Korean J Gastroenterol.
2011 Jan;57(1):38-41. 10.4166/kjg.2011.57.1.38.
Spontaneous Dissolution of Isolated Superior Mesenteric Vein Thrombosis in Acute Pancreatitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, KwangMyung SungAe Hospital, Gwangmyeong, Korea. internist@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, SungAe Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 991467
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2011.57.1.38
Abstract
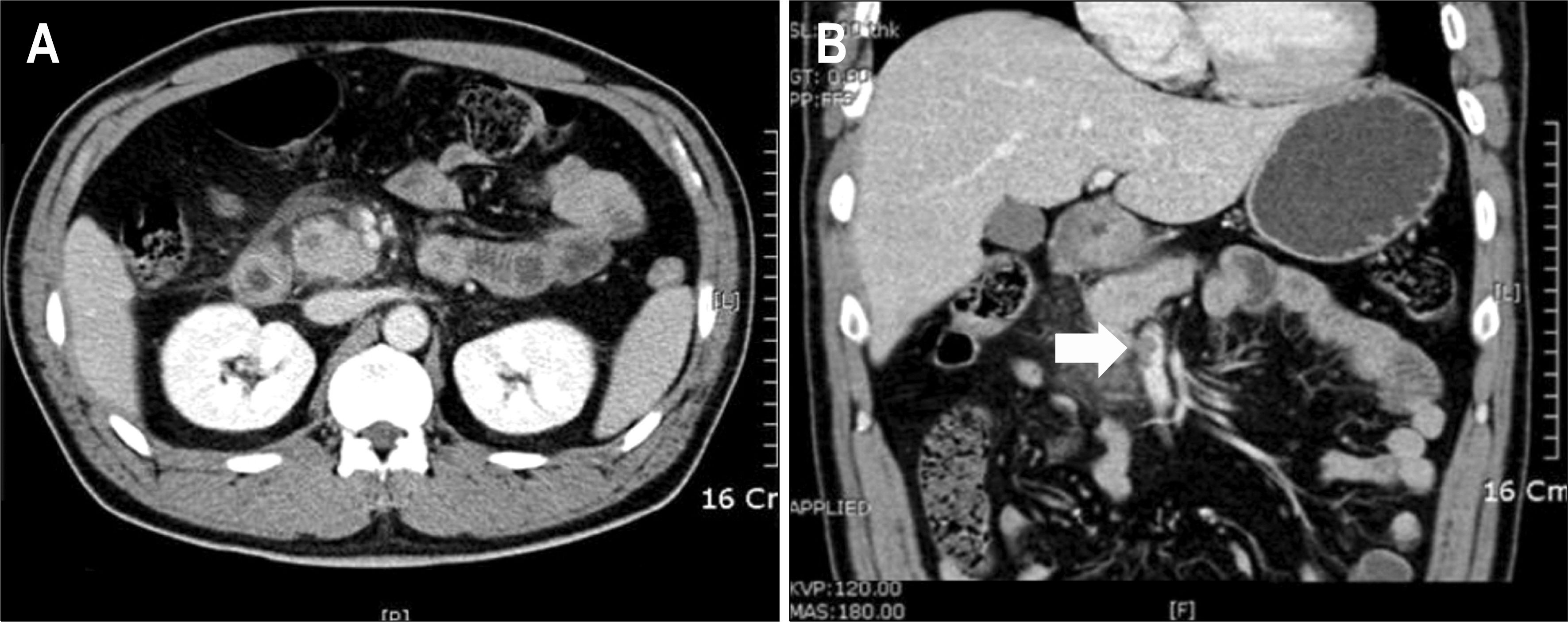
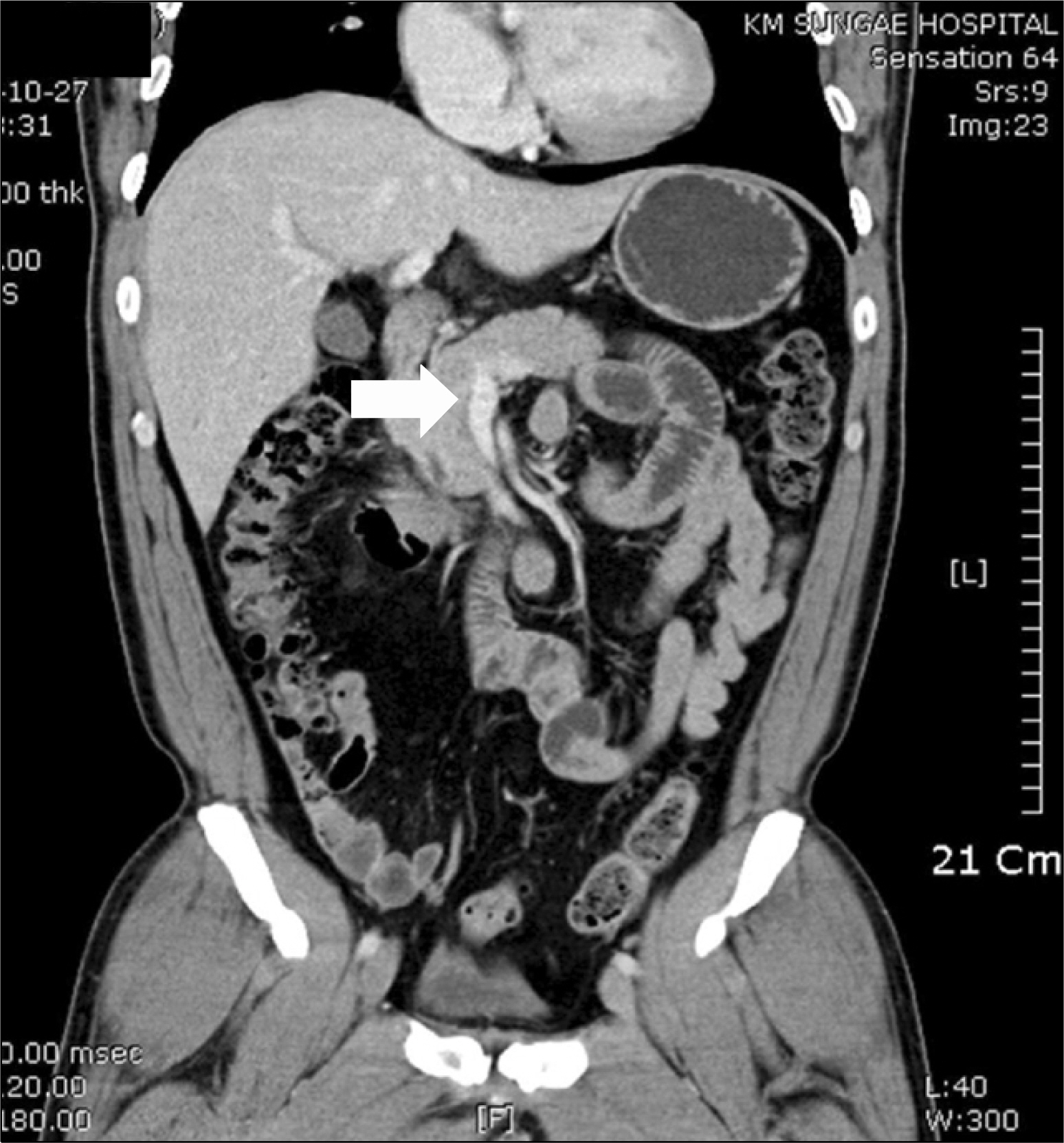
- Acute pancreatitis can result in many vascular complications in both artery and vein. Venous complication usually occurs as a form of splenic or portal vein thrombosis, and also can simultaneously occur in superior mesenteric vein as well. Rarely, isolated superior mesenteric vein thrombosis occurs as a venous complication. Although it is uncommon, mesenteric vein thrombosis is an important clinical entity because of the possibility of mesenteric ischemia and infarction of small bowel. The treatments of mesenteric venous thrombosis include anticoagulation therapy, transcatheter therapy and surgical intervention. We report a case of 45-year-old man who had acute pancreatitis with isolated superior mesenteric vein thrombosis, which was spontaneously dissolved with the resolution of underlying inflammation without anticoagulation or surgical intervention.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Morasch MD, Ebaugh JL, Chiou AC, Matsumura JS, Pearce WH, Yao JS. Mesenteric venous thrombosis: a changing clinical entity. J Vasc Surg. 2001; 34:680–684.
