J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2014 Dec;40(6):301-307. 10.5125/jkaoms.2014.40.6.301.
Mouth opening limitation caused by coronoid hyperplasia: a report of four cases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea. omshuh@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Yongin Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Yongin, Korea.
- KMID: 1799565
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2014.40.6.301
Abstract
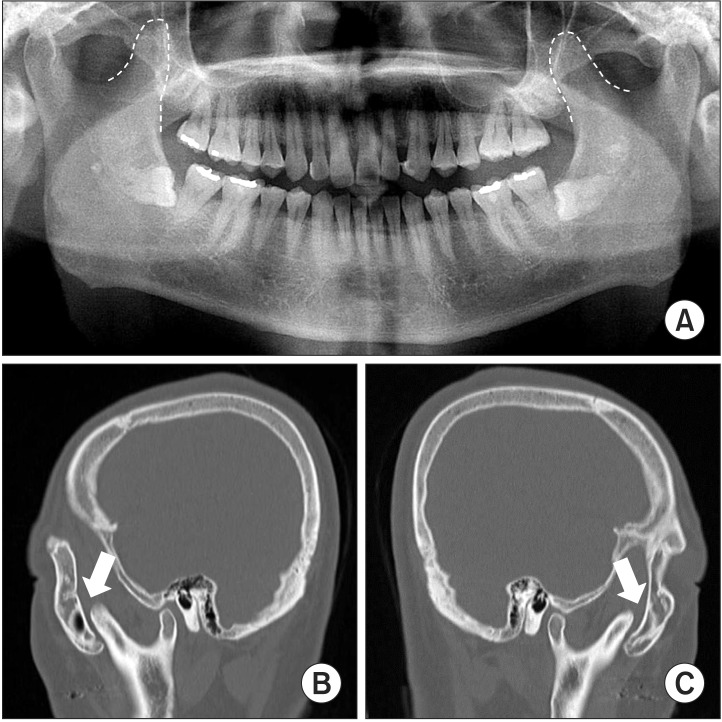
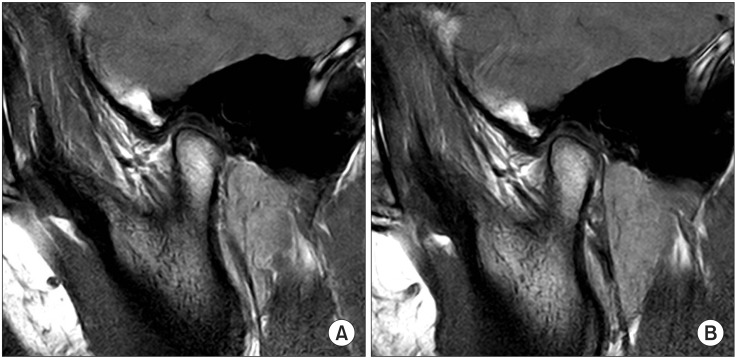
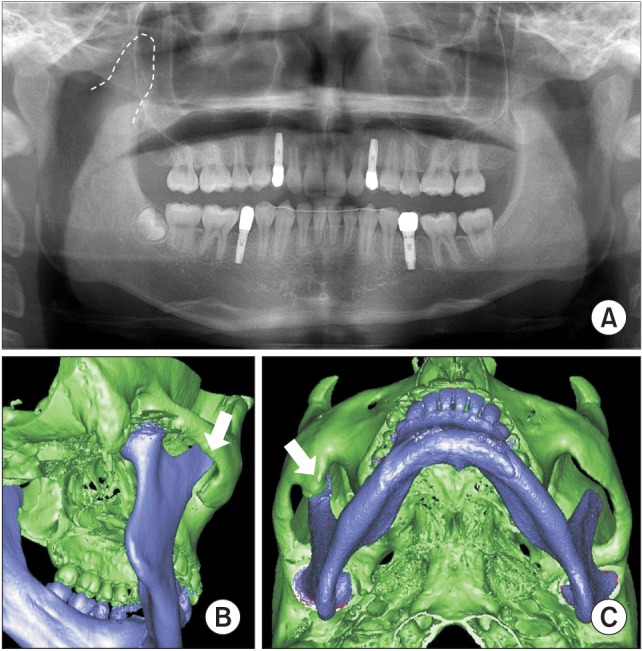
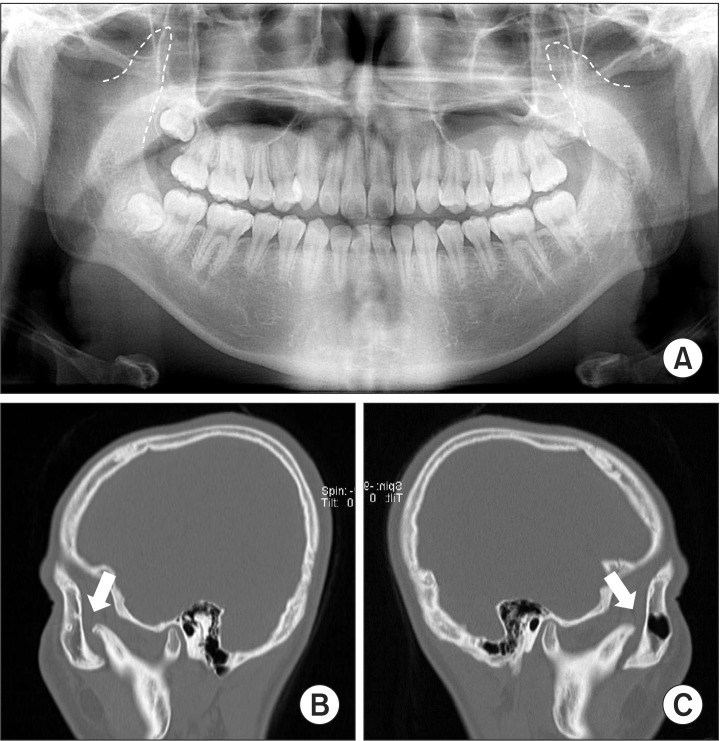
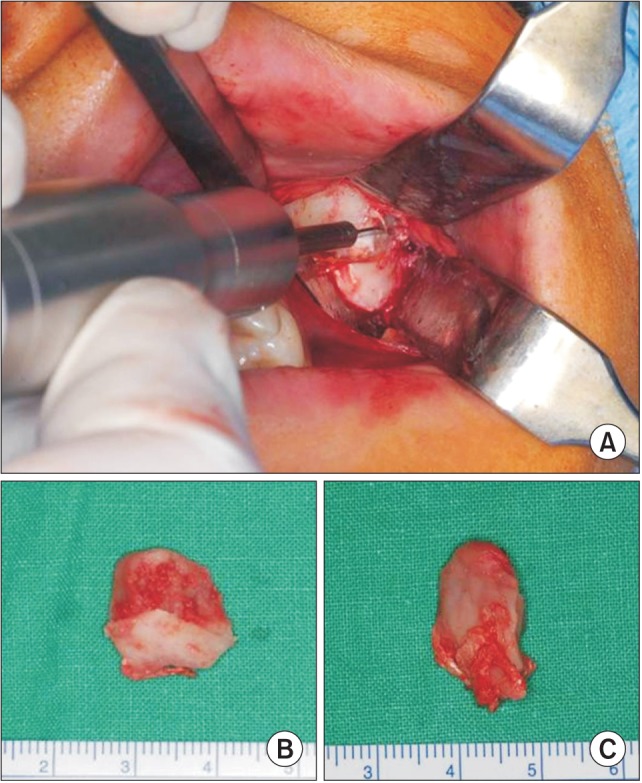
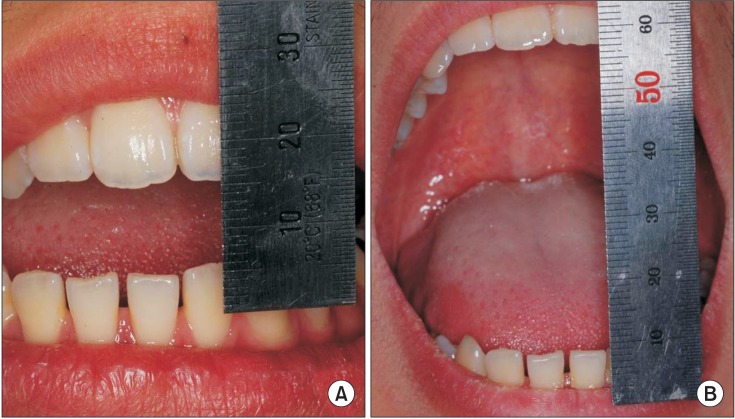
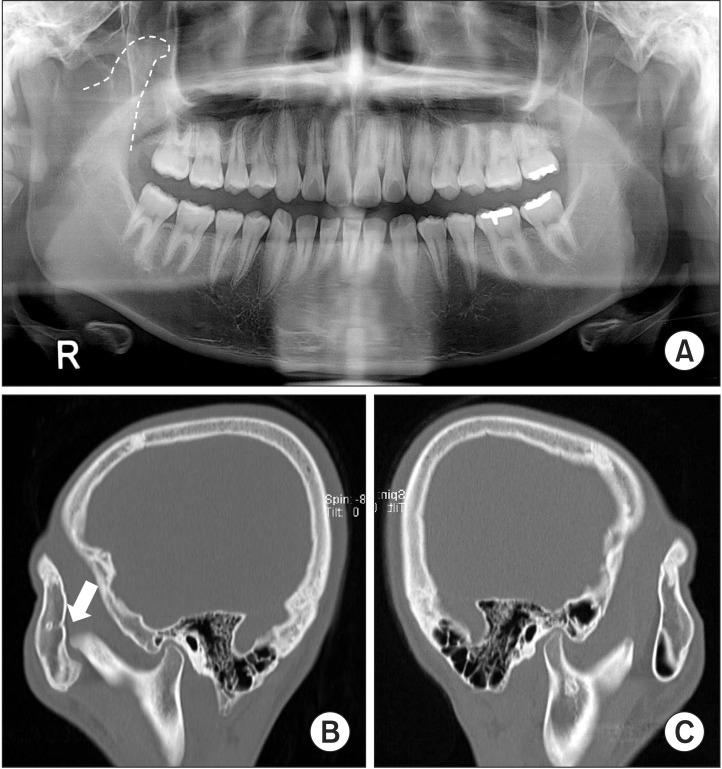
