Korean J Urol.
2014 Aug;55(8):527-532. 10.4111/kju.2014.55.8.527.
Effect of Histological Inflammation on Total and Free Serum Prostate-Specific Antigen Values in Patients Without Clinically Detectable Prostate Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Clinical Department of Urology, "Sestre milosrdnice" University Hospital Center, Zagreb, Croatia. goran.stimac2@zg.t-com.hr
- 2"Ljudevit Jurak" Department of Pathology, "Sestre milosrdnice" University Hospital Center, Zagreb, Croatia.
- KMID: 1794587
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2014.55.8.527
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We are often confronted with patients in the "gray zone" (prostate-specific antigen [PSA]<10 ng/mL) whose biopsies reveal no malignancy but only inflammation. We investigated the relationship between histological inflammation and total PSA (tPSA), free PSA (fPSA), and percentage of free PSA (f/tPSA) levels in patients without prostate cancer (PC).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
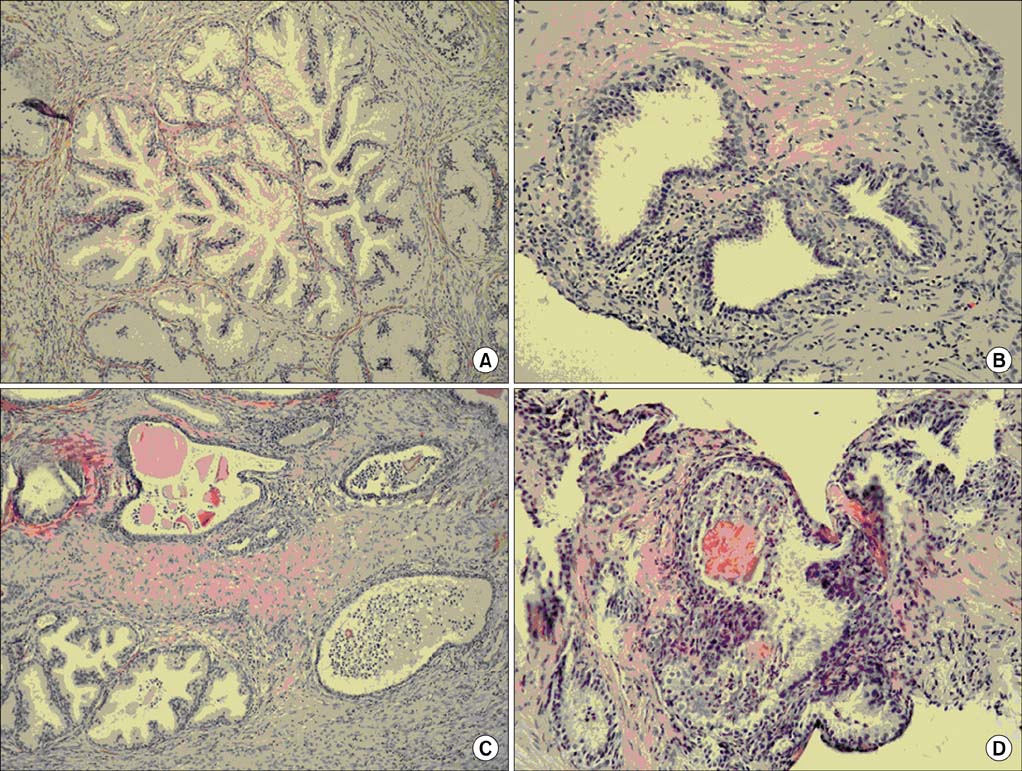
We studied 106 men with tPSA<10 ng/mL who had undergone biopsy that was negative for PC and who had no clinical prostatitis. Inflammation observed at biopsies was scored for inflammation type in each biopsy core by use of a four-point scale and was then correlated with tPSA, fPSA, and f/tPSA.
