Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2008 Aug;12(4):211-216. 10.4196/kjpp.2008.12.4.211.
The Inhibition of TREK2 Channel by an Oxidizing Agent, 5,5'-dithio- bis (2-nitrobenzoic acid), via Interaction with the C-terminus Distal to the 353rd Amino Acid
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Molecular and Life Sciences, Hanyang University, Ansan, Korea.
- 2Department of Physiology, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Biochemistry, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea.
- 4Department of Pharmacology, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea.
- 5Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea. yangmik@chungbuk.ac.kr
- KMID: 1838361
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2008.12.4.211
Abstract
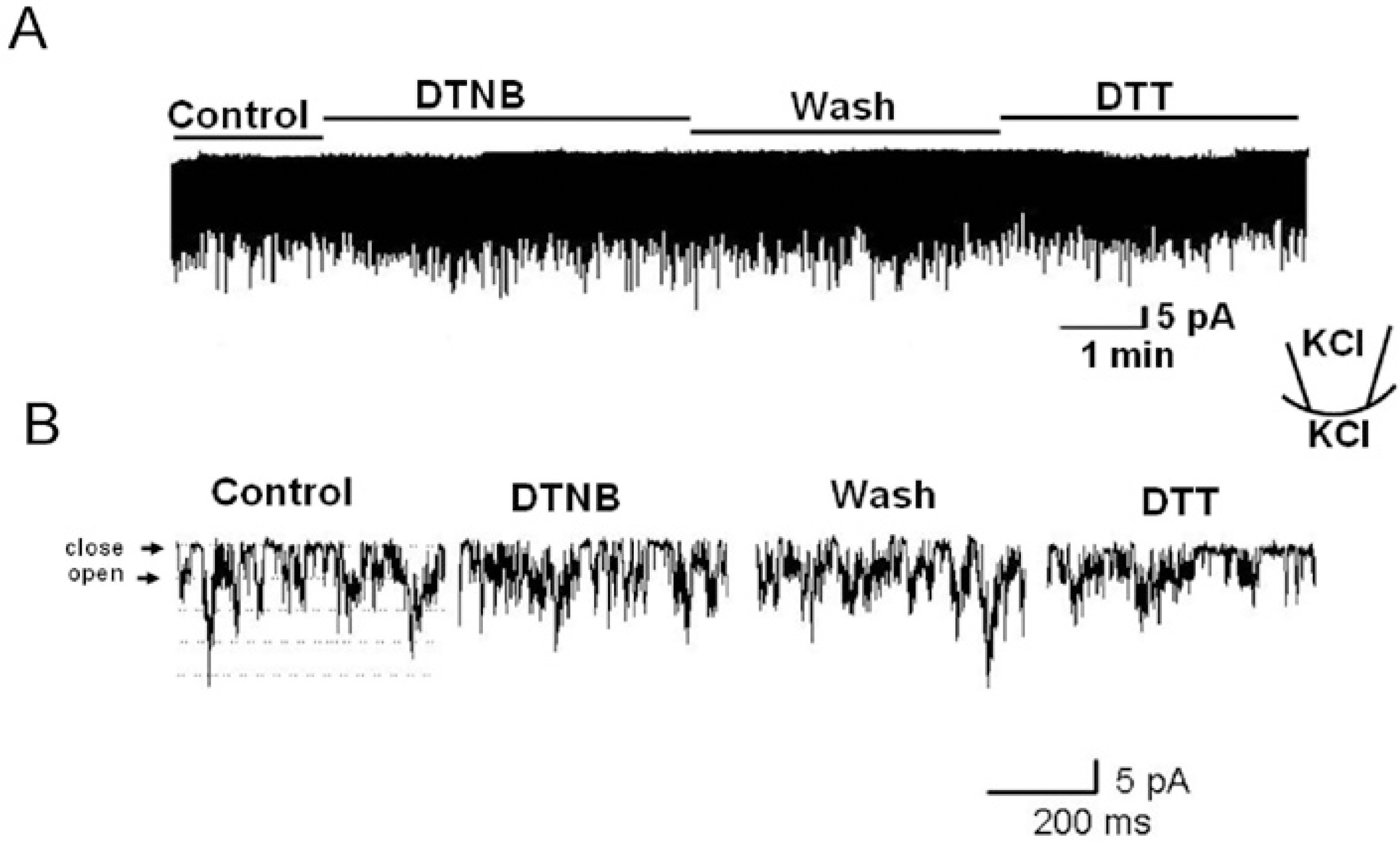
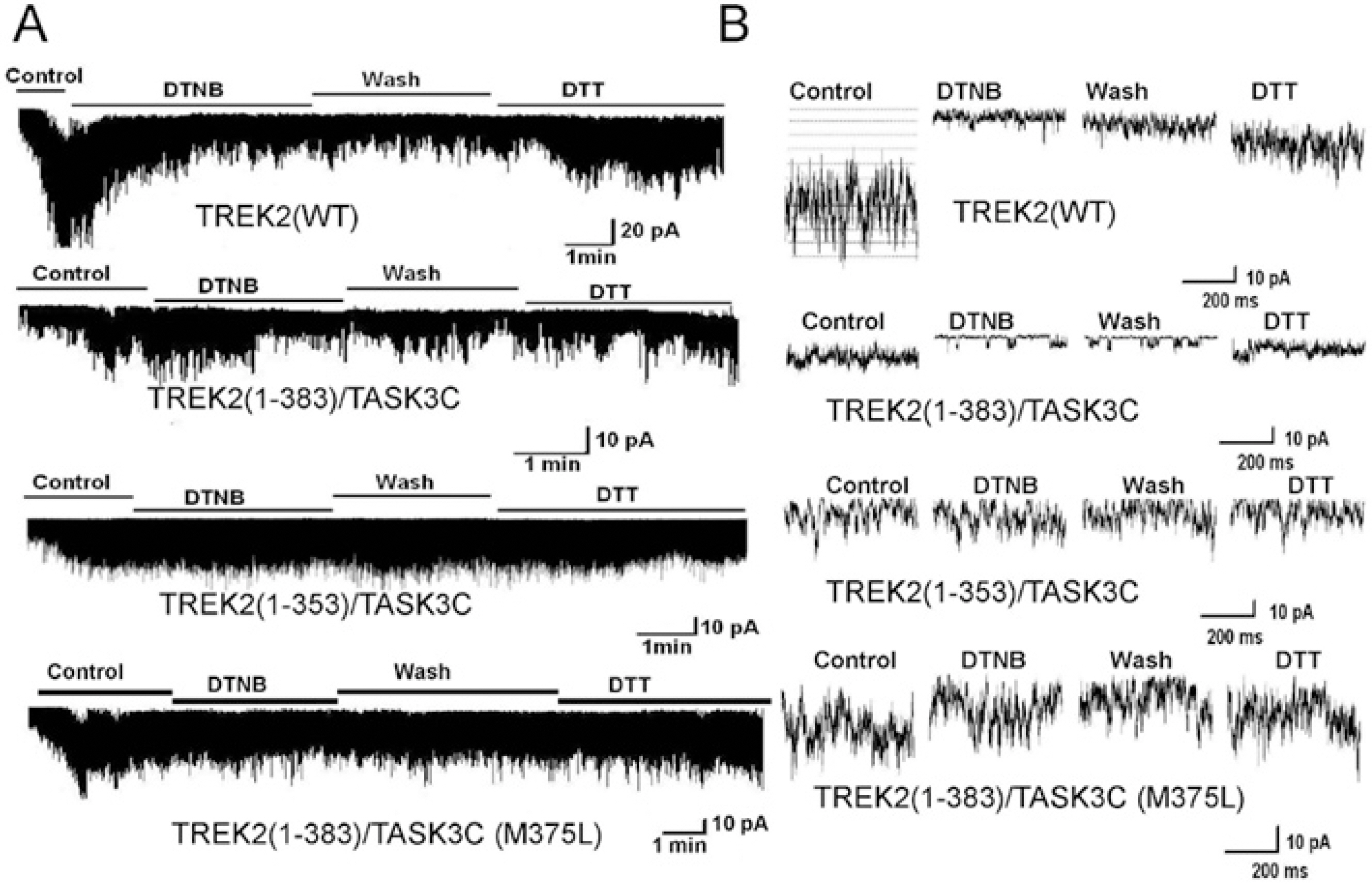
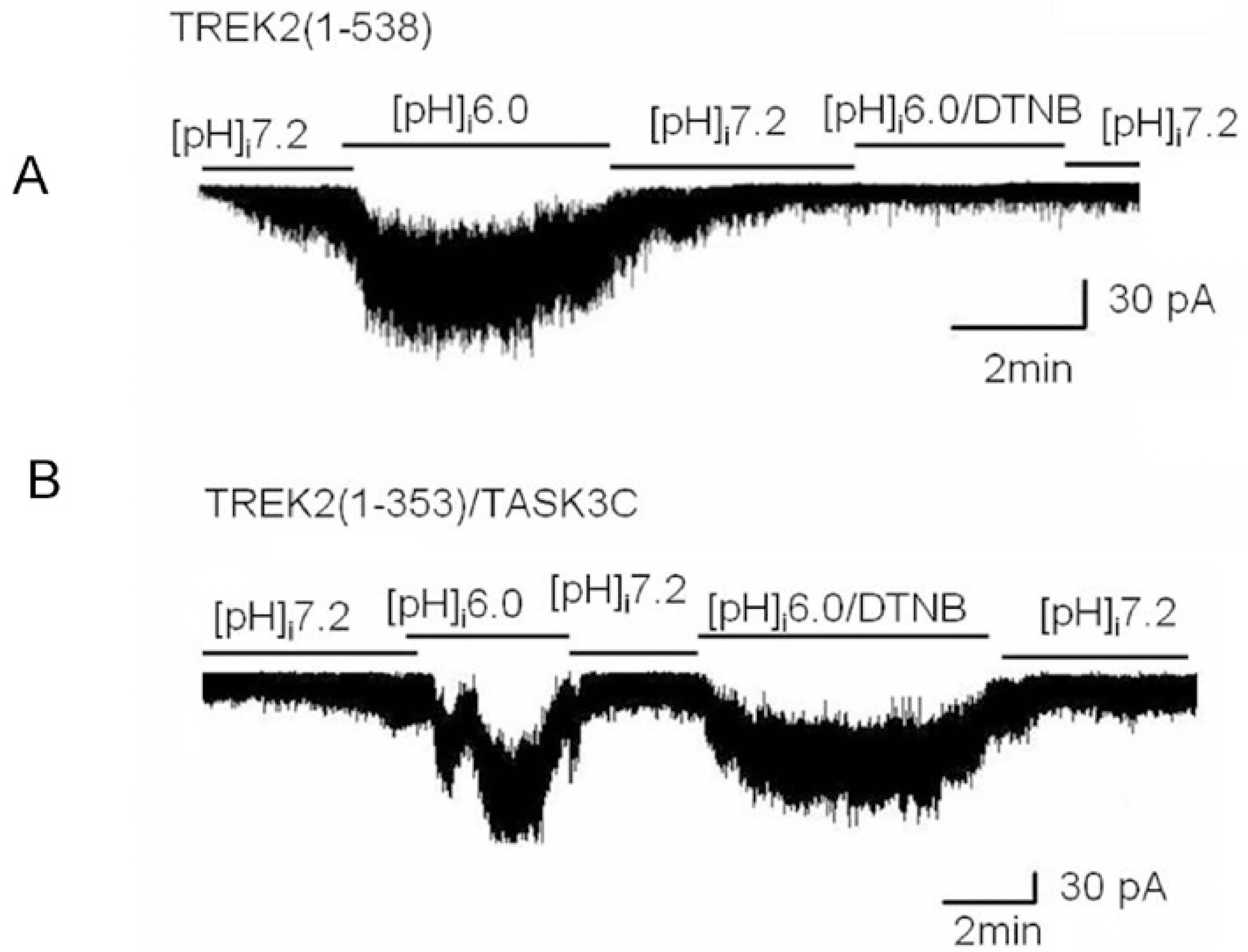
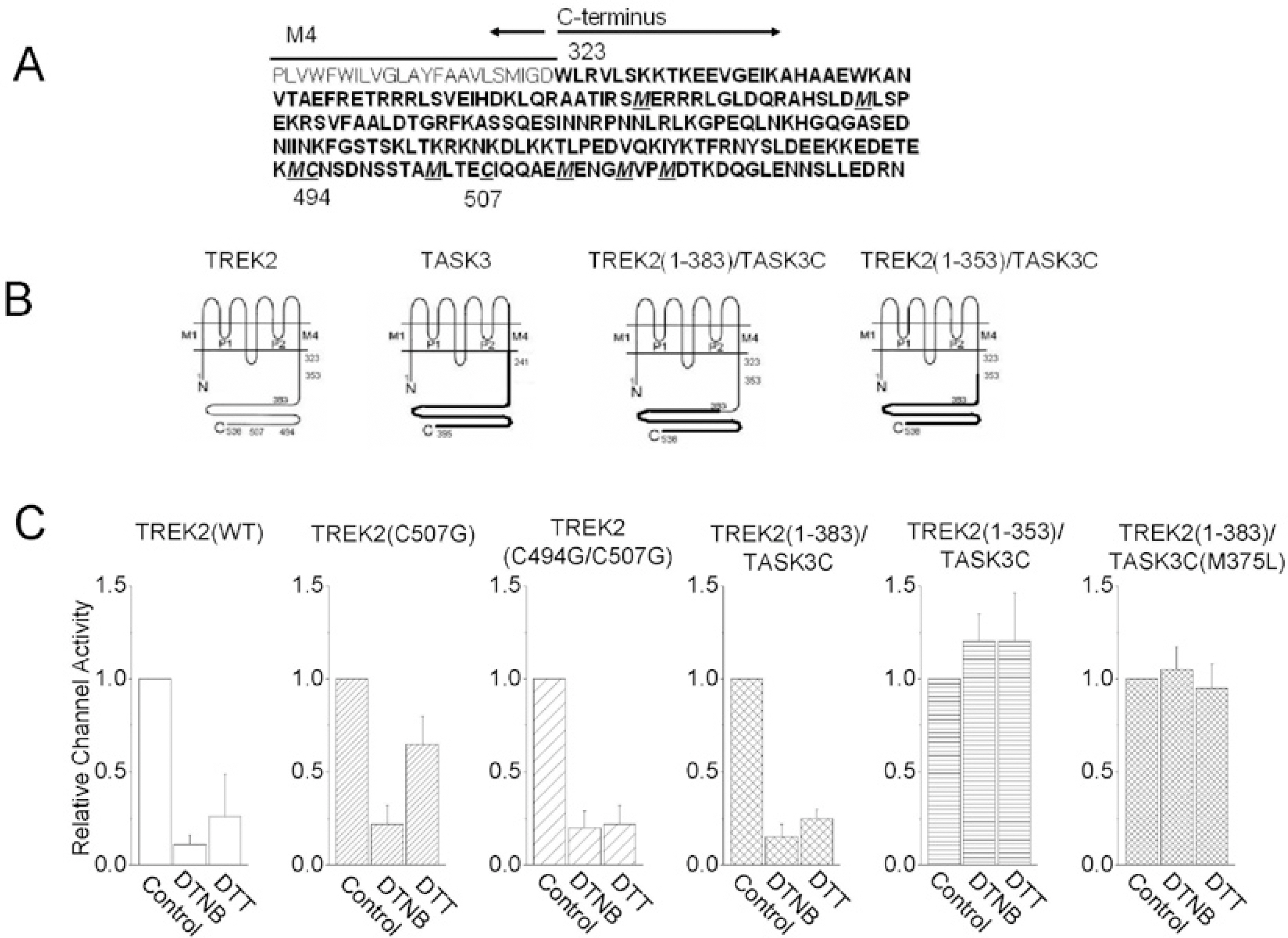
- TREK (TWIK-RElated K+ channels) and TRAAK (TWIK-Related Arachidonic acid Activated K+ channels) were expressed in COS-7 cells, and the channel activities were recorded from inside-out membrane patches using holding potential of -40 mV in symmetrical 150 mM K+ solution. Intracellular