J Korean Med Sci.
2014 Jun;29(6):818-824. 10.3346/jkms.2014.29.6.818.
Diffuse Metastasis to the Thyroid: Unique Ultrasonographic Finding and Clinical Correlation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. drkang@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 1796945
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2014.29.6.818
Abstract
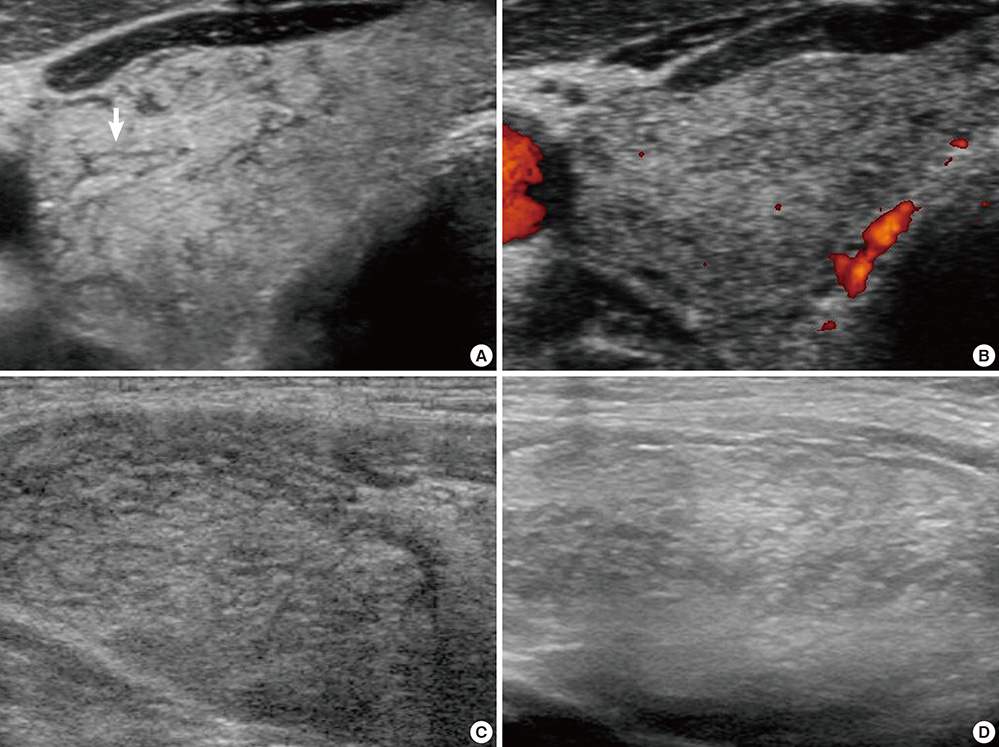
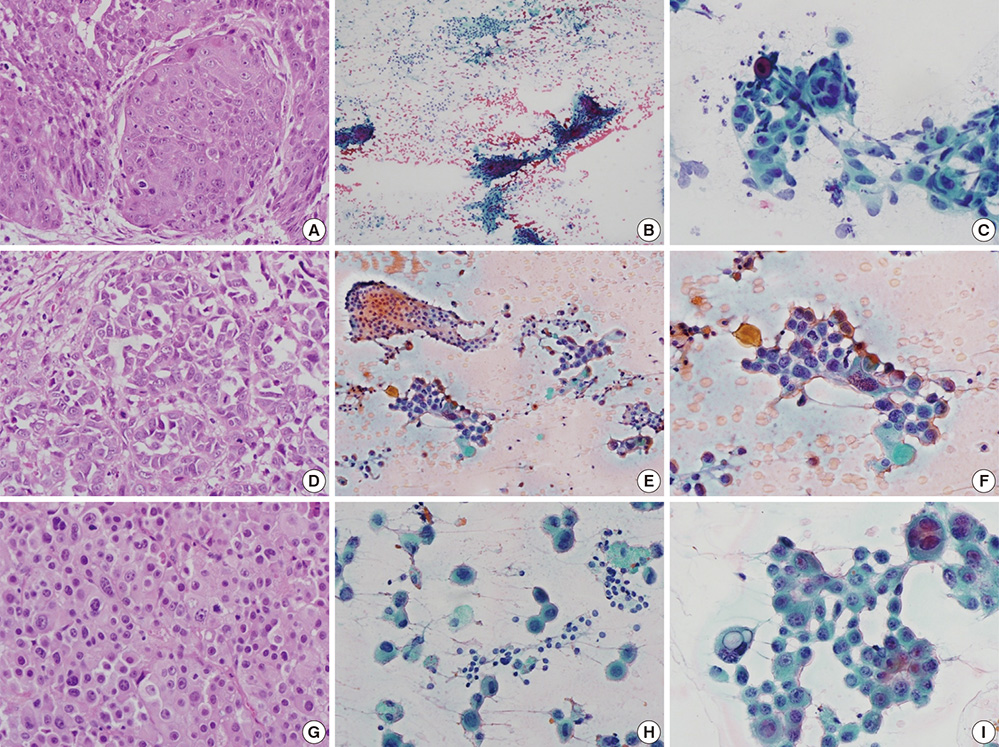
- Cases of metastases to the thyroid gland seem to be increasing in recent years. The clinical and ultrasonographic findings of diffuse metastases have been sparsely reported. Thirteen cases of diffuse metastases to the thyroid gland were documented by thyroid ultrasonography-guided fine needle aspiration cytology between 2004 and 2013. We retrospectively reviewed the patients with diffuse thyroid metastases. The most common primary site was the lung (n=9), followed by unknown origin cancers (n=2), cholangiocarcinoma (n=1), and penile cancer (n=1). Eleven patients were incidentally found to have thyroid metastases via surveillance or staging FDG-PET. Other 2 patients were diagnosed during work-up for hypothyroidism and palpable cervical lymph nodes. On ultrasonography, the echogenicity of the enlarged thyroid gland was heterogeneously hypoechoic or isoechoic, and reticular pattern internal hypoechoic lines were observed without increased vascularity found by power Doppler ultrasonography (3 right lobe, 2 left lobe, and 8 both lobes). In the 8 patients who had involvement of both lobes, 3 had hypothyroidism. In conclusion, ultrasonographic finding of diffuse metastasis is a diffusely enlarged heterogeneous thyroid with reticular pattern internal hypoechoic lines. Thyroid function testing should be performed in all patients with diffuse thyroid metastases, especially those with bilateral lobe involvement.
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Bile Duct Neoplasms/pathology
Biopsy, Fine-Needle
Cholangiocarcinoma/pathology
Female
Fluorodeoxyglucose F18/diagnostic use
Humans
Hypothyroidism/complications
Lung Neoplasms/pathology
Male
Middle Aged
Penile Neoplasms/pathology
Positron-Emission Tomography
Radiopharmaceuticals/diagnostic use
Thyroid Function Tests
Thyroid Gland/pathology/*ultrasonography
Thyroid Neoplasms/pathology/secondary/*ultrasonography
Fluorodeoxyglucose F18
Radiopharmaceuticals
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nakhjavani MK, Gharib H, Goellner JR, van Heerden JA. Metastasis to the thyroid gland: a report of 43 cases. Cancer. 1997; 79:574–578.2. Calzolari F, Sartori PV, Talarico C, Parmeggiani D, Beretta E, Pezzullo L, Bovo G, Sperlongano P, Monacelli M, Lucchini R, et al. Surgical treatment of intrathyroid metastases: preliminary results of a multicentric study. Anticancer Res. 2008; 28:2885–2888.3. Cichoń S, Anielski R, Konturek A, Barczyński M, Cichoń W. Metastases to the thyroid gland: seventeen cases operated on in a single clinical center. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2006; 391:581–587.4. Wychulis AR, Beahrs OH, Woolner LB. Metastasis of carcinoma to the thyroid gland. Ann Surg. 1964; 160:169–177.5. Lam KY, Lo CY. Metastatic tumors of the thyroid gland: a study of 79 cases in Chinese patients. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1998; 122:37–41.6. Papi G, Fadda G, Corsello SM, Corrado S, Rossi ED, Radighieri E, Miraglia A, Carani C, Pontecorvi A. Metastases to the thyroid gland: prevalence, clinicopathological aspects and prognosis: a 10-year experience. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2007; 66:565–571.7. Wood K, Vini L, Harmer C. Metastases to the thyroid gland: the Royal Marsden experience. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2004; 30:583–588.8. Shimaoka K, Sokal JE, Pickren JW. Metastatic neoplasms in the thyroid gland: pathological and clinical findings. Cancer. 1962; 15:557–565.9. Czech JM, Lichtor TR, Carney JA, van Heerden JA. Neoplasms metastatic to the thyroid gland. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1982; 155:503–505.10. Smith SA, Gharib H, Goellner JR. Fine-needle aspiration. Usefulness for diagnosis and management of metastatic carcinoma to the thyroid. Arch Intern Med. 1987; 147:311–312.11. Watts NB. Carcinoma metastatic to the thyroid: prevalence and diagnosis by fine-needle aspiration cytology. Am J Med Sci. 1987; 293:13–17.12. Chung SY, Kim EK, Kim JH, Oh KK, Kim DJ, Lee YH, An HJ, Kim JS. Sonographic findings of metastatic disease to the thyroid. Yonsei Med J. 2001; 42:411–417.13. Gkountouvas A, Chatjimarkou F, Sevastiadou M, Ntoula E, Georgiadis P, Kaldrimidis P. Diffuse goiter and severe hypothyroidism due to metastasis to the thyroid. Case Rep Oncol. 2010; 3:439–444.14. Youn JC, Rhee Y, Park SY, Kim WH, Kim SJ, Chung HC, Hong SW, Lim SK. Severe hypothyroidism induced by thyroid metastasis of colon adenocarcinoma: a case report and review of the literature. Endocr J. 2006; 53:339–343.15. Miyakawa M, Sato K, Hasegawa M, Nagai A, Sawada T, Tsushima T, Takano K. Severe thyrotoxicosis induced by thyroid metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma: a case report and review of the literature. Thyroid. 2001; 11:883–888.16. Hayashi N, Tamaki N, Konishi J, Yonekura Y, Senda M, Kasagi K, Yamamoto K, Iida Y, Misaki T, Endo K, et al. Sonography of Hashimoto's thyroiditis. J Clin Ultrasound. 1986; 14:123–126.17. Yeh HC, Futterweit W, Gilbert P. Micronodulation: ultrasonographic sign of Hashimoto thyroiditis. J Ultrasound Med. 1996; 15:813–819.18. Chung AY, Tran TB, Brumund KT, Weisman RA, Bouvet M. Metastases to the thyroid: a review of the literature from the last decade. Thyroid. 