Familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease with V180I Mutation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine and Medical Research Institute, Busan, Korea. eunjookim@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Ilsong Institute of Life Science, Hallym University, Anyang, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Memory and Aging Center, Department of Neurology, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, USA.
- KMID: 1792966
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.7.1097
Abstract
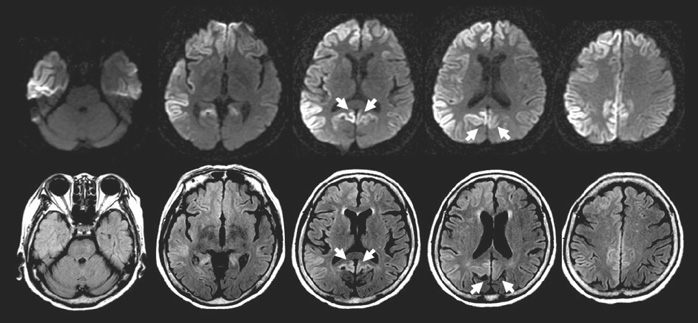
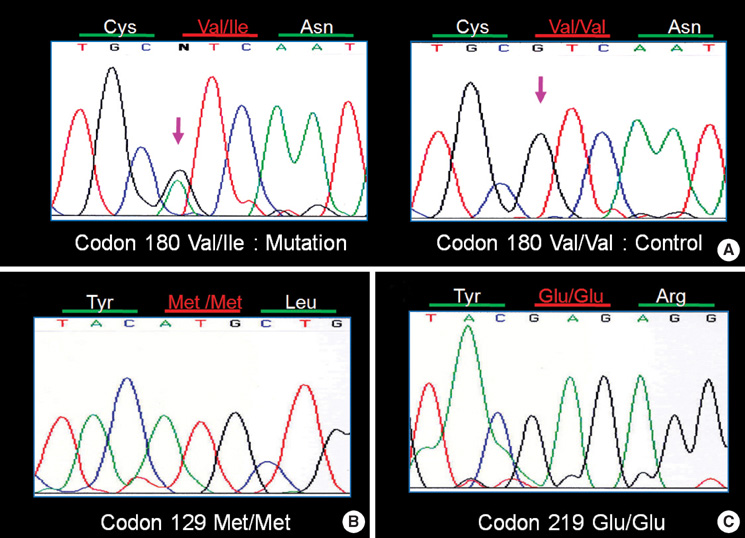
- Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) is an uncommon neurodegenerative disorder with an incidence of 1 per 1000,000 per year typically characterized by rapidly progressive dementia, ataxia, myoclonus and behavioral changes. Genetic prion diseases, which develop due to a mutations in the prion protein gene (PRNP), account for an estimated 10 to 15% of all CJD cases. We report a 75-yr-old woman with familial CJD carrying a V180I mutation which features late onset, slow progression, no periodic sharp wave complexes on electroencephalography, and extensive cortical ribboning with spared the cerebellum and the medial occipital lobes posterior to the parieto-occipital sulcus on MRI. To our knowledge, this is the first documented case of a point mutation at codon 180 in South Korea.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 5 articles
-
Real-Time Quaking-Induced Conversion Analysis for the Diagnosis of Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease in Korea
Jeong-Ho Park, Yeong-Gon Choi, Yun-Jung Lee, Seok-Joo Park, Hong-Seok Choi, Kyung-Chan Choi, Eun-Kyoung Choi, Yong-Sun Kim
J Clin Neurol. 2016;12(1):101-106. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2016.12.1.101.A Case of Familial Creutzfeldt-Jacob Disease (V180I) Initially Presenting with Depression
JaeJeong Joo, YoungSoon Yang, Jin Ho Kang, Sun Hwa Lee, Sang Won Ha, Jung Ho Han, Eun Kyung Cho, Doo Eung Kim
Dement Neurocogn Disord. 2012;11(2):74-77. doi: 10.12779/dnd.2012.11.2.74.A Case of Familial Creutzfeldt-Jacob Disease (V180I) Initially Presenting with Depression
JaeJeong Joo, YoungSoon Yang, Jin Ho Kang, Sun Hwa Lee, Sang Won Ha, Jung Ho Han, Eun Kyung Cho, Doo Eung Kim
Dement Neurocogn Disord. 2012;11(2):74-77. doi: 10.12779/dnd.2012.11.2.74.A Case of Familial Creutzfeldt-Jacob Disease (V180I) Initially Presenting with Depression
JaeJeong Joo, YoungSoon Yang, Jin Ho Kang, Sun Hwa Lee, Sang Won Ha, Jung Ho Han, Eun Kyung Cho, Doo Eung Kim
Dement Neurocogn Disord. 2012;11(2):74-77. doi: 10.12779/dnd.2012.11.2.74.Familial Creutzfeldt–Jakob Disease with a PRNP Mutation at Codon 180 Presented with Visual Hallucinations and Illusions
Dong Woo Ryu, Yun Jeong Hong, Jeong Wook Park, Si Baek Lee, Seong Hoon Kim, Yongbang Kim, Min Jae Seong, Byung Seok Kim
Dement Neurocogn Disord. 2019;18(3):105-107. doi: 10.12779/dnd.2019.18.3.105.
