Ann Surg Treat Res.
2014 Jul;87(1):41-43. 10.4174/astr.2014.87.1.41.
Delayed hepatic rupture after radiofrequency ablation for colorectal hepatic metastasis: management with transcatheter arterial embolization
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yjkim@kuh.ac.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1804098
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2014.87.1.41
Abstract
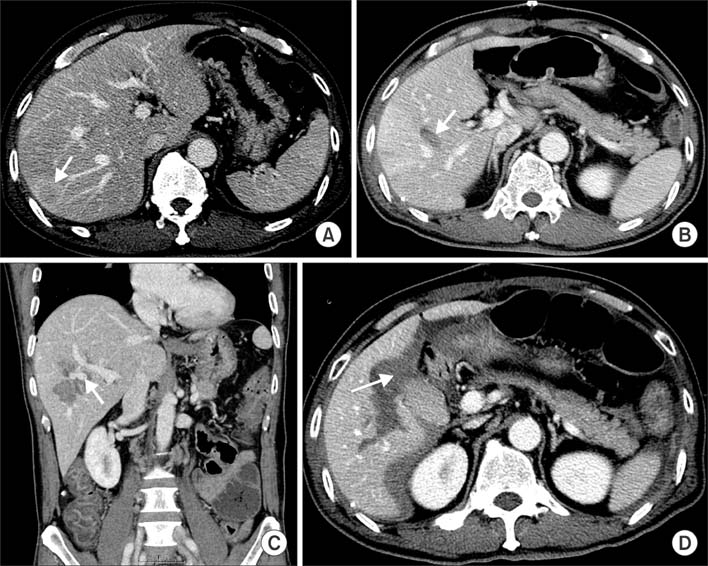
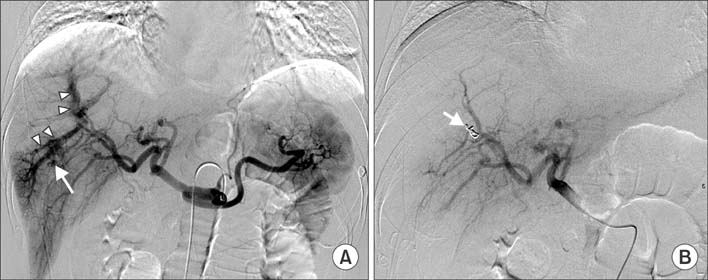
- Intraperitoneal bleeding after radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is the most common major vascular complication due to direct needle injury to a vessel or liver capsule. However, intraperitoneal bleeding as a result of a delayed hepatic rupture after RFA for liver tumors is an extremely rare complication. The present report describes a case of intraperitoneal hemorrhage caused by delayed hepatic rupture resulting from arterioportal fistula after RFA for hepatic metastasis from colorectal cancer and successful management using transcatheter embolization.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Local ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: 2024 expert consensus-based practical recommendation of the Korean Liver Cancer Association
Seungchul Han, Pil Soo Sung, Soo Young Park, Jin Woong Kim, Hyun Pyo Hong, Jung-Hee Yoon, Dong Jin Chung, Joon Ho Kwon, Sanghyeok Lim, Jae Hyun Kim, Seung Kak Shin, Tae Hyung Kim, Dong Ho Lee, Jong Young Choi
J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(2):131-144. doi: 10.17998/jlc.2024.08.04.
Reference
-
1. Wu YZ, Li B, Wang T, Wang SJ, Zhou YM. Radiofrequency ablation vs hepatic resection for solitary colorectal liver metastasis: a meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol. 2011; 17:4143–4148.2. Bismuth H, Adam R, Levi F, Farabos C, Waechter F, Castaing D, et al. Resection of nonresectable liver metastases from colorectal cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Ann Surg. 1996; 224:509–520.3. Gillams AR, Lees WR. Radiofrequency ablation of colorectal liver metastases. Abdom Imaging. 2005; 30:419–426.4. Rhim H. Complications of radiofrequency ablation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Abdom Imaging. 2005; 30:409–418.5. Curley SA, Marra P, Beaty K, Ellis LM, Vauthey JN, Abdalla EK, et al. Early and late complications after radiofrequency ablation of malignant liver tumors in 608 patients. Ann Surg. 2004; 239:450–458.6. Rhim H, Dodd GD 3rd, Chintapalli KN, Wood BJ, Dupuy DE, Hvizda JL, et al. Radiofrequency thermal ablation of abdominal tumors: lessons learned from complications. Radiographics. 2004; 24:41–52.7. Kaplan U, Hatoum OA, Chulsky A, Menzal H, Kopelman D. Two weeks delayed bleeding in blunt liver injury: case report and review of the literature. World J Emerg Surg. 2011; 6:14.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Ruptured Metastatic Hepatic Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Treated by Angiographic Embolization
- Spontaneous Hepatic Rupture Associated with Preeclampsia: Treatment with Hepatic Artery Embolization
- Clinical Application of Hepatic Arterial Embolization
- A case of spontaneous rupture of hepatic angiomyolipoma
- Transcatheter hepatic arterial embolization of ruptured hepatoma with massive intraperitoneal bleeding