human omohyoid muscle: regarding intermediate morphologies between normal and anomalous morphologies of the superior belly. Anat Sci Int. 2006; 81:107–114.3. Tubbs RS, Salter EG, Oakes WJ. Unusual origin of the omohyoid muscle. Clin Anat. 2004; 17:578–582.4. Bolla SR, Nayak S, Vollala VR, Rao M, Rodrigues V. Cleidohyoideus: a case report. Indian J Pract Dr. 2007; 3:1–2.5. Miura M, Kato S, Itonaga I, Usui T. The double omohyoid muscle in humans: report of one case and review of the literature. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn. 1995; 72:81–97.6. Anderson RJ. The morphology of the omohyoid muscle. J Med Sci. 1881; 10:1–17.7. Wood J. Additional varieties in human myology. Proc R Soc Lond. 1865; 14:379–392.8. Tamega OJ, Garcia PJ, Soares JC, Zorzetto NL. About a case of absence of the superior belly of the omohyoid muscle. Anat Anz. 1983; 154:39–42.9. Lewis WH. The development of the muscular system. In : Keibel F, Mall FP, editors. Manual of Human Embryology. Philadelphia: Lippincott;1910. p. 454–522.10. Song J, Wang Q, Wang X, Qu Y, Qin Z, Li J, Wang P, Zhang J. Study on post-laryngectomy partial laryngeal defect repaired with omohyoid myofascial flap. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Ke Za Zhi. 2003; 17:519–521.11. Kojima H, Hirano S, Shoji K, Omori K, Honjo I. Omohyoid muscle transposition for the treatment of bowed vocal fold. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1996; 105:536–540.12. Crumley RL. Muscle transfer for laryngeal paralysis: restoration of inspiratory vocal cord abduction by phrenic-omohyoid transfer. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1991; 117:1113–1117.13. Krishnan KG, Pinzer T, Reber F, Schackert G. Endoscopic exploration of the brachial plexus: technique and topographic anatomy: a study in fresh human cadavers. Neurosurgery. 2004; 54:401–408.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Variation of the Infrahyoid Muscle: Duplicated Omohyoid and Appearance of the Levator Glandulae Thyroideae Muscles
- Unilateral Accessory Cleidohyoid Muscle: A Case Report
- Unusual muscle of the anterior neck: cadaveric findings with surgical applications
- Omohyoid Muscle Syndrome
- Anatomic Variation of the Anterior Belly of Digastric Muscle and Positional Relationship between the Posterior Belly of Digastric and Stylohyoid Muscle