Article2. Kumar S, Sarr MG, Kamath PS. Mesenteric venous thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 2001; 345:1683–1688.
Article3. Dörffel T, Wruck T, Rückert RI, Romaniuk P, Dörffel Q, Wermke W. Vascular complications in acute pancreatitis assessed by color duplex ultrasonography. Pancreas. 2000; 21:126–133.
Article4. Crowe PM, Sagar G. Reversible superior mesenteric vein thrombosis in acute pancreatitis. The CT appearances. Clin Radiol. 1995; 50:628–633.
Article5. Kim HS, Lee WJ, Lee ES, et al. A case of isolated superior mesenteric vein thrombosis in acute pancreatitis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2002; 40:68–71.6. Weber SM, Rikkers LF. Splenic vein thrombosis and gastrointestinal bleeding in chronic pancreatitis. World J Surg. 2003; 27:1271–1274.
Article7. Bradbury MS, Kavanagh PV, Bechtold RE, et al. Mesenteric venous thrombosis: diagnosis and noninvasive imaging. Radiographics. 2002; 22:527–541.
Article8. Warshauer DM, Lee JK, Mauro MA, White GC 2nd. Superior mesenteric vein thrombosis with radiologically occult cause: a retrospective study of 43 cases. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001; 177:837–841.9. Condat B, Pessione F, Hillaire S, et al. Current outcome of portal vein thrombosis in adults: risk and benefit of anticoagulant therapy. Gastroenterology. 2001; 120:490–497.
Article10. Heider TR, Azeem S, Galanko JA, Behrns KE. The natural history of pancreatitis-induced splenic vein thrombosis. Ann Surg. 2004; 239:876–880.
Article11. Sobhonslidsuk A, Reddy KR. Portal vein thrombosis: a concise review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002; 97:535–541.
Article12. Cheung DJ, Kim JK, Jo DH, et al. A case of portal vein thrombosis associated with acute pancreatitis and cholangitis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2005; 46:60–65.13. Chawla Y, Duseja A, Dhiman RK. Review article: the modern management of portal vein thrombosis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2009; 30:881–894.
Article14. Lee H, Kim TH, Oh HJ, et al. Portal and superior mesenteric venous thrombosis treated with urokinase infusion via superior mesenteric artery. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2006; 48:46–50.15. Poplausky MR, Kaufman JA, Geller SC, Waltman AC. Mesenteric venous thrombosis treated with urokinase via the superior mesenteric artery. Gastroenterology. 1996; 110:1633–1635.
Article16. Park JH, Jo YK, Lee MS, et al. A case report of superior mesenteric vein thrombosis associated with diverticulitis. Korean J Med. 1999; 57:114–117.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Isolated Superior Mesenteric Vein Thrombosis in Acute Pancreatitis
- Acute Appendicitis with Superior Mesenteric Vein Thrombosis and Portal Vein Thrombosis
- A Case of Superior Mesenteric Vein and Portal Vein Thrombosis Associated with Normal Delivery Presented by Acute Pancreatitis
- Portal and Splenic Vein Thrombosis Successfully Treated with Anticoagulants in Acute Pancreatitis
- Combination of Surgical Thrombectomy and Direct Thrombolysis in Acute Abdomen with Portal and Superior Mesenteric Vein Thrombosis