J Korean Surg Soc.
2011 Dec;81(Suppl 1):S55-S58. 10.4174/jkss.2011.81.Suppl1.S55.
Solid pseudopapillary tumor with hepatic metastasis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, St. Vincent's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. wonys@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, St. Vincent's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, St. Vincent's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 1445787
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2011.81.Suppl1.S55
Abstract
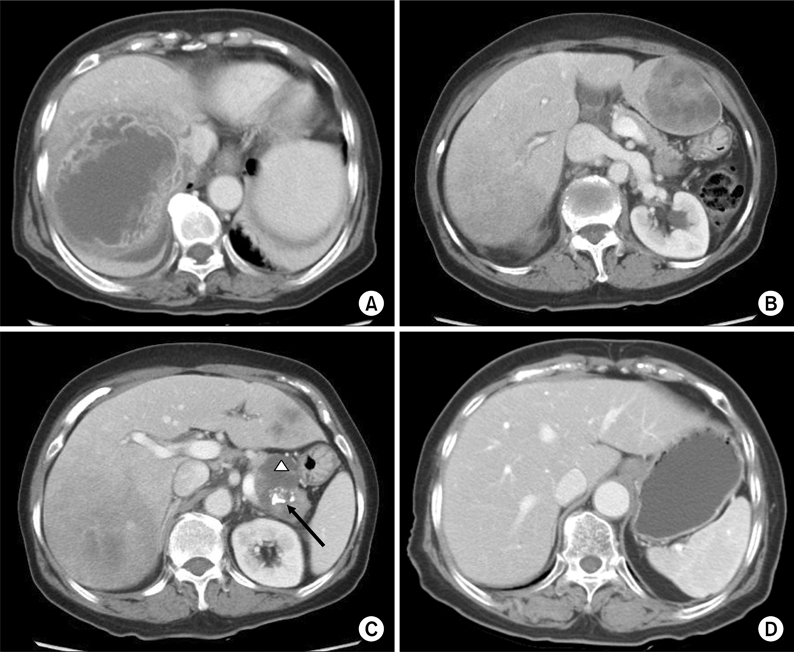
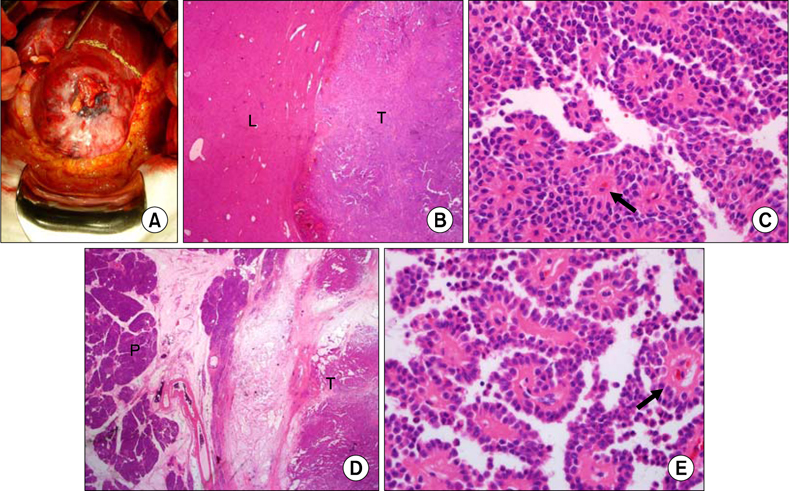
- Solid pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas is a rare tumor that affects young females with low malignant potential and good prognosis with more than 90% survival at 5 years. Metastasis is very rare. We report the case of a 74-year-old female who had pancreatic solid-pseudopapillary tumor and synchronous hepatic metastasis.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kloppel G, Solcia E, Longnecker DS, Capella C, Sobin LH. Histological typing of tumours of the exocrine pancreas. 1996. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.2. Mao C, Guvendi M, Domenico DR, Kim K, Thomford NR, Howard JM. Papillary cystic and solid tumors of the pancreas: a pancreatic embryonic tumor? Studies of three cases and cumulative review of the world's literature. Surgery. 1995. 118:821–828.3. Madan AK, Weldon CB, Long WP, Johnson D, Raafat A. Solid and papillary epithelial neoplasm of the pancreas. J Surg Oncol. 2004. 85:193–198.4. Martin RC, Klimstra DS, Brennan MF, Conlon KC. Solid-pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas: a surgical enigma? Ann Surg Oncol. 2002. 9:35–40.5. Horisawa M, Niinomi N, Sato T, Yokoi S, Oda K, Ichikawa M, et al. Frantz's tumor (solid and cystic tumor of the pancreas) with liver metastasis: successful treatment and long-term follow-up. J Pediatr Surg. 1995. 30:724–726.6. Matsunou H, Konishi F. Papillary-cystic neoplasm of the pancreas. A clinicopathologic study concerning the tumor aging and malignancy of nine cases. Cancer. 1990. 65:283–291.7. Ogawa T, Isaji S, Okamura K, Noguchi T, Mizumoto R, Ishihara A. A case of radical resection for solid cystic tumor of the pancreas with widespread metastases in the liver and greater omentum. Am J Gastroenterol. 1993. 88:1436–1439.8. Sclafani LM, Reuter VE, Coit DG, Brennan MF. The malignant nature of papillary and cystic neoplasm of the pancreas. Cancer. 1991. 68:153–158.9. Klimstra DS, Wenig BM, Heffess CS. Solid-pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas: a typically cystic carcinoma of low malignant potential. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2000. 17:66–80.10. Nishihara K, Nagoshi M, Tsuneyoshi M, Yamaguchi K, Hayashi I. Papillary cystic tumors of the pancreas. Assessment of their malignant potential. Cancer. 1993. 71:82–92.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Solid Pseudopapillary Tumor of the Pancreas with Hepatic Metastasis: Spontaneous Regression Over 10-Year Follow-Up Period
- An Unusual Presentation of a Solid Pseudopapillary Tumor of the Pancreas Mimicking Adenocarcinoma
- Solid Pseudopapillary Tumor of the Pancreas with Liver Metastasis in Children
- Solid Pseudopapillary Tumor of the Pancreas in Child: A Case Report
- A case of a solid pseudopapillary tumor in a male child