- Coronoid process hyperplasia is a rare condition that causes mouth opening limitation, otherwise known as trismus. The elongated coronoid processes impinge on the medial surfaces of the zygomatic arches when opening the mouth, which limits movement of the mandible and leads to trismus. Patients with trismus due to coronoid process hyperplasia do not have any definite symptoms such as temporomandibular joint pain or sounds upon clinical examination, and no significant abnormal signs are observed on panoramic radiographs or magnetic resonance images of the temporomandibular joint. Thus, the diagnosis of trismus is usually very difficult. However, computed tomography can help with the diagnosis, and the condition can be treated by surgery and postoperative physical therapy. This paper describes four cases of patients who visited our clinic for trismus and were subsequently diagnosed with coronoid process hyperplasia. Three were successfully treated with a coronoidectomy and postoperative physical therapy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A systematic review of treatment and outcomes in patients with mandibular coronoid process hyperplasia
Griet I.L. Parmentier, Margaux Nys, Laurence Verstraete, Constantinus Politis
J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2022;48(3):133-148. doi: 10.5125/jkaoms.2022.48.3.133.
Reference
-
1. Marra LM. Bilateral coronoid hyperplasia, a developmental defect. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1983; 55:10–13. PMID: 6572342.
Article2. Kreutz RW, Sanders B. Bilateral coronoid hyperplasia resulting in severe limitation of mandibular movement. Report of a case. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1985; 60:482–484. PMID: 3864110.3. Kraut RA. Bilateral coronoid hyperplasia: report of two cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1985; 43:612–614. PMID: 3859611.
