Korean J Leg Med.
2014 May;38(2):48-58. 10.7580/kjlm.2014.38.2.48.
Sequence Generation and Genotyping of 15 Autosomal STR Markers Using Next Generation Sequencing
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Forensic Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. graduate@nate.com
- 2Brain Korea 21 PLUS Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1849353
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7580/kjlm.2014.38.2.48
Abstract
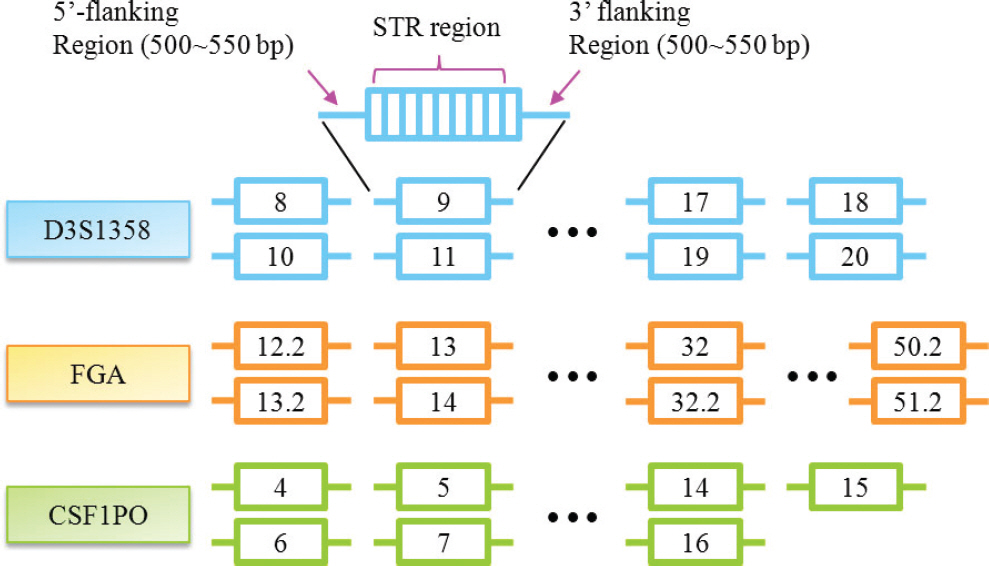
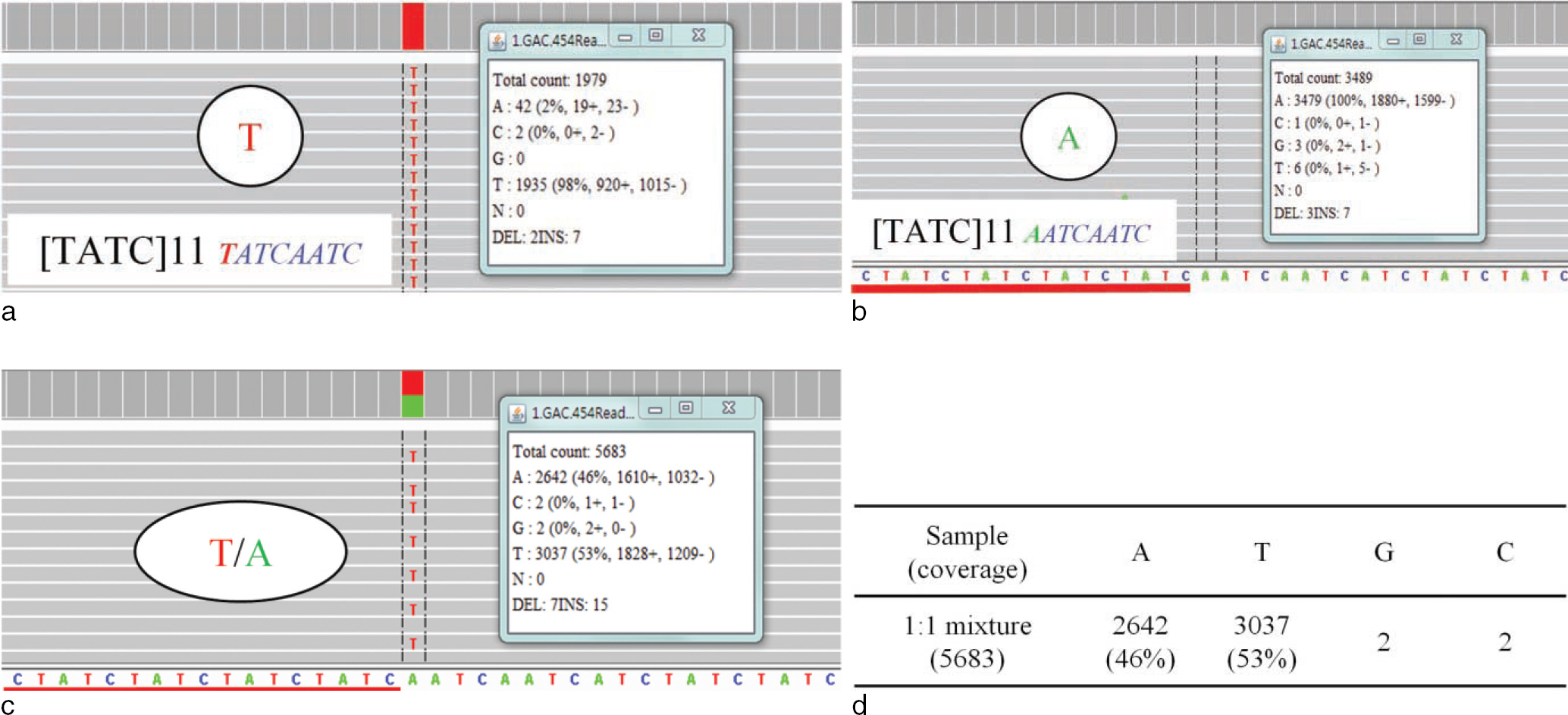
- Recently, next generation sequencing (NGS) has received attention as the ultimate genotyping method to overcome the limitations of capillary electrophoresis (CE)-based short tandem repeat (STR) analysis, such as the limited number of STR loci that can be measured simultaneously using fluorescent-labeled primers and the maximum size of STR amplicons. In this study, we analyzed 15 autosomal STR markers via the NGS method and evaluated their effectiveness in STR analysis. Using male and female standard DNA as single-sources and their 1:1 mixture, we sequentially generated sample amplicons by the multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method, constructed DNA libraries by ligation of adapters with a multiplex identifier (MID), and sequenced DNA using the Roche GS Junior Platform. Sequencing data for each sample were analyzed via alignment with pre-built reference sequences. Most STR alleles could be determined by applying a coverage threshold of 20% for the two single-sources and 10% for the 1:1 mixture. The structure of the STR in each allele was accurately determined by examining the sequences of the target STR region. The mixture ratio of the mixed sample was estimated by analyzing the coverage ratios between assigned alleles at each locus and the reference/variant ratios from the observed sequence variations. In conclusion, the experimental method used in this study allowed the successful generation of NGS data. In addition, the NGS data analysis protocol enables accurate STR allele call and repeat structure determination at each locus. Therefore, this approach using the NGS system will be helpful to interpret and analysis the STR profiles from singe-source and even mixed samples in forensic investigation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Thompson R, Zoppis S, McCord B. An overview of DNA typing methods for human identification: past, present, and future. Methods Mol Biol. 2012; 830:3–16.
Article2. Kayser M, de Knijff P. Improving human forensics through advances in genetics, genomics and molecular biology. Nat Rev Genet. 2011; 12:179–92.
Article3. Berglund EC, Kiialainen A, Syva ¨nen AC. Next-generation sequencing technologies and applications for human genetic history and forensics. Investig Genet. 2011; 2:23.
Article4. Metzker ML. Sequencing technologies - the next generation. Nat Rev Genet. 2010; 11:31–46.
Article5. Cho IS, Blaser MJ. The human microbiome: at the interface of health and disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2012; 13:260–70.
