Yonsei Med J.
2008 Aug;49(4):672-675. 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.4.672.
A Spindle Cell Predominant Pancreatic Solid-pseudopapillary Tumor
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Dankook University Hospital, Cheonan, Chungnam, Korea. jaihyang@yahoo.co.kr
- KMID: 1793207
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2008.49.4.672
Abstract
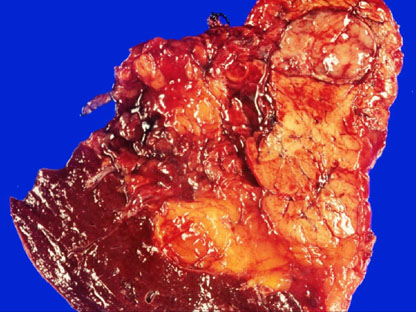
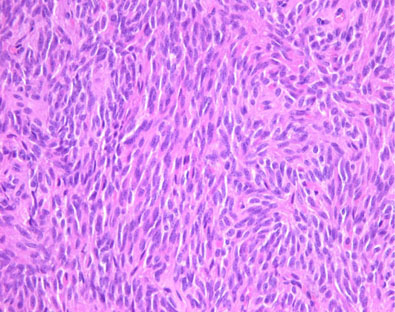
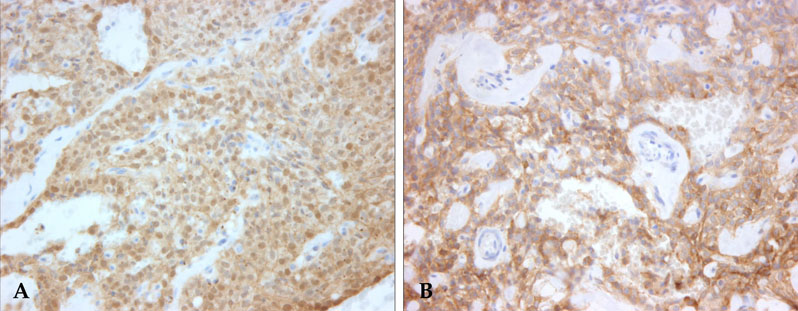
- A hitherto unrecognized variant of solid-pseudopapillary tumor (SPT) of the pancreas is reported. The tumor presented in the pancreatic tail of a 44-year-old female patient. It was a well-defined, solid nodule measuring 25mm in diameter, with homogenous tan gray cut surface. Histologically, the neoplasm was mostly composed of sheets of spindle cells. No cellular atypia and mitosis was identified. The periphery of the tumor showed typical feature of SPT. Immunohistochemically, the tumor cells were positive for vimentin, CD10, CD56, beta-catenin, and alpha;1-antichymotrypsin, but negative for cytokeratin, chromogranin, synaptophysin and S-100 protein. Ultrastructurally, the tumor showed a few acinar spaces with microvilli between tumor cells. This case is peculiar in that the tumor did not show gross cystic change and predominantly consists of spindle shaped tumor cells, so may cause difficult diagnostic problem.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Solcia E, Capella C, Kloppel G. Rosai J, Sobin LH, editors. Solid-pseudopapillary tumor. Tumors of the exocrine pancreas. Atlas of tumor pathology. Tumors of the pancreas. 1997. 3rd ed. Washington, D.C.: Armed Forces Institute of Pathology;120–128.2. Klimstra DS, Wenig BM, Heffess CS. Solid-pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas: a typically cystic carcinoma of low malignant potential. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2000. 17:66–80.3. Papavramidis T, Papavramidis S. Solid pseudopapillary tumors of the pancreas: review of 718 patients reported in English literature. J Am Coll Surg. 2005. 200:965–972.
Article4. Madan AK, Weldon CB, Long WP, Johnson D, Raafat A. Solid and papillary epithelial neoplasm of the pancreas. J Surg Oncol. 2004. 85:193–198.
Article5. Notohara K, Hamazaki S, Tsukayama C, Nakamoto S, Kawabata K, Mizobuchi K, et al. Solid-pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas: immunohistochemical localization of neuroendocrine markers and CD10. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000. 24:1361–1371.6. Santini D, Poli F, Lega S. Solid-papillary tumors of the pancreas: histopathology. JOP. 2006. 7:131–136.7. Weiss SW, Goldbrum JR. Strauss M, Gery L, editors. Benign tumors of peripheral nerves. Soft tissue tumors. 2001. 4th ed. St. Louis: Mosby;1146–1160.8. Weiss SW, Goldbrum JR. Strauss M, Gery L, editors. Benign fibrohistiocytic tumors. Soft tissue tumors. 2001. 4th ed. St. Louis: Mosby;441–455.9. Solcia E, Capella C, Kloppel G. Rosai J, Sobin LH, editors. Acinar cell carcinoma. Tumors of the exocrine pancreas. Atlas of tumor pathology. Tumors of the pancreas. 1997. 3rd ed. Washington, D.C.: Armed Forces Institute of Pathology;103–112.10. Tanaka Y, Notohara K, Kato K, Ijiri R, Nishimata S, Miyake T, et al. Usefulness of beta-catenin immunostaining for the differential diagnosis of solidpseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas. Am J Surg Pathol. 2002. 26:818–820.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Solid Pseudopapillary Tumor of the Pancreas in Child: A Case Report
- The Growth of an Extrapancreatic Solid Pseudopapillary Tumor from the Greater Omentum: A Case Report
- Solid pseudopapillary tumor with hepatic metastasis
- A case of a solid pseudopapillary tumor in a male child
- A Case of Solid Pseudopapillary Tumor of the Pancreas Presenting as a Submucosal Tumor with Hemorrhage