Article4. McLoughlin PM, Hopper C, Bowley NB. Hyperplasia of the mandibular coronoid process: an analysis of 31 cases and a review of the literature. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1995; 53:250–255. PMID: 7861274.5. Rowe NL. Bilateral developmental hyperplasia of the mandibular coronoid process. A report of two cases. Br J Oral Surg. 1963; 1:90–104. PMID: 14089492.6. Sarnat BG, Feigenbaum JA, Krogman WM. Adult monkey coronoid process after resection of trigeminal nerve motor root. Am J Anat. 1977; 150:129–137. PMID: 412408.
Article7. van Hoof RF, Besling WF. Coronoid process enlargement. Br J Oral Surg. 1973; 10:339–348. PMID: 4516118.
Article8. Kai S, Hijiya T, Yamane K, Higuchi Y. Open-mouth locking caused by unilateral elongated coronoid process: report of case. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1997; 55:1305–1308. PMID: 9371124.
Article9. Mulder CH, Kalaykova SI, Gortzak RA. Coronoid process hyperplasia: a systematic review of the literature from 1995. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012; 41:1483–1489. PMID: 22608198.
Article10. Isberg AM, McNamara JA Jr, Carlson DS, Isacsson G. Coronoid process elongation in rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) after experimentally induced mandibular hypomobility. A cephalometric and histologic study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1990; 70:704–710. PMID: 2263326.11. Wenghoefer M, Merkx M, Steiner M, Götz W, Meijer GJ, Bergg SJ. Hyperplasia of the coronoid process. Asian J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006; 18:51–58.
Article12. Costa YM, Porporatti AL, Stuginski-Barbosa J, Cassano DS, Bonjardim LR, Conti PC. Coronoid process hyperplasia: an unusual cause of mandibular hypomobility. Braz Dent J. 2012; 23:252–255. PMID: 22814695.
Article13. Kubota Y, Takenoshita Y, Takamori K, Kanamoto M, Shirasuna K. Levandoski panographic analysis in the diagnosis of hyperplasia of the coronoid process. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1999; 37:409–411. PMID: 10577758.
Article14. Asaumi J, Kawai N, Honda Y, Shigehara H, Wakasa T, Kishi K. Comparison of three-dimensional computed tomography with rapid prototype models in the management of coronoid hyperplasia. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2001; 30:330–335. PMID: 11641732.
Article15. Smyth AG, Wake MJ. Recurrent bilateral coronoid hyperplasia: an unusual case. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1994; 32:100–104. PMID: 8199139.
Article16. Robiony M, Casadei M, Costa F. Minimally invasive surgery for coronoid hyperplasia: endoscopically assisted intraoral coronoidectomy. J Craniofac Surg. 2012; 23:1838–1840. PMID: 23147302.17. Tavassol F, Spalthoff S, Essig H, Bredt M, Gellrich NC, Kokemüller H. Elongated coronoid process: CT-based quantitative analysis of the coronoid process and review of literature. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012; 41:331–338. PMID: 22192388.
Article18. Bronstein SL, Osborne JJ. Mandibular limitation due to bilateral coronoid enlargement: management by surgery and physical therapy. Cranio. 1984-85; 3:58–62. PMID: 6594401.
Article19. Fernández Ferro M, Fernández Sanromán J, Sandoval Gutierrez J, Costas López A, López de Sánchez A, Etayo Pérez A. Treatment of bilateral hyperplasia of the coronoid process of the mandible. Presentation of a case and review of the literature. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2008; 13:E595–E598. PMID: 18758406.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Coronoid Process Hyperplasia: A Rare Case of Restricted Mouth Opening Masquerading as Temporomandibular Disorder
- The diagnosis of coronoid impingement using computed tomography
- Severe trismus due to bilateral coronoid process hyperplasia in growth hormone therapy patient: a case report
- Coronoid impingement syndrome: literature review and clinical management
- Trismus Due to Bilateral Coronoid Hyperplasia