2012; 22:258–268.19. Berge T, Lundberg S. Cancer in Malmö 1958-1969. An autopsy study. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Suppl. 1977; (260):1–235.20. De Ridder M, Sermeus AB, Urbain D, Storme GA. Metastases to the thyroid gland-a report of six cases. Eur J Intern Med. 2003; 14:377–379.21. Papi G, Corrado S, Scaltriti L, Carapezzi C, Ezzat S. Metastasis of urothelial sarcomatoid carcinoma to a toxic multinodular goiter. Endocr Pathol. 2005; 16:153–156.22. Eriksson M, Ajmani SK, Mallette LE. Hyperthyroidism from thyroid metastasis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. JAMA. 1977; 238:1276–1278.23. Chen H, Nicol TL, Udelsman R. Clinically significant, isolated metastatic disease to the thyroid gland. World J Surg. 1999; 23:177–181.24. Rosen IB, Walfish PG, Bain J, Bedard YC. Secondary malignancy of the thyroid gland and its management. Ann Surg Oncol. 1995; 2:252–256.25. Gault EW, Leung TH, Thomas DP. Clear cell renal carcinoma masquerading as thyroid enlargement. J Pathol. 1974; 113:21–25.26. Madore P, Lan S. Solitary thyroid metastasis from clear-cell renal carcinoma. Can Med Assoc J. 1975; 112:719. 721.27. Saito Y, Sugitani I, Toda K, Yamada K, Fujimoto Y. Metastatic thyroid tumors: ultrasonographic features, prognostic factors and outcomes in 29 cases. Surg Today. 2014; 44:55–61.28. Yokoe T, Iino Y, Takei H, Horiguchi J, Koibuchi Y, Maemura M, Ohwada S, Morishita Y. Relationship between thyroid-pituitary function and response to therapy in patients with recurrent breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 1996; 16:2069–2072.29. Cristofanilli M, Yamamura Y, Kau SW, Bevers T, Strom S, Patangan M, Hsu L, Krishnamurthy S, Theriault RL, Hortobagyi GN. Thyroid hormone and breast carcinoma: primary hypothyroidism is associated with a reduced incidence of primary breast carcinoma. Cancer. 2005; 103:1122–1128.30. Carcangiu ML, Steeper T, Zampi G, Rosai J. Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: a study of 70 cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1985; 83:135–158.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Carcinoma with Benign Ultrasonographic Findings in the Thyroid Gland
- Ultrasound Findings of Diffuse Sclerosing Subtype of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
- Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma of a Diffuse Sclerosing Variant: Ultrasonographic Monitoring from a Normal Thyroid Gland to Mass Formation
- Association of BRAF(V600E) Mutation with Poor Clinical Prognostic Factors and Ultrasonographic Findings in Cases of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
- Risk of Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: Predictive Finding of Ultrasonography