J Korean Med Sci.
2010 Dec;25(12):1759-1765. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.12.1759.
Improved Gastrointestinal Symptoms and Quality of Life after Conversion from Mycophenolate Mofetil to Enteric-Coated Mycophenolate Sodium in Renal Transplant Patients Receiving Tacrolimus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. yangch@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Bioengineering, University of Pensylvania, Philadelphia, PA, USA.
- 3Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Bong Seng Memorial Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 6Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Busan Paik Hospital College of Medicine, Inje University, Busan, Korea.
- 7Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 8Department of Nephrology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 1792900
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.12.1759
Abstract
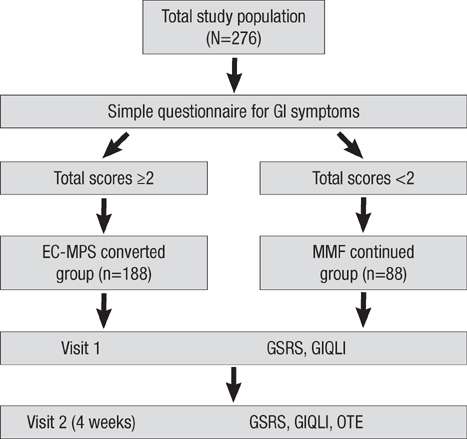
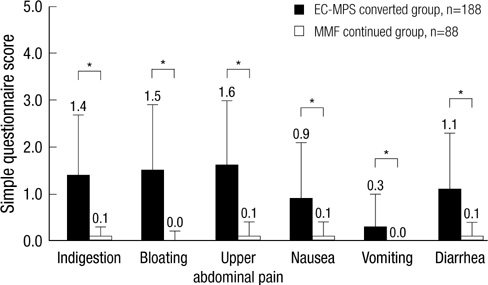
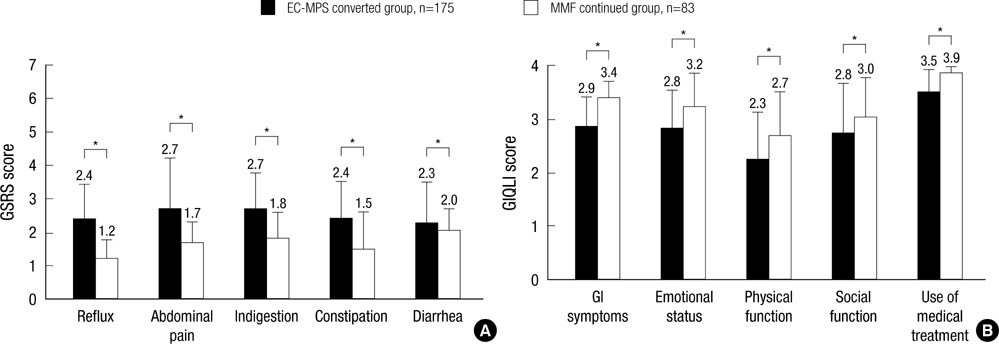
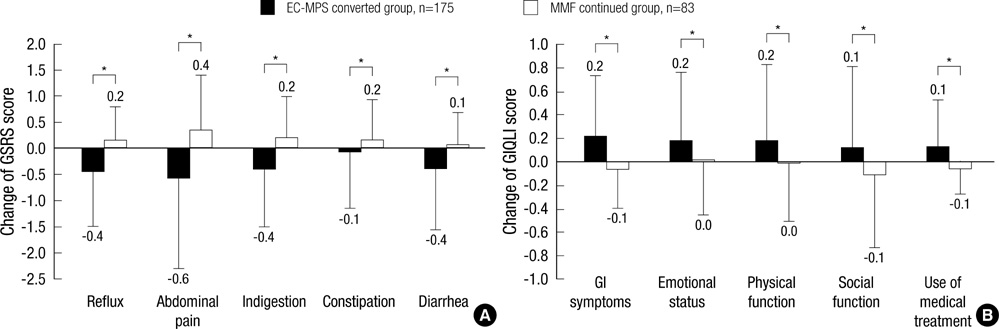
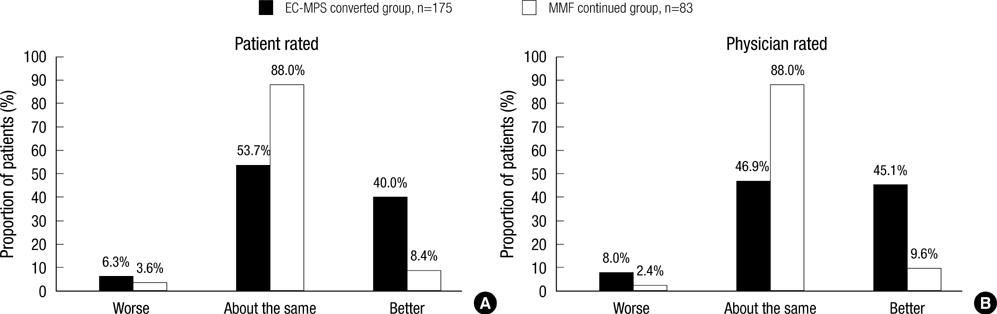
- It is reported that a conversion from mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) to enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium (EC-MPS) relieves gastrointestinal (GI) symptom burden and improves health-related quality of life (HRQoL). However, it is unclear whether renal transplant recipients using tacrolimus receive the same benefit from the conversion. In this prospective, multi-center, open-label trial, patients were categorized into two groups by their GI symptom screening. Equimolar EC-MPS (n=175) was prescribed for patients with GI burdens; those with no complaints remained on MMF (n=83). Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale (GSRS) and Gastrointestinal Quality of Life Index (GIQLI) were evaluated at baseline and after one month. Patients and physicians completed Overall Treatment Effect (OTE) at one month. EC-MPS-converted patients had worse GSRS and GIQLI scores at baseline than MMF-continued patients (all P<0.001). Significant improvements in GSRS and GIQLI scores were observed for EC-MPS-converted patients at one month, but MMF-continued patients showed worsened GSRS scores (all P<0.05). OTE scale indicated that EC-MPS patients improved in overall GI symptoms and HRQoL more than MMF patients did (P<0.001). In tacrolimus-treated renal transplant recipients with GI burdens, a conversion from MMF to EC-MPS improves GI-related symptoms and HRQoL.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Aged