application of an oxidizing agent, 5,5'-dithio-bis (2-nitrobenzoic acid) (DTNB), markedly decreased the activity of the TREK2, and the activity was partially reversed by the reducing agent, dithiothreitol (DTT). In order to examine the possibility that the target sites for the oxidizing agents might be located in the C-terminus of TREK2, two chimeras were constructed: TREK2 (1-383)/TASK3C and TREK2 (1-353)/TASK3C. The channel activity in the TREK2 (1-383)/TASK3C chimera was still inhibited by DTNB, but not in the TREK2 (1-353)/TASK3C chimera. These results indicate that TREK2 is inhibited by oxidation, and that the target site for oxidation is located between the amino acid residues 353 and 383 in the C-terminus of the TREK2 protein.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
Bang H., Kim Y., Kim D. TREK-2, a new member of the mecha-nosensitive tandem-pore K+ channel family. J Biol Chem. 275:17412–17419. 2000.Buckler KJ., Honore E. The lipid-activated two-pore domain K+ channel TREK-1 is resistant to hypoxia: implication for ischaemic neuroprotection. J Physiol. 562(Pt 1):213–222. 2005.Caley AJ., Gruss M., Franks NP. The effects of hypoxia on the modulation of human TREK-1 potassium channels. J Physiol. 562(Pt 1):205–212. 2005.
