Tuberc Respir Dis.
2011 Aug;71(2):106-113. 10.4046/trd.2011.71.2.106.
Relationship between Exhaled Nitric Oxide and Levels of Asthma Control in Asthma Patients Treated with Inhaled Corticosteroid
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Family Medicine, Sahmyook Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sangheonkim@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 1846417
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2011.71.2.106
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
While asthma control is defined as the extent to which the various manifestations of asthma are reduced by treatment, current guidelines of asthma recommend assessment of asthma control without consideration of airway inflammation. Our aim was to investigate the relationships between fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO), a reliable marker of airway inflammation, and levels of asthma control in patients treated with inhaled corticosteroids (ICS).
METHODS
We enrolled 71 adult patients with asthma who had been treated with ICS for more than four months. FeNO was measured and spirometry was performed at the time of enrollment. Asthma control was assessed (a) by the physician based on the Global Initiative for Asthma guidelines, (b) by the patients, and (c) by using the Asthma Control Test (ACT). Statistical analyses were done to analyze the relationships between (i) FeNO and (ii) measures of asthma control and clinical indices for asthma manifestations.
RESULTS
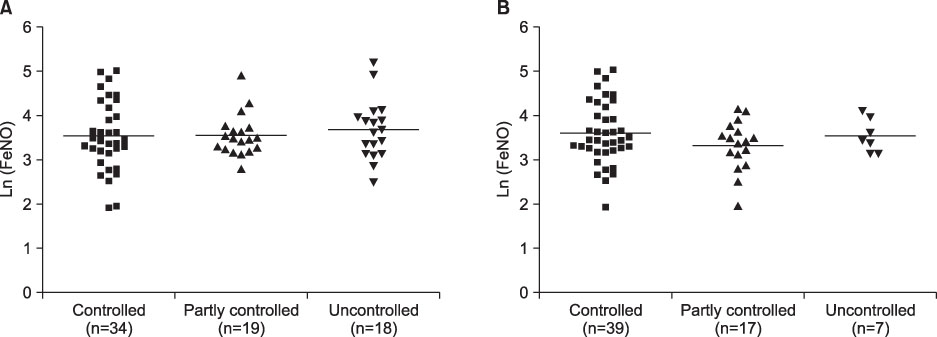
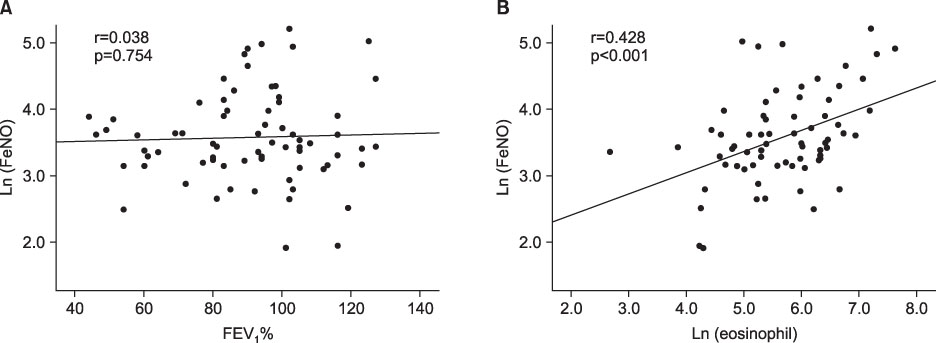
There was no significant difference in FeNO levels between the three groups according to levels of asthma control (controlled, partly controlled and uncontrolled) as determined by the physician (p=0.81), or by the patients (p=0.81). In addition, FeNO values were not significantly correlated with the ACT scores (r=0.031, p=0.807), while FeNO showed a correlation with peripheral blood eosinophil counts (p<0.001).