Female
Gastrointestinal Diseases/*chemically induced
Graft Rejection/drug therapy
Humans
Immunosuppressive Agents/administration & dosage/*adverse effects/therapeutic use
Kidney Failure, Chronic/therapy
*Kidney Transplantation
Male
Middle Aged
Mycophenolic Acid/administration & dosage/*adverse effects/*analogs & derivatives/therapeutic use
Quality of Life
Questionnaires
Tablets, Enteric-Coated
Tacrolimus/therapeutic use
Figure
Reference
-
1. The Tricontinental Mycophenolate Mofetil Renal Transplantation Study Group. A blinded, randomized clinical trial of mycophenolate mofetil for the prevention of acute rejection in cadaveric renal transplantation. Transplantation. 1996. 61:1029–1037.2. Meier-Kriesche HU, Steffen BJ, Hochberg AM, Gordon RD, Liebman MN, Morris JA, Kaplan B. Long-term use of mycophenolate mofetil is associated with a reduction in the incidence and risk of late rejection. Am J Transplant. 2003. 3:68–73.
Article3. Kang NR, Lee JE, Huh W, Kim SJ, Kim YG, Kim DJ, Oh HY. Minimal proteinuria one year after transplant is a risk factor for graft survival in kidney transplantation. J Korean Med Sci. 2009. 24:Suppl 1. S129–S134.
Article4. Bunnapradist S, Lentine KL, Burroughs TE, Pinsky BW, Hardinger KL, Brennan DC, Schnitzler MA. Mycophenolate mofetil dose reductions and discontinuations after gastrointestinal complications are associated with renal transplant graft failure. Transplantation. 2006. 82:102–107.
Article5. Salvadori M, Holzer H, de Mattos A, Sollinger H, Arns W, Oppenheimer F, Maca J, Hall M. ERL B301 Study Groups. Enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium is therapeutically equivalent to mycophenolate mofetil in de novo renal transplant patients. Am J Transplant. 2004. 4:231–236.6. Budde K, Curtis J, Knoll G, Chan L, Neumayer HH, Seifu Y, Hall M. ERL B301 Study Groups. Enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium can be safely administered in maintenance renal transplant recipients: results of a 1-year study. Am J Transplant. 2004. 4:237–243.7. Ekberg H, Kyllönen L, Madsen S, Grave G, Solbu D, Holdaas H. Increased prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms associated with impaired quality of life in renal transplant recipients. Transplantation. 2007. 83:282–289.
Article8. Bolin P, Tanriover B, Zibari GB, Lynn ML, Pirsch JD, Chan L, Cooper M, Langone AJ, Tomlanovich SJ. Improvement in 3-month patient-reported gastrointestinal symptoms after conversion from mycophenolate mofetil to enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium in renal transplant patients. Transplantation. 2007. 84:1443–1451.
