Brain Neurorehabil.
2014 Sep;7(2):147-150. 10.12786/bn.2014.7.2.147.
Trial of Metoclopramide on Oro-facial Dyskinesia Following Traumatic Brain Injury: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Severance Hospital, Research Institute of Rehabilitation Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea. rekhs@nhimc.or.kr
- KMID: 1797650
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12786/bn.2014.7.2.147
Abstract
- Oro-facial dyskinesia is characterized by involuntary repetitive movements of the tongue, lip, or jaw, which is known to be derived by variable causes. Pre- and post-synaptic dopamine receptor abnormalities by degenerative changes in the brain seem to be the key pathophysiology, but the exact mechanism still remained to be unknown. Metoclopramide can pass the blood-brain barrier, which is known for a selective presynaptic autoregulating dopamine D2 receptor antagonist in the brain, and is usually prescribed for dyspepsia, nausea and vomiting. In particular, it was also reported to improve the symptoms of diurnal bruxism after brain injury. With reviewing some of literatures, we present a case of 27 year old man with traumatic brain injury who showed improvement of oro-facial dyskinesia after taking oral metoclopramide.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
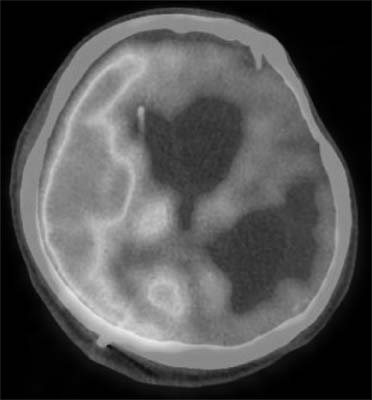
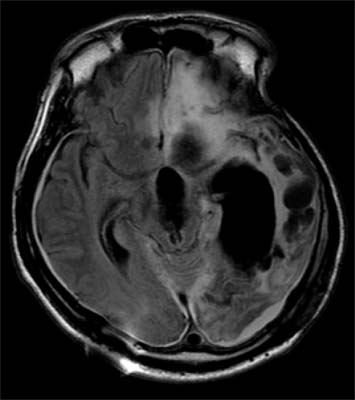
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Seven Cases of Successful Remission after Trial of Metoclopramide on Orofacial Dyskinesia of Stroke Patients: a Case Series
Myeong Hwan Bang, Jiseong Hong, Hyoung Seop Kim
Brain Neurorehabil. 2018;11(1):. doi: 10.12786/bn.2018.11.e3.
Reference
-
1. Blanchet PJ, Rompre PH, Lavigne GJ, Lamarche C. Oral dyskinesia: a clinical overview. Int J Prosthodont. 2005; 18:10–19.2. Koller WC. Edentulous orodyskinesia. Ann Neurol. 1983; 13:97–99.
Article3. Weiner WJ, Klawans HL Jr. lingual-facial-buccal movements in the elderly. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1973; 21:314–317.4. Bedard P, Boucher R, Di Paolo T, Labrie F. Biphasic effect of estradiol and domperidone on lingual dyskinesia in monkeys. Exp Neurol. 1983; 82:172–182.5. Fukasawa T, Takahashi M, Otani K. A successful clonazepam treatment without tolerance in a patient with spontaneous oral dyskinesia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2001; 25:1477–1480.
Article6. Rotrosen J, Adler L, Lohr J, Edson R, Lavori P. Antioxidant treatment of tardive dyskinesia. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 1996; 55:77–81.
Article7. Rana AQ, Chaudry ZM, Blanchet PJ. New and emerging treatments for symptomatic tardive dyskinesia. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2013; 7:1329–1340.
Article8. Fudge RC, Thailer SA, Alpert M, Intrator J, Sison CE. The effects of electromyographic feedback training on suppression of the oral-lingual movements associated with tardive dyskinesia. Biofeedback Self Regul. 1991; 16:117–129.
Article9. Narabayashi H, Yokochi F, Nakajima Y. Idiopathic oromandibular dyskinesia treated by Vo complex microstereotactic thalamotomy. Appl Neurophysiol. 1985; 48:309–314.
Article10. Sutcher HD, Underwood RB, Beatty RA, Sugar O. Orofacial dyskinesia. A dental dimension. JAMA. 1971; 216:1459–1463.
Article11. Clark GT, Ram S. Four oral motor disorders: bruxism, dystonia, dyskinesia and drug-induced dystonic extrapyramidal reactions. Dent Clin North Am. 2007; 51:225–243. vii–ix.
Article12. Chen WH, Lu YC, Lui CC, Liu JS. A proposed mechanism for diurnal/nocturnal bruxism: hypersensitivity of presynaptic dopamine receptors in the frontal lobe. J Clin Neurosci. 2005; 12:161–163.
Article13. Yi HS, Kim HS, Seo MR. Trial of oral metoclopramide on diurnal bruxism of brain injury. Ann Rehabil Med. 2013; 37:871–874.
Article14. Seo MW. Four cases of senile oro-facial dyskinesia and discussion on the pathophysiology. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 1998; 16(4):458–466.15. Kobayashi RM. Orofacial dyskinesia: Clinical features, mechanisms and drug therapy. West J Med. 1976; 125:277–288.16. Rosengarten H, Schweitzer J, Friedhoff A. Selective dopamine D2 receptor reduction enhances AD1 mediated oral dyskinesia in rats. Life Sci. 1986; 39:29–35.17. Waddington JL, O'Sullivan GJ, Tomiyama K. Regulation of orofacial movement: dopamine receptor mechanisms and mutant models. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2011; 97:39–36.
Article18. Tonini M, Cipollina L, Poluzzi E, Crema F, Corazza G, De Ponti F. Clinical implications of enteric and central D2 receptor blockade by antidopaminergic gastrointestinal prokinetics. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004; 19:379–390.
Article19. Metoclopramide-Containing Drugs. 2009. 02. 26. http://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch/SafetyInformation/SafetyAlertsforHumaNMedicalProducts/ucm106942.htm.20. Rao AS, Camilleri M. Review article: metoclopramide and tardive dyskinesia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010; 31:11–19.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Seven Cases of Successful Remission after Trial of Metoclopramide on Orofacial Dyskinesia of Stroke Patients: a Case Series
- Four cases of Senile Oro-facial Dyskinesia and Discussion on the pathophysiology
- Trial of Oral Metoclopramide on Diurnal Bruxism of Brain Injury
- Delayed Bilateral Facial Nerve Palsy Manifesting 3 Months after Traumatic Brain Injury: A Case Report
- The Relationship of the Facial Injury Location and the Traumatic Brain Hemorrhage