RESULTS
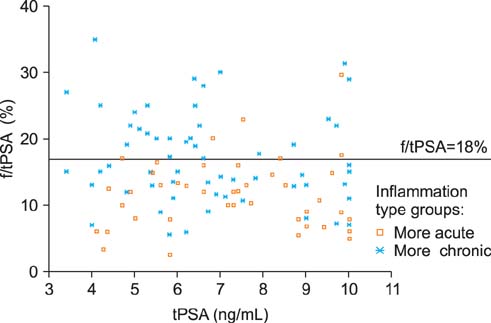
Different patterns of inflammation were found in each set of biopsies. Regression factor analysis was used to form two groups according to inflammation type: more chronic and more acute. Median tPSA, fPSA, and f/tPSA levels in the more chronic and more acute inflammation groups were 6.4 ng/mL, 1.09 ng/mL, and 15%, and 7.3 ng/mL, 0.79 ng/mL, and l2%, respectively. A significant difference was found in fPSA (p=0.003) and f/tPSA (p<0.001), whereas the difference in tPSA was not significant (p=0.200). Total PSA correlated with fPSA (r=0.4, p<0.001) but not with inflammation type (r=0.12, p>0.010). A correlation existed between inflammation type and fPSA (r=-0.31, p=0.001) and f/tPSA (r=-0.43, p<0.001) in that the fPSA and f/tPSA were lower in the group with more acute inflammation.
CONCLUSIONS
Subclinical inflammation has a significant influence on fPSA in patients with tPSA<10 ng/mL but without PC or clinical prostatitis. Subclinical inflammation is not characterized by elevated tPSA alone but also by a decreased fPSA, a tendency similar to that in PC.
MeSH Terms
-
Acute Disease
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Asymptomatic Diseases
Biopsy, Large-Core Needle
Chronic Disease
Diagnosis, Differential
Humans
Kallikreins/*blood
Male
Middle Aged
Prostate/pathology
Prostate-Specific Antigen/*blood
Prostatic Neoplasms/blood/diagnosis
Prostatitis/*blood/diagnosis/pathology
Kallikreins
Prostate-Specific Antigen
Figure
Reference
-
1. Oesterling JE. Prostate specific antigen: a critical assessment of the most useful tumor marker for adenocarcinoma of the prostate. J Urol. 1991; 145:907–923.2. Catalona WJ, Richie JP, Ahmann FR, Hudson MA, Scardino PT, Flanigan RC, et al. Comparison of digital rectal examination and serum prostate specific antigen in the early detection of prostate cancer: results of a multicenter clinical trial of 6,630 men. J Urol. 1994; 151:1283–1290.3. Benson MC, Whang IS, Olsson CA, McMahon DJ, Cooner WH. The use of prostate specific antigen density to enhance the predictive value of intermediate levels of serum prostate specific antigen. J Urol. 1992; 147(3 Pt 2):817–821.4. Dalton DL. Elevated serum prostate-specific antigen due to acute bacterial prostatitis. Urology. 1989; 33:465.5. Socher S, Oleary MP, Rrichie JP, Loughlin KR, Kumar S, Descotes JL. Prevalence of prostatitis in men undergoing biopsy for elevated PSA or abnormal DRE exam. J Urol. 1996; 155:457.6. Brawer MK, Rennels MA, Nagle RB, Schifman R, Gaines JA. Serum prostate-specific antigen and prostate pathology in men having simple prostatectomy. Am J Clin Pathol. 1989; 92:760–764.7. Pansadoro V, Emiliozzi P, Defidio L, Scarpone P, Sabatini G, Brisciani A, et al. Prostate-specific antigen and prostatitis in men under fifty. Eur Urol. 1996; 30:24–27.8. Kwak C, Ku JH, Kim T, Park DW, Choi KY, Lee E, et al. Effect of subclinical prostatic inflammation on serum PSA levels in men with clinically undetectable prostate cancer. Urology. 2003; 62:854–859.9. Nickel JC, Downey J, Young I, Boag S. Asymptomatic inflammation and/or infection in benign prostatic hyperplasia. BJU Int. 1999; 84:976–981.10. Ornstein DK, Smith DS, Humphrey PA, Catalona WJ. The effect of prostate volume, age, total prostate specific antigen level and acute inflammation on the percentage of free serum prostate specific antigen levels in men without clinically detectable prostate cancer. J Urol. 1998; 159:1234–1237.11. Morote J, Lopez M, Encabo G, de Torres IM. Effect of inflammation and benign prostatic enlargement on total and percent free serum prostatic specific antigen. Eur Urol. 2000; 37:537–540.12. Jung K, Meyer A, Lein M, Rudolph B, Schnorr D, Loening SA. Ratio of free-to-total prostate specific antigen in serum cannot distinguish patients with prostate cancer from those with chronic inflammation of the prostate. J Urol. 1998; 159:1595–1598.13. Meyer A, Jung K, Lein M, Rudolph B, Schnorr D, Loening SA. Factors influencing the ratio of free to total prostate-specific antigen in serum. Int J Cancer. 