J Cardiovasc Ultrasound.
2012 Sep;20(3):154-156. 10.4250/jcu.2012.20.3.154.
Recurrent Mesalazine-Induced Myopericarditis in a Patient with Ulcerative Colitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. bjjake.kim@samsung.com
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Hana General Hospital, Cheongju, Korea.
- KMID: 1808352
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jcu.2012.20.3.154
Abstract
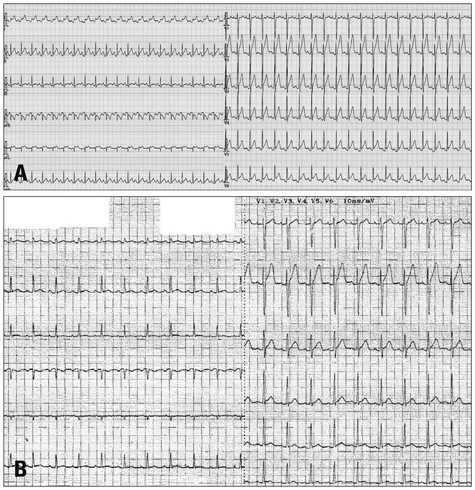
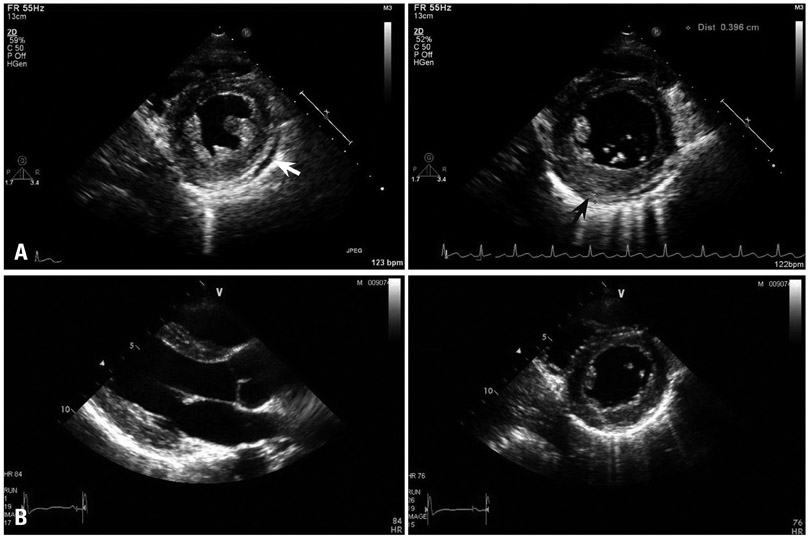
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is considered as a dysregulated immune mediated disease. Pericarditis in IBD is a very rare disease both as an extra-intestinal manifestation of IBD and an adverse reaction of therapeutic drug for IBD such as mesalazine or sulfasalazine. A 26-year-old IBD male patient who had been taking mesalazine regularly for about 1 month was referred to our hospital because of fever, chest discomfort, and abnormal electrocardiographic findings. The patients was diagnosed as acute myopericarditis, and recovered after cessation of mesalazine using steroid and aspirin. When mesalazine was re-medicated some days after discharge, he suffered from myopericarditis again. Subsequently, myopericarditis was resolved just after cessation of mesalazine again. These findings suggest that the development of myopericarditis is caused by mesalazine.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
비전형적 궤양성 대장염 환자에서 5-아미노살리실산에 의해 유발된 심근염
Hyo Yeop Song, Geom Seog Seo
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2022;79(1):31-34. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2021.152.
Reference
-
1. Bernal-Sprekelsen JC, de las Marinas MD, Salvador A, Landete FJ, Morera FJ. Recurrent pericarditis in a patient with ulcerative proctitis due to mesalazine suppositories. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2010. 25:1143–1144.
Article2. Ishikawa N, Imamura T, Nakajima K, Yamaga J, Yuchi H, Ootsuka M, Inatsu H, Aoki T, Eto T. Acute pericarditis associated with 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) treatment for severe active ulcerative colitis. Intern Med. 2001. 40:901–904.
Article3. García-Morán S, Sáez-Royuela F, Pérez-Alvarez JC, Gento E, Téllez J. Myopericarditis and mitral insufficiency associated with ulcerative colitis treated with mesalazine. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2006. 12:334–335.
Article4. Vayre F, Vayre-Oundjian L, Monsuez JJ. Pericarditis associated with longstanding mesalazine administration in a patient. Int J Cardiol. 1999. 68:243–245.5. Bernstein CN, Wajda A, Blanchard JF. The clustering of other chronic inflammatory diseases in inflammatory bowel disease: a population-based study. Gastroenterology. 2005. 129:827–836.
Article6. Sentongo TA, Piccoli DA. Recurrent pericarditis due to mesalamine hypersensitivity: a pediatric case report and review of the literature. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1998. 27:344–347.
Article7. Perrot S, Aslangul E, Szwebel T, Gadhoum H, Romnicianu S, Le Jeunne C. Sulfasalazine-induced pericarditis in a patient with ulcerative colitis without recurrence when switching to mesalazine. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2007. 22:1119–1121.
Article8. Jenss H, Becker EW, Weber P. Pericardial effusion during treatment with 5-aminosalicylic acid in a patient with Crohn's disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 1990. 85:332–333.9. Kristensen KS, Høegholm A, Bohr L, Friis S. Fatal myocarditis associated with mesalazine. Lancet. 1990. 335:605.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recurrent Eosinophilic Pneumonia Associated with Mesalazine Suppository in a Patient with Ulcerative Colitis
- A Case of Pyoderma Gangrenosum with Ulcerative Colitis Treated with Mesalazine
- A Case of Acute Pancreatitis Caused by 5-aminosalicylic Acid Suppositories in a Patient with Ulcerative Colitis
- A Case of Mesalazine-induced Eosinophilic Pneumonia in a Patient with Ulcerative Colitis
- Acute Pancreatitis Induced by 5-Aminosalicylic Acid in a Patient with Ulcerative Colitis