Article9. Chan L, Mulgaonkar S, Walker R, Arns W, Ambühl P, Schiavelli R. Patient-reported gastrointestinal symptom burden and health-related quality of life following conversion from mycophenolate mofetil to enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium. Transplantation. 2006. 81:1290–1297.
Article10. Kaplan B, Meier-Kriesche HU, Minnick P, Bastien MC, Sechaud R, Yeh CM, Balez S, Picard F, Schmouder R. Randomized calcineurin inhibitor cross over study to measure the pharmacokinetics of co-administered enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium. Clin Transplant. 2005. 19:551–558.
Article11. Zucker K, Rosen A, Tsaroucha A, de Faria L, Roth D, Ciancio G, Esquenazi V, Burke G, Tzakis A, Miller J. Unexpected augmentation of mycophenolic acid pharmacokinetics in renal transplant patients receiving tacrolimus and mycophenolate mofetil in combination therapy, and analogous in vitro findings. Transpl Immunol. 1997. 5:225–232.
Article12. Filler G, Zimmering M, Mai I. Pharmacokinetics of mycophenolate mofetil are influenced by concomitant immunosuppression. Pediatr Nephrol. 2000. 14:100–104.
Article13. Pirsch JD, Miller J, Deierhoi MH, Vincenti F, Filo RS. FK506 Kidney Transplant Study Group. A comparison of tacrolimus (FK506) and cyclosporine for immunosuppression after cadaveric renal transplantation. Transplantation. 1997. 63:977–983.14. Kleinman L, Faull R, Walker R, Ramesh Prasad GV, Ambuehl P, Bahner U. Gastrointestinal-specific patient-reported outcome instruments differentiate between renal transplant patients with or without GI complications. Transplant Proc. 2005. 37:846–849.15. Cofan F, Rosich E, Arias M, Torregrosa V, Oppenheimer F, Campistol JM. Quality of life in renal transplant recipients following conversion from mycophenolate mofetil to enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium. Transplant Proc. 2007. 39:2179–2181.
Article16. Darji P, Vijayaraghavan R, Thiagarajan CM, Sharma RK, Subbarao B, Pishardy R, Dakshinamurthy KV, Vijaykumar R, Abraham G, Bhaskar S, Agarwal L, Shah B, Abraham A, John M, Sampathkumar K, Das T, Umesh L, Sundar S, Ballal H, Jasuja S, Saxena S, Saha TK. Conversion from mycophenolate mofetil to enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium in renal transplant recipients with gastrointestinal tract disorders. Transplant Proc. 2008. 40:2262–2267.
Article17. Shehata M, Bhandari S, Venkat-Raman G, Moore R, D'Souza R, Riad H, Bakran A, Baker R, Needham C, Andrews C. Effect of conversion from mycophenolate mofetil to enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium on maximum tolerated dose and gastrointestinal symptoms following kidney transplantation. Transpl Int. 2009. 22:821–830.
Article18. McColl E, Junghard O, Wiklund I, Revicki DA. Assessing symptoms in gastroesophageal reflux disease: how well do clinicians' assessments agree with those of their patients? Am J Gastroenterol. 2005. 100:11–18.
Article19. Fallone CA, Guyatt GH, Armstrong D, Wiklund I, Degl'Innocenti A, Heels-Ansdell D, Barkun AN, Chiba N, Zanten SJ, El-Dika S, Austin P, Tanser L, Schünemann HJ. Do physicians correctly assess patient symptom severity in gastro-oesophageal reflux disease? Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004. 20:1161–1169.
Article20. Jones RH, Hungin AP, Phillips J, Mills JG. Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in primary care in Europe: clinical presentation and endoscopic findings. Eur J Gen Pract. 1995. 1:149–154.
Article21. Behrend M. Adverse gastrointestinal effects of mycophenolate mofetil: aetiology, incidence and management. Drug Saf. 2001. 24:645–663.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Oral Ulceration an Overlooked Complication of Mycophenolate Mofetil in a Renal Transplant Recipient
- The Efficacy and Outcome of Reduced Dose of Tacrolimus in Renal Transplantation
- Prospective Controlled Protocol for Three Months Steroid Withdrawal with Tacrolimus, Basiliximab, and Mycophenolate Mofetil in Renal Transplant Recipients
- The impact of omeprazole on mycophenolate pharmacokinetics in kidney transplant recipients
- Mycophenolate Mofetil and Prednisolone as Maintenance Therapy in Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome after Kidney Transplantation