Lab Med Online.
2013 Jan;3(1):45-49. 10.3343/lmo.2013.3.1.45.
Neonatal Alloimmune Thrombocytopenia Caused by Anti-HLA-A2 Alloantibodies Determined by Luminex Single Antigen Bead Assay
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yonggoo@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pediatrics, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1845396
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/lmo.2013.3.1.45
Abstract
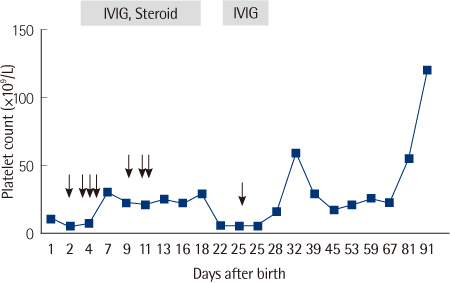
- Neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia (NAIT) occurs when maternal alloantibodies react to antigens expressed on fetal platelets, which is mainly platelet-specific alloantigen or HLA, resulting in their immune destruction. Here, we described a patient who suffered from NAIT caused by anti-HLA-A2 antibody. Sera from the mother and the newborn were screened for human platelet antigen-specific antibodies and HLA antibodies by ELISA, and HLA antibodies were detected in both of them. The antibody specificity was identified as anti-HLA-A2 by Luminex single antigen bead assay. HLA typing results showed that patient's father descended HLA-A2 antigen on the patient and the mother was HLA-A2 negative. It is most conceivable that anti-HLA-A2 alloantibody in the mother's sera crossed the placenta and subsequently caused NAIT in the case presented. The patient received platelet concentrates, oral steroid and intravenous globulin and platelet count increased to 120x10(9)/L on the 90th day of life. The Luminex single antigen bead assay used in this case is highly sensitive and specific assay to determine antibody specificity and it is faster and more convenient for routine use in clinical laboratory so that this assay could be useful to diagnose NAIT caused by HLA antibodies and treat such NAIT patients with HLA matched platelet transfusion.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Antibodies
Antibody Specificity
Blood Platelets
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Fathers
Histocompatibility Testing
HLA-A2 Antigen
Humans
Infant, Newborn
Isoantibodies
Isoantigens
Mothers
Placenta
Platelet Count
Platelet Transfusion
Thrombocytopenia, Neonatal Alloimmune
Antibodies
HLA-A2 Antigen
Isoantibodies
Isoantigens
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Case of Neonatal Alloimmune Thrombocytopenia Due to Anti-HLA A29 Antibody
Eunjin Choi, Jung Yoon, Chae Seung Lim, Young Sook Hong
Perinatology. 2017;28(2):74-78. doi: 10.14734/PN.2017.28.2.74.
Reference
-
1. Kaplan C. Foetal and neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2006. 1:39.2. Davoren A, Curtis BR, Aster RH, McFarland JG. Human platelet antigen-specific alloantibodies implicated in 1162 cases of neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia. Transfusion. 2004. 44:1220–1225.
Article3. Shibata Y, Matsuda I, Miyaji T, Ichikawa Y. Yuka, a new platelet antigen involved in two cases of neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia. Vox Sang. 1986. 50:177–180.
Article4. Kim SY, Kim ER, Kim YJ, Park MH, Song EY, Han KS. A case of neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia due to anti-HLA A2. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 2000. 43:861–865.5. Han KS, Park MH, Han BY, Choi JH, Choi JM, Chung HR, et al. A case of neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia due to anti-HLA B44. Korean J Blood Transfus. 1993. 4:239–245.6. Shin BM, Han KS, Um TH, Park MH, Park YW, Kim SW. A case of neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia due to anti-HLA-B7+B60+B61. Korean J Blood Transfus. 1994. 5:45–51.7. Han KS, Um TH, Park MH, LeShine BM, Park YW, Kim SW. A case of neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia related to HLA antibody. Korean J Blood Transfus. 1993. 4:247–251.8. Lee JS, Park BS, Park HJ, Sun YH, Song EY, Park MH, et al. A case of neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia due to anti-HLA-B62+B75. Korean J Blood Transfus. 2002. 13:173–179.9. Bussel J. Diagnosis and management of the fetus and neonate with alloimmune thrombocytopenia. J Thromb Haemost. 2009. 7:Suppl 1. S253–S257.