Reference
-
1. Rabinovici GD, Wang PN, Levin J, Cook L, Pravdin M, Davis J, DeArmond SJ, Barbaro NM, Martindale J, Miller BL, Geschwind MD. First symptom in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology. 2006. 66:286–287.
Article2. Heinemann U, Krasnianski A, Meissner B, Grasbon-Frodl EM, Kretzschmar HA, Zerr I. Novel PRNP mutation in a patient with a slow progressive dementia syndrome. Med Sci Monit. 2008. 14:CS41–CS43.3. Kong QK, Surewicz WK, Petersen RB, Zhou W, Chen SG, Gambetti P, Parchi P, Capellari S, Goldfarb L, Montagna P, Lugaresi E, Piccardo P, Ghetti B. Prusiner SB, editor. Inherited Prion Diseases. Prion Biology and Disease. 2004. 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press;673–776.4. Zerr I, Poser S. Clinical diagnosis and differential diagnosis of CJD and vCJD. With special emphasis on laboratory tests. APMIS. 2002. 110:88–98.5. World Health Organization. WHO Global surveillance, diagnosis and therapy of human transmissible spongiform encephalopathies: Report of a WHO consultation. Emerging and other communicable diseases, surveillance and control. 1998 February 9-11; Geneva: WHO.6. Shiga Y, Miyazawa K, Sato S, Fukushima R, Shibuya S, Sato Y, Konno H, Doh-ura K, Mugikura S, Tamura H, Higano S, Takahashi S, Itoyama Y. Diffusion-weighted MRI abnormalities as an early diagnostic marker for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology. 2004. 63:443–449.
Article7. Young GS, Geschwind MD, Fischbein NJ, Martindale JL, Henry RG, Liu S, Lu Y, Wong S, Liu H, Miller BL, Dillon WP. Diffusion-weighted and fluid-attenuated inversion recovery imaging in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: high sensitivity and specificity for diagnosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005. 26:1551–1562.8. Collins SJ, Sanchez-Juan P, Masters CL, Klug GM, van Duijn C, Poleggi A, Pocchiari M, Almonti S, Cuadrado-Corrales N, de Pedro-Cuesta J, Budka H, Gelpi E, Glatzel M, Tolnay M, Hewer E, Zerr I, Heinemann U, Kretszchmar HA, Jansen GH, Olsen E, Mitrova E, Alpérovitch A, Brandel JP, Mackenzie J, Murray K, Will RG. Determinants of diagnostic investigation sensitivities across the clinical spectrum of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Brain. 2006. 129:2278–2287.
Article9. Steinhoff BJ, Zerr I, Glatting M, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Poser S, Kretzschmar HA. Diagnostic value of periodic complexes in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Ann Neurol. 2004. 56:702–708.
Article10. Geschwind MD, Josephs KA, Parisi JE, Keegan BM. A 54-year-old man with slowness of movement and confusion. Neurology. 2007. 69:1881–1887.
Article11. Yamada M. Prion diseases in Japan: analysis of 918 patients. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2007. 47:805–808.12. Chasseigneaux S, Haik S, Laffont-Proust I, De Marco O, Lenne M, Brandel JP, Hauw JJ, Laplanche JL, Peoc'h K. V180I mutation of the prion protein gene associated with atypical PrPSc glycosylation. Neurosci Lett. 2006. 408:165–169.
Article13. Nixon R, Camicioli R, Jamison K, Cervenakova L, Mastrianni JA. The PRNP-V180I mutation is associated with abnormally glycosylated PrPCJD and Intracellular PrP accumulations. Presented at XIVth International Congress of Neuropathology Scientific Programme. Brain Pathology. 2000. 10:670.14. Jin K, Shiga Y, Shibuya S, Chida K, Sato Y, Konno H, Doh-ura K, Kitamoto T, Itoyama Y. Clinical features of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease with V180I mutation. Neurology. 2004. 62:502–505.
Article15. Alperovitch A, Zerr I, Pocchiari M, Mitrova E, de Pedro Cuesta J, Hegyi I, Collins S, Kretzschmar H, van Duijn C, Will RG. Codon 129 prion protein genotype and sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Lancet. 1999. 353:1673–1674.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease with V180I Mutation Presented with Broca's Aphasia
- A Case of Familial Creutzfeldt-Jacob Disease (V180I) Initially Presenting with Depression
- Familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease with M232R Mutation Progressed Slowly like Alzheimer's Disease
- A case of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
- Clinical Features of Genetic Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease with E200K Mutation