Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2014 Aug;18(3):101-103. 10.14701/kjhbps.2014.18.3.101.
Superior mesenteric vein thrombosis accompanied with severe appendicitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan Universitiy School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Surgery, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. tsojc@naver.com
- KMID: 1802223
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/kjhbps.2014.18.3.101
Abstract
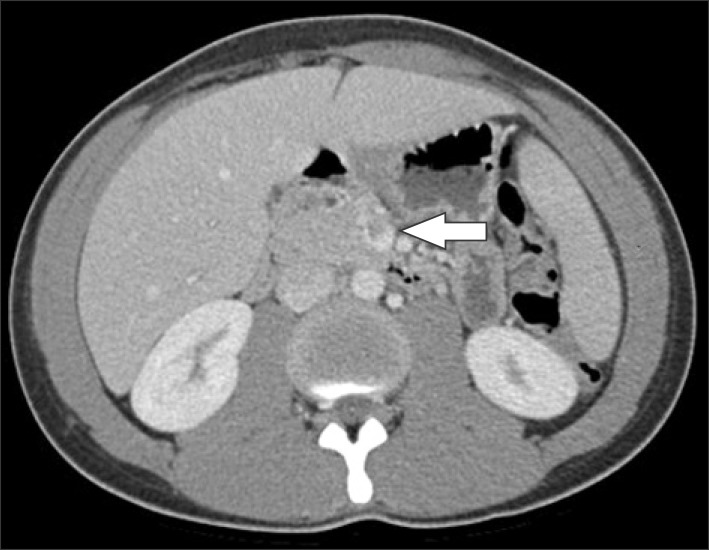
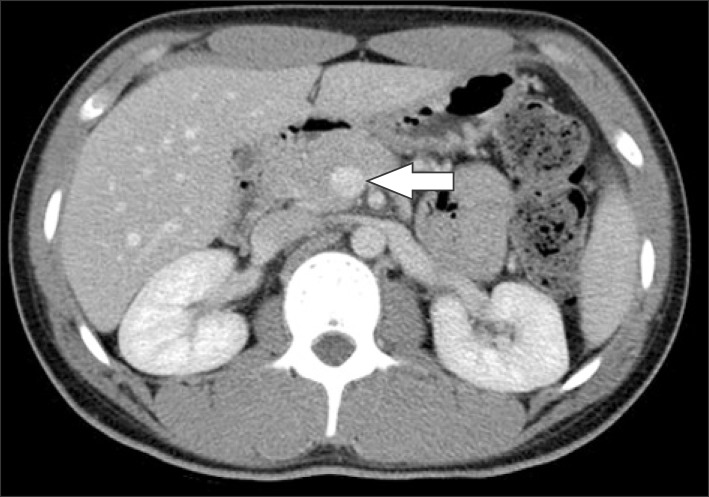
- Superior mesenteric vein (SMV) thrombosis caused by acute appendicitis is a very rare entity nowadays. We report a successfully treated case of a 21-year-old man with SMV thrombosis associated with severe acute appendicitis. Intravenous heparin was administered, and it was later substituted with warfarin. Systemic antibiotic therapy was continued for 1 week, and it was substituted with oral antibiotics, which were administered for 3 weeks. On the 45th postoperative day, follow-up computed tomography scan demonstrated dissolution of SMV thrombosis. Anticoagulation therapy was maintained for 3 months. He was discharged without any complications. SMV thrombosis can be treated successfully with emergency appendectomy, broad-spectrum antibiotics, and anticoagulation therapy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Recurrent Abdominal Pain after Laparoscopic Appendectomy
Kwang Il Seo, Sung Eun Kim, Moo In Park, Seun Ja Park, Won Moon, Jae Hyun Kim, Kyoungwon Jung, Jung Gu Park
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2017;69(3):187-190. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2017.69.3.187.
Reference
-
1. Baril N, Wren S, Radin R, Ralls P, Stain S. The role of anticoagulation in pylephlebitis. Am J Surg. 1996; 172:449–452. PMID: 8942542.
Article2. Nishimori H, Ezoe E, Ura H, Imaizumi H, Meguro M, Furuhata T, et al. Septic thrombophlebitis of the portal and superior mesenteric veins as a complication of appendicitis: report of a case. Surg Today. 2004; 34:173–176. PMID: 14745623.
Article3. Plemmons RM, Dooley DP, Longfield RN. Septic thrombophlebitis of the portal vein (pylephlebitis): diagnosis and management in the modern era. Clin Infect Dis. 1995; 21:1114–1120. PMID: 8589130.
Article4. Singh P, Yadav N, Visvalingam V, Indaram A, Bank S. Pylephlebitis--diagnosis and management. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001; 96:1312–1313. PMID: 11316205.
Article5. Saxena R, Adolph M, Ziegler JR, Murphy W, Rutecki GW. Pylephlebitis: a case report and review of outcome in the antibiotic era. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996; 91:1251–1253. PMID: 8651182.6. Waxman BP, Cavanagh LL, Nayman J. Suppurative pyephlebitis and multiple hepatic abscesses with silent colonic diverticulitis. Med J Aust. 1979; 2:376–378. PMID: 390346.7. Balthazar EJ, Gollapudi P. Septic thrombophlebitis of the mesenteric and portal veins: CT imaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2000; 24:755–760. PMID: 11045699.
Article8. Chang TN, Tang L, Keller K, Harrison MR, Farmer DL, Albanese CT. Pylephlebitis, portal-mesenteric thrombosis, and multiple liver abscesses owing to perforated appendicitis. J Pediatr Surg. 2001; 36:E19. PMID: 11528636.
Article9. Dean JW, Trerotola SO, Harris VJ, Snidow JJ, Hawes D. Percutaneous management of suppurative pylephlebitis. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 1995; 6:585–588. PMID: 7579869.
Article10. Stitzenberg KB, Piehl MD, Monahan PE, Phillips JD. Interval laparoscopic appendectomy for appendicitis complicated by pylephlebitis. JSLS. 2006; 10:108–113. PMID: 16709373.11. Kasper DL, Sahani D, Misdraji J. Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Case 25-2005. A 40-year-old man with prolonged fever and weight loss. N Engl J Med. 2005; 353:713–722. PMID: 16107625.12. Lim HE, Cheong HJ, Woo HJ, Kim WJ, Kim MJ, Lee CH, et al. Pylephlebitis associated with appendicitis. Korean J Intern Med. 1999; 14:73–76. PMID: 10063317.
Article13. Vanamo K, Kiekara O. Pylephlebitis after appendicitis in a child. J Pediatr Surg. 2001; 36:1574–1576. PMID: 11584411.
Article14. Condat B, Pessione F, Helene Denninger M, Hillaire S, Valla D. Recent portal or mesenteric venous thrombosis: increased recognition and frequent recanalization on anticoagulant therapy. Hepatology. 2000; 32:466–470. PMID: 10960436.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute Appendicitis with Superior Mesenteric Vein Thrombosis and Portal Vein Thrombosis
- Spontaneous Dissolution of Isolated Superior Mesenteric Vein Thrombosis in Acute Pancreatitis
- Spontaneous Superior Mesenteric Artery Branch Pseudoaneurysm
- Portal Vein and Superior Mesenteric Vein Thrombosis following Cholecystectomy and Choledochostomy
- A Case of Superior Mesenteric Artery Thrombosis Treated with Intra-arterial Urokinase Infusion and Intraluminal Stent Insertion