Article10. Mueller-Eckhardt C, Kiefel V, Grubert A, Kroll H, Weisheit M, Schmidt S, et al. 348 cases of suspected neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia. Lancet. 1989. 1:363–366.
Article11. Ghevaert C, Campbell K, Walton J, Smith GA, Allen D, Williamson LM, et al. Management and outcome of 200 cases of fetomaternal alloimmune thrombocytopenia. Transfusion. 2007. 47:901–910.
Article12. Han KS, Cho HI, Kim SI. Frequency of platelet-specific antigens among Koreans determined by a simplified immunofluorescence test. Transfusion. 1989. 29:708–710.
Article13. Santoso S, Santoso S, Kiefel V, Masri R, Mueller-Eckhardt C. Frequency of platelet-specific antigens among Indonesians. Transfusion. 1993. 33:739–741.
Article14. Tanaka S, Ohnoki S, Shibata H, Okubo Y, Yamaguchi H, Shibata Y. Gene frequencies of human platelet antigens on glycoprotein IIIa in Japanese. Transfusion. 1996. 36:813–817.
Article15. von dem Borne AE, van Leeuwen EF, von Riesz LE, van Boxtel CJ, Engelfriet CP. Neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia: detection and characterization of the responsible antibodies by the platelet immunofluorescence test. Blood. 1981. 57:649–656.
Article16. King KE, Kao KJ, Bray PF, Casella JF, Blakemore K, Callan NA, et al. The role of HLA antibodies in neonatal thrombocytopenia: a prospective study. Tissue Antigens. 1996. 47:206–211.
Article17. Taaning E. HLA antibodies and fetomaternal alloimmune thrombocytopenia: myth or meaningful. Transfus Med Rev. 2000. 14:275–280.
Article18. Han KS, Park MH, Kim HO. Comparison of platelet antibody detection methods-platelet suspension immunofluorescence test, mixed passive hemagglutination test, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Korean J Blood Transfus. 1991. 2:1–9.19. Um TH, Han KS, Kim DC, Hwang YS, Kim DS, Kim SI. Detection of platelet-specific antibodies employing modified antigen capture ELISA (MACE). Korean J Blood Transfus. 1995. 6:123–129.20. Jung S, Oh EJ, Yang CW, Ahn WS, Kim Y, Park YJ, et al. Comparative evaluation of ELISA and Luminex panel reactive antibody assays for HLA alloantibody screening. Korean J Lab Med. 2009. 29:473–480.
Article21. Ki CS, Yang YS, Kim DW. Comparison of complement-dependent cytotoxicity, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and flow cytometric assay for the detection of HLA class I alloantibodies. Korean J Clin Pathol. 1998. 18:624–629.22. Oh EJ, Lee J, Yang CW, Moon IS, Park YJ, Han K. Comparison of anti-HLA detecting methods; cytotoxicity, flow cytometric crossmatch, multiple antigen-ELISA, single antigen-ELISA. J Korean Soc Transplant. 2008. 22:85–91.23. Colombo MB, Haworth SE, Poli F, Nocco A, Puglisi G, Innocente A, et al. Luminex technology for anti-HLA antibody screening: evaluation of performance and of impact on laboratory routine. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2007. 72:465–471.
Article24. Joo DJ, Huh KH, Kim YS, Yoon SJ, Kim HJ, Sohn SS, et al. Predictive value of donor specific antibody measured by luminex single antigen assay for antibody mediated rejection after kidney transplantation. J Korean Soc Transplant. 2011. 25:169–175.
Article25. Hyun J, Lim YM, Park KD, Han BY, Kim YH, Han KS, et al. An evaluation of platelet transfusion response using HLA crossmatch-compatible donors in patients with platelet refractoriness. Korean J Lab Med. 2009. 29:481–489.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Neonatal Alloimmune Thrombocytopenia dut to Anti-HLA A2
- A Case of Neonatal Alloimmune Thrombodytopenia Due to Anti - HLA Antibody
- A Case of Saethre - Chotzen Syndrome
- A Case of Neonatal Alloimmune Thrombocytopenia Related to HLA Antibody
- A Case of Neonatal Alloimmune Thrombocytopenia Due to Anti-HLA A29 Antibody