Article6. Bamshad MJ, Ng SB, Bigham AW, et al. Exome sequencing as a tool for Mendelian disease gene discovery. Nat Rev Genet. 2012; 12:745–55.
Article7. Ozsolak F, Milos PM. RNA sequencing: advances, challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Genet. 2011; 12:87–98.
Article8. Meyerson M, Gabriel S, Getz G. Advances in understanding cancer genomes through second-generation sequencing. Nat Rev Genet. 2010; 11:685–96.
Article9. Laird PW. Principles and challenges of genomewide DNA methylation analysis. Nat Rev Genet. 2010; 11:191–203.
Article10. Van Neste C, Van Nieuwerburgh F, Van Hoofstat D, et al. Forensic STR analysis using massive parallel sequencing. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2012; 6:810–8.
Article11. Rockenbauer E, Hansen S, Mikkelsen M, et al. Characterization of mutations and sequence variants in the D21S11 locus by next generation sequencing. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2014; 8:68–72.
Article12. Fordyce SL, A′vila-Arcos MC, Rockenbauer E, et al. High-throughput sequencing of core STR loci for forensic genetic investigations using the Roche Genome Sequencer FLX platform. Biotechniques. 2011; 51:127–33.
Article13. Dalsgaard S, Rockenbauer E, Buchard A, et al. Non-uniform phenotyping of D12S391 resolved by second generation sequencing. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2014; 8:195–9.
Article14. Scheible M, Loreille O, Just R, et al. Short tandem repeat sequencing on the 454 platforms. Forensic Sci Int Genet Suppl Ser. 2011; 3:357–8.15. Bornman DM, Hester ME, Schuetter JM, et al. Short-read, high-throughput sequencing technology for STR genotyping. Biotechniques. 2012; 0:1–6.
Article16. Langmead B, Salzberg SL. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods. 2012; 9:357–9.
Article17. Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, et al. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics. 2009; 25:2078–9.
Article18. Quinlan AR, Hall IM. BEDTools: a flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics. 2010; 26:841–2.
Article19. Robinson JT, Thorvaldsdo ′ttir H, Winckler W, et al. Integrative genomics viewer. Nat Biotechnol. 2011; 29:24–6.
Article20. Van Neste C, Vandewoestyne M, Van Criekinge W, et al. My-Forensic-Loci-queries (MyFLq) framework for analysis of forensic STR data generated by massive parallel sequencing. Forensic Sci Int Genet. 2014; 9:1–8.
Article21. Gymrek M, Golan D, Rosset S, et al. lobSTR: a short tandem repeat profiler for personal genomes. Genome Res. 2012; 22:1154–62.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- misMM: An Integrated Pipeline for Misassembly Detection Using Genotyping-by-Sequencing and Its Validation with BAC End Library Sequences and Gene Synteny
- Comparison of Four Human Papillomavirus Genotyping Methods: Next-generation Sequencing, INNO-LiPA, Electrochemical DNA Chip, and Nested-PCR
- A Simple GUI-based Sequencing Format Conversion Tool for the Three NGS Platforms
- Choosing Optimal STR Markers for Quality Assurance of Distributed Biomaterials in Biobanking
- A Primer for Disease Gene Prioritization Using Next-Generation Sequencing Data