1997; 74:630–636.14. Catalona WJ. Clinical utility of measurements of free and total prostate-specific antigen (PSA): a review. Prostate Suppl. 1996; 7:64–69.15. Dalton DL. Elevated serum prostate-specific antigen due to acute bacterial prostatitis. Urology. 1989; 33:465.16. Yamamoto M, Hibi H, Myake K. Prostate specific antigen levels in acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis. Hinyokika Kiyo. 1993; 39:445–449.17. Okada K, Kojima M, Naya Y, Kamoi K, Yokoyama K, Takamatsu T, et al. Correlation of histological inflammation in needle biopsy specimens with serum prostate-specific antigen levels in men with negative biopsy for prostate cancer. Urology. 2000; 55:892–898.18. Lloyd SN, Collins GN, McKelvie GB, Hehir M, Rogers AC. Predicted and actual change in serum PSA following prostatectomy for BPH. Urology. 1994; 43:472–479.19. Scattoni V, Raber M, Montorsi F, Da Pozzo L, Brausi M, Calori G, et al. Percent of free serum prostate-specific antigen and histological findings in patients undergoing open prostatectomy for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Eur Urol. 1999; 36:621–630.20. Hasui Y, Marutsuka K, Asada Y, Ide H, Nishi S, Osada Y. Relationship between serum prostate specific antigen and histological prostatitis in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Prostate. 1994; 25:91–96.21. Jung K, Stephan C, Lein M, Henke W, Schnorr D, Brux B, et al. Analytical performance and clinical validity of two free prostate-specific antigen assays compared. Clin Chem. 1996; 42:1026–1033.22. Minardi D, Galosi AB, Recchioni A, Giammarco L, Polito M, Muzzonigro G. Diagnostic accuracy of percent free prostate-specific antigen in prostatic pathology and its usefulness in monitoring prostatic cancer patients. Urol Int. 2001; 67:272–282.23. Irani J, Levillain P, Goujon JM, Bon D, Dore B, Aubert J. Inflammation in benign prostatic hyperplasia: correlation with prostate specific antigen value. J Urol. 1997; 157:1301–1303.24. Neal DE Jr, Clejan S, Sarma D, Moon TD. Prostate specific antigen and prostatitis. I. Effect of prostatitis on serum PSA in the human and nonhuman primate. Prostate. 1992; 20:105–111.25. Nadler RB, Humphrey PA, Smith DS, Catalona WJ, Ratliff TL. Effect of inflammation and benign prostatic hyperplasia on elevated serum prostate specific antigen levels. J Urol. 1995; 154(2 Pt 1):407–413.26. Bjork T, Bjartell A, Abrahamsson PA, Hulkko S, di Sant'Agnese A, Lilja H. Alpha 1-antichymotrypsin production in PSA-producing cells is common in prostate cancer but rare in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology. 1994; 43:427–434.27. Zackrisson B, Ulleryd P, Aus G, Lilja H, Sandberg T, Hugosson J. Evolution of free, complexed, and total serum prostate-specific antigen and their ratios during 1 year of follow-up of men with febrile urinary tract infection. Urology. 2003; 62:278–281.28. Bozeman CB, Carver BS, Eastham JA, Venable DD. Treatment of chronic prostatitis lowers serum prostate specific antigen. J Urol. 2002; 167:1723–1726.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Factors Influencing the Percentage of Free Serum Prostate Specific Antigen Levels in Men without Clinically Detectable Prostate Cance
- Change of serum prostate specific antigen values after radiation therapy in prostate cancer
- The Diagnostic Value of Prostate-specific Antigen and the of Routine Laboratory Examination for Early Detection
- The Effect of Age, Prostate volume and Total PSA on Percent free PSA in Men with Benign Prostatic Disease
- Effects of digital rectal examination and transurethral resection of the prostate on serum prostate Specific antigen and acid phosphatase levels