ArticleDiChiara TJ., Reinhart PH. Redox modulation of hslo Ca2+ -activated K+ channels. J Neurosci. 17:4942–4955. 1997.Haarmann CS., Fink RH., Dulhunty AF. Oxidation and reduction of pig skeletal muscle ryanodine receptors. Biophys J. 77:3010–3022. 1999.
ArticleHonore E. The neuronal background K2P channels: focus on TREK1. Nat Rev Neurosci. 8:251–261. 2007.Honore E., Maingret F., Lazdunski M., Patel AJ. An intracellular proton sensor commands lipid- and mechano-gating of the K+ channel TREK-1. Embo J. 21:2968–2976. 2002.Kim D. Physiology and pharmacology of two-pore domain potassium channels. Curr Pharm Des. 11:2717–2736. 2005.
ArticleKim Y., Bang H., Gnatenco C., Kim D. Synergistic interaction and the role of C-terminus in the activation of TRAAK K+ channels by pressure, free fatty acids and alkali. Pflugers Arch. 442:64–72. 2001a.Kim Y., Gnatenco C., Bang H., Kim D. Localization of TREK-2 K+ channel domains that regulate channel kinetics and sensitivity to pressure, fatty acids and pHi. Pflugers Arch. 442:952–960. 2001b.Kim Y., Lee SH., Ho WK. Hydrogen peroxide selectively increases TREK-2 currents via myosin light chain kinases. Front Biosci. 12:1642–1650. 2007.
ArticleMaingret F., Lauritzen I., Patel AJ., Heurteaux C., Reyes R., Lesage F., Lazdunski M., Honore E. TREK-1 is a heat-activated background K+ channel. Embo J. 19:2483–2491. 2000.Maingret F., Patel AJ., Lesage F., Lazdunski M., Honore E. Mechanoor acid stimulation, two interactive modes of activation of the TREK-1 potassium channel. J Biol Chem. 274:26691–26696. 1999.Miller P., Kemp PJ., Lewis A., Chapman CG., Meadows HJ., Peers C. Acute hypoxia occludes hTREK-1 modulation: re-evaluation of the potential role of tandem P domain K+ channels in central neuroprotection. J Physiol. 548(Pt 1):31–37. 2003.Miller P., Kemp PJ., Peers C. Structural requirements for O2 sensing by the human tandem-P domain channel, hTREK1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 331:1253–1256. 2005.Miller P., Peers C., Kemp PJ. Polymodal regulation of hTREK1 by pH, arachidonic acid, and hypoxia: physiological impact in acidosis and alkalosis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 286:C272–282. 2004.
ArticlePatel AJ., Honore E., Maingret F., Lesage F., Fink M., Duprat F., Lazdunski M. A mammalian two pore domain mechano-gated S-like K+ channel. Embo J. 17:4283–4290. 1998.Ruppersberg JP., Fakler B. Complexity of the regulation of Kir2.1 K+ channels. Neuropharmacology. 35:887–893. 1996.Ruppersberg JP., Stocker M., Pongs O., Heinemann SH., Frank R., Koenen M. Regulation of fast inactivation of cloned mammalian IKA channels by cysteine oxidation. Nature. 352:711–714. 1991.
ArticleSullivan JM., Traynelis SF., Chen HS., Escobar W., Heinemann SF., Lipton SA. Identification of two cysteine residues that are required for redox modulation of the NMDA subtype of glutamate receptor. Neuron. 13:929–936. 1994.
ArticleTang XD., Daggett H., Hanner M., Garcia ML., McManus OB., Brot N., Weissbach H., Heinemann SH., Hoshi T. Oxidative regulation of large conductance calcium-activated potassium channels. J Gen Physiol. 117:253–274. 2001.
ArticleZeidner G., Sadja R., Reuveny E. Redox-dependent gating of G protein-coupled inwardly rectifying K+ channels. J Biol Chem. 276:35564–35570. 2001.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Thiol-dependent Redox Mechanisms in the Modification of ATP-Sensitive Potassium Channels in Rabbit Ventricular Myocytes
- Amino Acid Transporters as Potential Therapeutic Targets in Thyroid Cancer
- Homo-dimerization of RyR1 C-terminus via charged residues in random coils or in an alpha-helix
- Reduced dihydroxyacetone sensitivity and normal sensitivity to glyceraldehyde and oxidizing agent of ATP-sensitive K+ channels of pancreatic beta cells in NIDDM rats
- Expression and functional characterization of amino acid transport system L in Saos2 human osteogenic sarcoma cells