Korean J Urol.
2014 Jul;55(7):482-486. 10.4111/kju.2014.55.7.482.
Relationship Between Uncommon Computed Tomography Findings and Clinical Aspects in Patients With Acute Pyelonephritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea. urojun@schmc.ac.kr
- KMID: 1794578
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2014.55.7.482
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Computed tomography (CT) has become popular in the diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis (APN) and its related complications in adults. The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between uncommon CT findings and clinical and laboratory data in patients with APN.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From July 2009 to July 2012, CT findings and clinical data were collected from 125 female patients with APN. The six uncommon CT findings (excluding a wedge-shaped area of hypoperfusion in the renal parenchyma) studied were perirenal fat infiltration, ureteral wall edema, renal abscess formation, pelvic ascites, periportal edema, and renal scarring. The clinical parameters analyzed were the age and body mass index of the patients as well as the degree and duration of fever. Laboratory parameters related to inflammation and infection included white blood cell count, C-reactive protein (CRP) level, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, pyuria, and bacteriuria.
RESULTS
The most common CT finding was perirenal fat infiltration (69 cases, 55%). A longer duration of fever, higher CRP level, and grade of pyuria were related with perirenal fat infiltration (p=0.010, p=0.003, and p=0.049, respectively). The CRP level was significantly higher in patients with renal abscess and ureteral wall edema (p=0.005 and p=0.015, respectively).
CONCLUSIONS
The uncommon CT findings that were related to aggravated clinical and laboratory parameters of APN patients were perirenal fat infiltration, ureteral wall edema, and renal abscess formation. The inflammatory reaction and tissue destruction may be more aggressive in patients with these CT findings.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Abscess/etiology/radiography
Acute Disease
Adipose Tissue/pathology/radiography
Adult
Edema/etiology/radiography
Female
Humans
Kidney Diseases/radiography
Middle Aged
Pyelonephritis/complications/pathology/*radiography
Retrospective Studies
Tomography, X-Ray Computed/methods
Ureteral Diseases/etiology/radiography
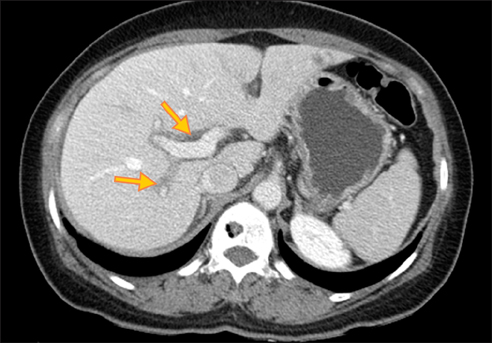
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Clinical Usefulness of Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography in Patients with Non-Obstructive Acute Pyleonephritis
In O Sun, Ji Hye Lim, Ju Hwan Oh, A Young Cho, Beum Jin Kim, Kwang Young Lee, Mi Sook Lee
Kosin Med J. 2020;35(1):38-46. doi: 10.7180/kmj.2020.35.1.38.
Reference
-
1. Jung YH, Cho IR, Lee SE, Lee KC, Kim JG, Jeon JS, et al. Comparative analysis of clinical parameters in acute pyelonephritis. Korean J Urol. 2007; 48:29–34.2. Ki M, Park T, Choi B, Foxman B. The epidemiology of acute pyelonephritis in South Korea, 1997-1999. Am J Epidemiol. 2004; 160:985–993.3. Stunell H, Buckley O, Feeney J, Geoghegan T, Browne RF, Torreggiani WC. Imaging of acute pyelonephritis in the adult. Eur Radiol. 2007; 17:1820–1828.4. Goldman SM. Acute and chronic urinary infection: present concepts and controversies. Urol Radiol. 1988; 10:17–24.5. Goldman SM, Fishman EK. Upper urinary tract infection: the current role of CT, ultrasound, and MRI. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 1991; 12:335–360.6. Rabushka LS, Fishman EK, Goldman SM. Pictorial review: computed tomography of renal inflammatory disease. Urology. 1994; 44:473–480.7. Soulen MC, Fishman EK, Goldman SM, Gatewood OM. Bacterial renal infection: role of CT. Radiology. 1989; 171:703–707.8. Gold RP, McClennan BL, Rottenberg RR. CT appearance of acute inflammatory disease of the renal interstitium. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1983; 141:343–349.9. Talner LB, Davidson AJ, Lebowitz RL, Dalla Palma L, Goldman SM. Acute pyelonephritis: can we agree on terminology? Radiology. 1994; 192:297–305.10. Tsugaya M, Hirao N, Sakagami H, Ohtaguro K, Washida H. Renal cortical scarring in acute pyelonephritis. Br J Urol. 1992; 69:245–249.11. Scholes D, Hooton TM, Roberts PL, Gupta K, Stapleton AE, Stamm WE. Risk factors associated with acute pyelonephritis in healthy women. Ann Intern Med. 2005; 142:20–27.12. Craig WD, Wagner BJ, Travis MD. Pyelonephritis: radiologic-pathologic review. Radiographics. 2008; 28:255–277.13. June CH, Browning MD, Smith LP, Wenzel DJ, Pyatt RS, Checchio LM, et al. Ultrasonography and computed tomography in severe urinary tract infection. Arch Intern Med. 1985; 145:841–845.14. Vourganti S, Agarwal PK, Bodner DR, Dogra VS. Ultrasonographic evaluation of renal infections. Radiol Clin North Am. 2006; 44:763–775.15. Kim SH, Kim YW, Lee HJ. Serious acute pyelonephritis: a predictive score for evaluation of deterioration of treatment based on clinical and radiologic findings using CT. Acta Radiol. 2012; 53:233–238.16. Abshire TC. The anemia of inflammation: a common cause of childhood anemia. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1996; 43:623–637.17. Shin TS, Kim TH, Chang IH, Myung SC, Kim KD. The clinical significance of serum and urine cytokines in patients with acute uncomplicated pyelonephritis. Korean J Urol. 2009; 50:33–38.18. Schaeffer AJ, Schaeffer EM. Infections of the urinary tract. In : Wein AJ, Kavoussi LR, Novick AC, Partin AW, Peters CA, editors. Campbell-Walsh urology. 10th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier;2012. p. 46–55.19. Zissin R, Osadchy A, Gayer G, Kitay-Cohen Y. Extrarenal manifestations of severe acute pyelonephritis: CT findings in 21 cases. Emerg Radiol. 2006; 13:73–77.20. Vollmann R, Schaffler GJ, Spreizer C, Quehenberger F, Schoellnast H. Clinical significance of periportal tracking as an extrarenal manifestation of acute pyelonephritis. Abdom Imaging. 2011; 36:557–560.21. Zissin R, Kots E, Rachmani R, Hadari R, Shapiro-Feinberg M. Hepatic periportal tracking associated with severe acute pyelonephritis. Abdom Imaging. 2000; 25:251–254.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The clinical features and relationship with sepsis according to the number of computed tomography findings in patients with acute pyelonephritis with urolithiasis
- Altered Mentality Patient with Emphysematous Pyelonephritis Disclosed by Abdominal Computed Tomography
- The Renal Scan in Acute Pyelonephritis
- Analysis of Kidney Computed Tomographic Findings in Patients with Acute Pyelonephritis and Septic Shock
- Two cases of subcapsular renal hematoma as a complication of acute pyelonephritis