CONCLUSION
These findings demonstrate that FeNO levels are not associated with measures of asthma control in patients treated with ICS. Information on airway inflammation from FeNO concentrations seems to be unrelated to levels of asthma control.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. National Asthma Education and Prevention Program. Expert panel report 3 (EPR-3): guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma-summary report 2007. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007. 120:5 Suppl. S94–S138.2. Bateman ED, Hurd SS, Barnes PJ, Bousquet J, Drazen JM, FitzGerald M, et al. Global strategy for asthma management and prevention: GINA executive summary. Eur Respir J. 2008. 31:143–178.3. Bateman ED, Boushey HA, Bousquet J, Busse WW, Clark TJ, Pauwels RA, et al. Can guideline-defined asthma control be achieved? The gaining optimal asthma control study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004. 170:836–844.4. Nathan RA, Sorkness CA, Kosinski M, Schatz M, Li JT, Marcus P, et al. Development of the asthma control test: a survey for assessing asthma control. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004. 113:59–65.5. Juniper EF, Bousquet J, Abetz L, Bateman ED. GOAL Committee. Identifying 'well-controlled' and 'not well-controlled' asthma using the Asthma Control Questionnaire. Respir Med. 2006. 100:616–621.6. Kim SH, Yoon HJ. Use of the exhaled nitric oxide for management of asthma and respiratory diseases. Korean J Med. 2008. 74:579–586.7. Smith AD, Cowan JO, Filsell S, McLachlan C, Monti-Sheehan G, Jackson P, et al. Diagnosing asthma: comparisons between exhaled nitric oxide measurements and conventional tests. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004. 169:473–478.8. Petsky HL, Cates CJ, Li A, Kynaston JA, Turner C, Chang AB. Tailored interventions based on exhaled nitric oxide versus clinical symptoms for asthma in children and adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009. (4):CD006340.9. Sippel JM, Holden WE, Tilles SA, O'Hollaren M, Cook J, Thukkani N, et al. Exhaled nitric oxide levels correlate with measures of disease control in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000. 106:645–650.10. Senna G, Passalacqua G, Schiappoli M, Lombardi C, Wilcock L. Correlation among FEV, nitric oxide and asthma control test in newly diagnosed asthma. Allergy. 2007. 62:207–208.11. Shirai T, Furuhashi K, Suda T, Chida K. Relationship of the asthma control test with pulmonary function and exhaled nitric oxide. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008. 101:608–613.12. Khalili B, Boggs PB, Shi R, Bahna SL. Discrepancy between clinical asthma control assessment tools and fractional exhaled nitric oxide. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008. 101:124–129.13. Lopes C, Fonseca J, Delgado L, Moreira A, Barros R, Moreira P, et al. Assessing asthma control: questionnaires and exhaled nitric oxide provide complementary information. Eur Respir J. 2008. 32:1419–1420.14. Quaedvlieg V, Sele J, Henket M, Louis R. Association between asthma control and bronchial hyperresponsiveness and airways inflammation: a cross-sectional study in daily practice. Clin Exp Allergy. 2009. 39:1822–1829.15. Bernstein JA, Davis B, Alvarez-Puebla MJ, Nguyen D, Levin L, Olaguibel JM. Is exhaled nitric oxide a useful adjunctive test for assessing asthma? J Asthma. 2009. 46:955–960.16. American Thoracic Society. European Respiratory Society. ATS/ERS recommendations for standardized procedures for the online and offline measurement of exhaled lower respiratory nitric oxide and nasal nitric oxide, 2005. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005. 171:912–930.17. Kim SH, Kim TH, Sohn JW, Yoon HJ, Shin DH, Park SS. Reference values and determinants of exhaled nitric oxide in healthy Korean adults. J Asthma. 2010. 47:563–567.18. Kwon HS, Lee SH, Yang MS, Lee SM, Kim SH, Kim DI, et al. Correlation between the Korean version of asthma control test and health-related quality of life in adult asthmatics. J Korean Med Sci. 2008. 23:621–627.19. Fanta CH. Asthma. N Engl J Med. 2009. 360:1002–1014.20. Reddel HK, Taylor DR, Bateman ED, Boulet LP, Boushey HA, Busse WW, et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: asthma control and exacerbations: standardizing endpoints for clinical asthma trials and clinical practice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009. 180:59–99.21. Taylor DR, Bateman ED, Boulet LP, Boushey HA, Busse WW, Casale TB, et al. A new perspective on concepts of asthma severity and control. Eur Respir J. 2008. 32:545–554.22. Wenzel SE. Asthma: defining of the persistent adult phenotypes. Lancet. 2006. 368:804–813.23. Haldar P, Pavord ID, Shaw DE, Berry MA, Thomas M, Brightling CE, et al. Cluster analysis and clinical asthma phenotypes. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008. 178:218–224.24. Moore WC, Meyers DA, Wenzel SE, Teague WG, Li H, Li X, et al. Identification of asthma phenotypes using cluster analysis in the Severe Asthma Research Program. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010. 181:315–323.25. Smith AD, Cowan JO, Brassett KP, Herbison GP, Taylor DR. Use of exhaled nitric oxide measurements to guide treatment in chronic asthma. N Engl J Med. 2005. 352:2163–2173.26. Green RH, Brightling CE, McKenna S, Hargadon B, Parker D, Bradding P, et al. Asthma exacerbations and sputum eosinophil counts: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2002. 360:1715–1721.27. Jayaram L, Pizzichini MM, Cook RJ, Boulet LP, Lemière C, Pizzichini E, et al. Determining asthma treatment by monitoring sputum cell counts: effect on exacerbations. Eur Respir J. 2006. 27:483–494.28. Haldar P, Brightling CE, Hargadon B, Gupta S, Monteiro W, Sousa A, et al. Mepolizumab and exacerbations of refractory eosinophilic asthma. N Engl J Med. 2009. 360:973–984.29. Nair P, Pizzichini MM, Kjarsgaard M, Inman MD, Efthimiadis A, Pizzichini E, et al. Mepolizumab for prednisone-dependent asthma with sputum eosinophilia. N Engl J Med. 2009. 360:985–993.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Utility of Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide in the Diagnosis of Asthma and the Assessment of Asthma Control
- Measurements of fractional exhaled nitric oxide in pediatric asthma
- Measurement and Interpretation of Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide
- Use of the exhaled nitric oxide for management of asthma and respiratory diseases
- Clinical Significance of Exhaled Nitric Oxide Concentration in Childhood Asthma