Kosin Med J.
2014 Jun;29(1):47-52. 10.7180/kmj.2014.29.1.47.
Characteristics of Peripheral versus Central Lung Cancer Since 2000
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Kosin University, Busan, Korea. oaksoyoung@naver.com
- KMID: 1882438
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2014.29.1.47
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The aim of this study was to explore the changes of bronchoscopic features according to epidemiologic change of lung cancer.
METHODS
We performed a retrospective review of the clinical characteristics of 1,139 lung cancer patient who underwent bronchoscopy at Kosin University Hospital from January 2000 to December 2010.
RESULTS
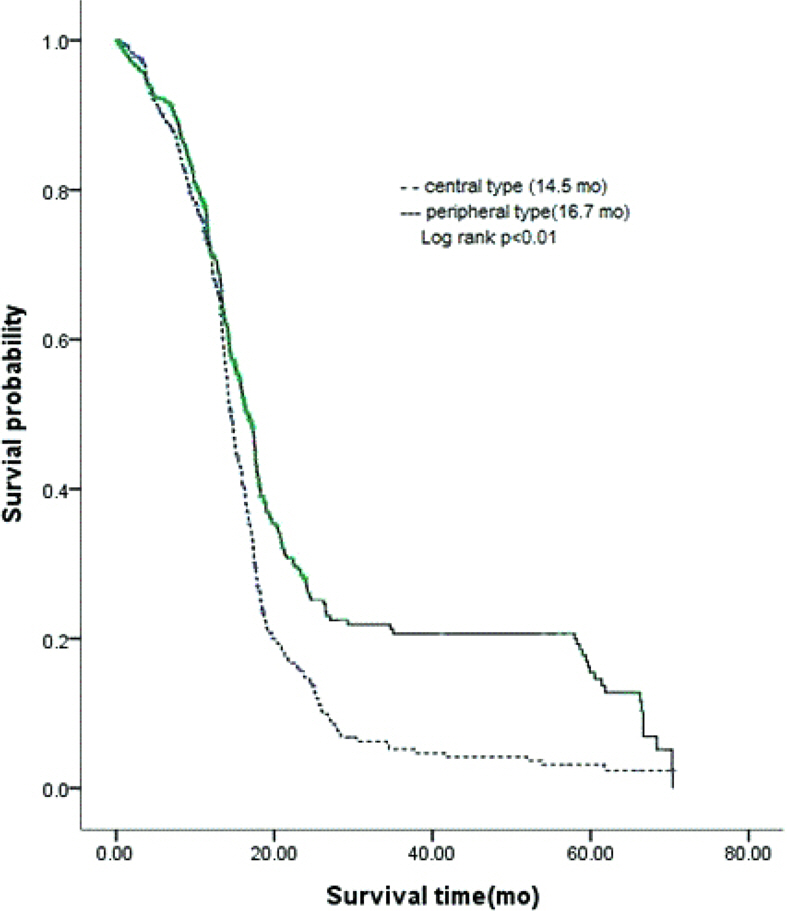
The age of patients increased significantly during the last decade (P < 0.001). The most common histological type was adenocarcinoma (38.1%), followed by squamous carcinoma (35.7%) and small cell carcinoma (15.3%). There was an increasing incidence of adenocarcinoma over the time (P < 0.001). Bronchoscopic feature were divided into two classes; central type, peripheral type. The peripheral type was predominant (62.3%). The proportion of peripheral type has been increased in process of time (49.7% vs. 63.7% vs. 73.7%; P < 0.01). Among the major histopathologic type of lung cancer, adenocarcinoma (81.3%) and unclassifiable non-small-cell lung cancer (73.4%), small cell carcinoma (56.9%) were associated with preferential occurrence of peripheral type. Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung more often arised in central type (59%). However, the proportion of peripheral squamous cell carcinoma has been increased. On the subgroup analysis, the median survival time of peripheral type with adenocarcinoma and small cell carcinoma were longer than central type (P < 0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
The age of the lung cancer patients at diagnosis was getting older. The most frequent histopathologic type was adenocarcinoma. The proportion of peripheral type lung cancer gradually increased over the time. The survival time of peripheral type lung cancer was longer than central type.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Korean National Statistical Office, Annual Report on the Cause of Death Statistics. Korea National Statistical Office. 2006.2. Travis WD, Travis LB, Devesa SS. Lung cancer. Cancer. 1995; 75:191–202.
