J Clin Neurol.
2005 Oct;1(2):166-173. 10.3988/jcn.2005.1.2.166.
The Closing-in Phenomenon in Alzheimer's Disease and Vascular Dementia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. dukna@smc.samsung.co.kr
- KMID: 1808487
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2005.1.2.166
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
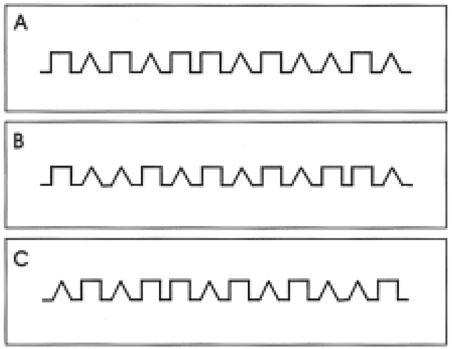
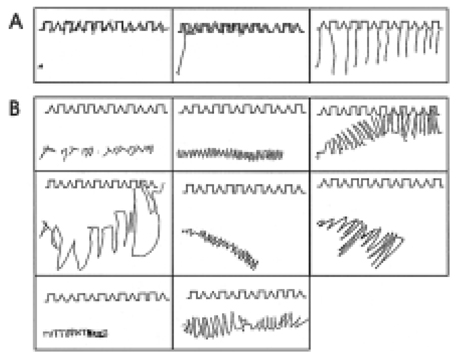
The closing-in phenomenon is the tendency to draw near or on the target when copying figures, which has been found mostly in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD). We attempted to quantify the degree of closing-in and to compare it between patients with AD and vascular dementia (VaD).
METHODS
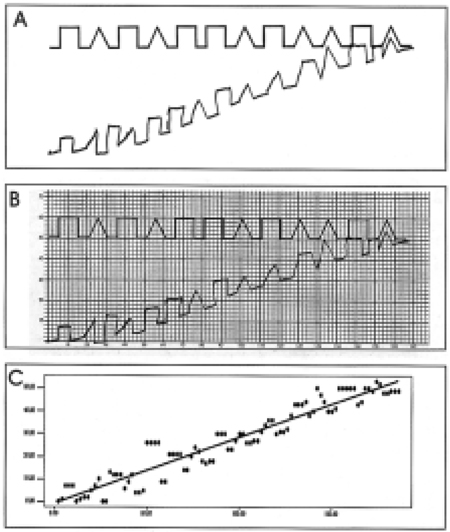
The subjects (55 AD, 39 VaD and 38 normal controls) were asked to copy the figure of alternating square and triangle, starting at the designated point and continuing from left to right. The patients with AD and VaD did not differ in age, education, severity of dementia or Rey Complex Figure Test copy score. The proximity (Y-axis) of the subject's drawing to the target was plotted at intervals of 2 mm along the X-axis and the degree of closing-in was computed from the slope of the regression line.
RESULTS
The AD and VaD patients showed a steeper slope than the controls. There was no significant difference, however, in the magnitude of closing-in of the AD and VaD patients. When closing-in was defined as a slope that was greater than the mean+2SD of the slope observed for the controls, 32.7% of the AD and 25.6% of the VaD patients showed closing-in.
CONCLUSIONS
Our study, using a new method of measuring the degree of closing-in, suggests that this phenomenon is not specific to AD.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
The Closing-in Phenomenon in Alzheimer's Disease and Vascular Dementia
Juhee Chin, Byung Hwa Lee, Sang Won Seo, Eun-Joo Kim, Mee K. Suh, Sue J. Kang, Duk L. Na
J Clin Neurol. 2005;1(2):166-173. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2005.1.2.166.Anatomical Correlates of the "Closing-In" Phenomenon
Se-Yoon Kwon, Eek-Sung Lee, Yun Jeong Hong, Sung-Chul Lim, Kook Jin Ahn, Bora Yoon, YongSoo Shim, Dong Won Yang
Dement Neurocogn Disord. 2015;14(1):17-23. doi: 10.12779/dnd.2015.14.1.17.
Reference
-
1. Gainotti G, Parlato V, Monteleone D, Carlomagno S. Neuropsychological markers of dementia on visual-spatial tasks: a comparison between Alzheimer's type and vascular forms of dementia. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 1992. 14:239–252.
Article2. Mayer-Gross W. Some observations on apraxia. Proc R Soc Med. 1935. 28:1203–1212.
Article3. Muncie W. Concrete model and abstract copy: a psychobiological interpretation of the "closing-in" symptom of Mayer-Gross. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1938. 88:1–11.4. Lhermitte J, Mouzon J. Sur l'apractognosie geometrique et l'apraxie constructive consecutives aux lesions du lobe occipital. Rev Neuol. 1941. 73:415–431.5. Ajuriaguerra J, De Muller M, Tissot R. A propos de quelques problemes poses par l'apraxie dans les demences. Encephale. 1960. 49:275–401.6. Gainotti G. A quantitative study of the "closing-in" symptom in normal children and in brain-damaged patients. Neuropsychologia. 1972. 10:429–436.
Article7. Gainotti G, Marra C, Villa G, Parlato V, Chiarotti F. Sensitivity and specificity of some neuropsychological markers of Alzheimer dementia. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 1998. 12:152–162.
Article8. Kwak YT. "Closing-in" phenomenon in Alzheimer's disease and subcortical vascular dementia. BMC Neurology. 2004. 4:3.
Article9. Lee BH, Chin J, Kang SJ, Kim EJ, Park KC, Na DL. Mechanism of the Closing-in phenomenon in a figure copying task in Alzheimer's disease. Neurocase. 2004. 10(5):393–397.
Article10. Midorikawa Y, Fukatsu R, Takahata N. Closing-in phenomena observed in patients with Alzheimer's disease - analysis of drawing behavior and eye movements. Seishin Shinkeigaku Zasshi. 1996. 98:151–169.11. Chin J, Baek MJ, Lee BH, Kang SJ, Jeong Y, Kwon J. The closing-in phenomenon in Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2003. 9:166.
Article12. Mckhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA work group under the auspices of department of health and human services task force on Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1984. 34:939–944.
Article13. Chui HC, Victoroff JI, Margolin D, Jagust W, Shankle R, Katzan R. Criteria for the diagnosis of ischemic vascular dementia proposed by the state of California Alzheimer's Disease Diagnostic and Treatment Centers. Neurology. 1992. 42:473–480.
Article14. Fazekas F, Chawluk JB, Alavi A, Hurtig HI, Zimmerman RA. MR signal abnormalities at 1.5 T in Alzheimenr's dementia and normal aging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1987. 8:421–426.15. Blennow K, Wallin A, Uhlemann C, Gottifries CG. White-matter lesions on CT in Alzheimer's patients: relation to clinical symptomatologic and vascular factors. Acta Neurol Scand. 1991. 83:187–193.
Article16. Oldfield RC. The assessment and analysis of handedness: The Edinburgh Inventory. Neuropsychologia. 1971. 9:97–113.
Article17. Luria A. Human brain and psychological processes. 1966. New York: Harper & Row.18. Kang YW, Na DL, Hahn SH. A validity study on the Korean Mini-Mental State Examination (K-MMSE) in dementia patients. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 1997. 15:300–308.19. Morris JC. The Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR): current version and scoring rules. Neurology. 1993. 43:2412–2414.20. Erkinjuntti T, Inzitari D, Pantoni L, Wallin A, Scheltens P, Rockwood K. Research Criteria for subcortical vascular dementia in clinical trials. J Neural Transm Suppl. 2000. 59:23–30.
Article