Article3. Kim YC, Kwon YS, Oh IJ, Kim KS, Kim SY, Ryu JS, et al. National survey of lung cancer in Korea, 2005. J Lung Cancer. 2007; 6:67–73.
Article4. Lim JH, Ban HJ, Oh IJ, Kim SO, Son JG, Jeong JP, et al. Clinical characteristics of lung cancer diagnosed in Chonnam National University Hospital (CNUH) since 2000. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2006; 61:427–32.5. Brooks DR, Austin JH, Heelan RT, Ginsberg MS, Shin V, Olson SH, et al. Influence of Type of Cigarette on Peripheral versus Central Lung Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2005; 14:576–81.
Article6. Ugur G, Ibrahim A, Tanseli E. Classification of fibreoptic bronchoscopic findings: analysis of 2,698 cases. Comp Clin Path. 2004; 13:1–3.
Article7. Mountain CF. Revisions in the International System for Staging Lung Cancer. Chest. 1997; 111:1710–7.
Article8. Jackman DM, Johnson BE. Small-cell lung cancer. Lancet. 2005; 366:1385–96.
Article9. Thun MJ, Lally CA, Flannery JT, Calle EE, Flanders WD, Heath CW Jr. Cigarette smoking and changes in the histopathology of lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1997; 89:1580–6.
Article10. Strauss GM, Jemal A, McKenna MB, Strauss JA, Cummings KM. The epidemic of smoking-related adenocarcinoma of the lung: The role of the tobacco industry and filtered and low-tar cigarettes: PRS-01. J Thorac Oncol. 2007; 2:S305.11. Yu IT, Chiu YL, Au JS, Wong TW, Tang JL. Dose-response relationship between cooking fumes exposures and lung cancer among Chinese nonsmoking women. Cancer Res. 2006; 66:4961–7.
Article12. Bryd RB, Carr DT, Miller WE, Payne WS, Woolner LB. Radiographic abnormlities in carcinoma of the lung as related to histological cell type. Thorax. 1969; 24:573–5.13. Lubin JH, Blot WJ, Berrino F, Flamant K, Gillis CR, Kunze M, et al. Patterns of lung cancer risk according to type of cigarette smoked. Int J Cancer. 1984; 33:569–76.
Article14. Yang CP, Gallagher RP, Weiss NS, Band PR, Thomas DB, Russell DA. Differences in incidence rates of cancers of the respiratory tract by anatomic subsite and histologic type: an etiologic implication. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1989; 81:1828–31.
Article15. Wynder EL, Muscat JE. The changing epidemiology of smoking and lung cancer histology. Environ Health Perspect. 1995; 103:143–8.
Article16. Huhti E, Saloheimo M, Sutinen S, Reinilä A. Does the location of lung cancer affect its prognosis? Eur J Respir Dis. 1983; 64:460–5.17. Jang TW, Kim YC, Kwon YS, Oh IJ, Kim KS, Kim SY, et al. Female lung cancer: Re-analysis of national survey of lung cancer in Korea, 2005. J lung cancer. 2010; 9:57–63.
Article18. Tomashefski JF Jr, Connors AF Jr, Rosenthal ES, Hsiue IL. Peripheral vs central squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. A comparison of clinical features, histopathology, and survival. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1990; 114:468–74.19. Ketchedjian A1. Daly BD, Fernando HC, Florin L, Hunter CJ, Morelli DM, et al. Location as an important predictor of lymph node involvement for pulmonary adenocarcinoma. J Thoracic Cardiovasc Surg. 2006; 132:544–8.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Role of CT in the Diagnosis of Bronchogenic Carcinoma not Detected by Plain Radiograph
- Peripheral type squamous cell carcinoma of the lung: clinicopathologic characteristics in comparison to the central type
- Immunohistochemical Assessment of Peripheral Squamous Lung Cancer: Comparison to Central Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Peripheral Adenocarcinoma
- A Study of SCC Antigen and EGFr in Tissues of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Lung
- Recent advances in diagnostic technologies in lung cancer