Korean J Gastroenterol.
2011 Jun;57(6):340-345. 10.4166/kjg.2011.57.6.340.
Usefulness of Model for End-stage Liver Disease Score for Predicting Mortality after Intra-abdominal Surgery in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis in a Single Hospital
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hongjoo3.kim@samsung.com
- KMID: 1792797
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2011.57.6.340
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
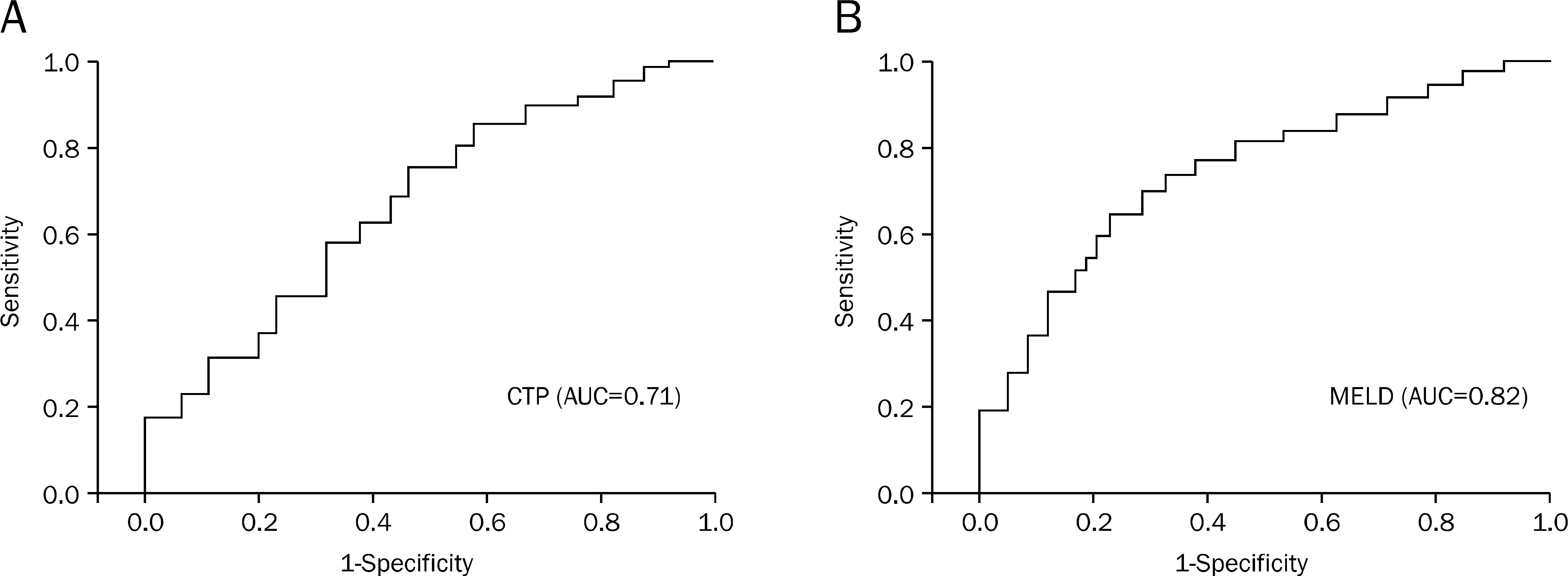
Recent studies have suggested that the model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) score is superior to the Child-Turcotte-Pugh (CTP) score as a predictor of postoperative mortality, especially up to 90 days. This study aimed to determine whether MELD score can predict the postoperative outcome of patients with liver cirrhosis in Korea.
METHODS
We reviewed the medical records of 98 patients with liver cirrhosis who underwent intra-abdominal surgery under generalized anesthesia between March 2003 and December 2008 at Kangbuk Samsung Hospital. Univariate and multivariate cox proportional hazards analyses were performed to determine the correlation between risk factors and mortality.
RESULTS
Eighty-two percent of patients (n=80) were male. Mean MELD score was 10.82+/-3.84. Common causes of liver cirrhosis were hepatitis B (57.2%) and alcohol (22.4%). Ninety-day mortality ranged from 2.1% (MELD score, < or =9) to 25% (MELD score, > or =17). By multivariate analysis, MELD score>9 (HR 2.490; [95% CI 1.116-5.554; p=.026]) and American Society of Anesthesiologists Class > or =IV (HR 2.433; [95% CI 1.039-5.695; p=.041]) predicted mortality at 30 days after surgery. Only MELD score was a predictor of prognosis at 90 days (HR 2.446; [95% CI 1.118-5.352; p=.025]). Etiology of cirrhosis and CTP score were not predictors of mortality.
CONCLUSIONS
MELD score was a useful predictive parameter of postoperative mortality at 30 days and 90 days, independent of the etiology of cirrhosis.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Tanaka R, Itoshima T, Nagashima H. Follow-up study of 582 liver cirrhosis patients for 26 years in Japan. Liver. 1987; 7:316–324.
Article2. Cowan RE, Jackson BT, Grainger SL, Thompson RP. Effects of an-esthetic agents and abdominal surgery on liver blood flow. Hepatology. 1991; 14:1161–1166.
Article3. Amitrano L, Guardascione MA, Brancaccio V, Balzano A. Coagu-lation disorders in liver disease. Semin Liver Dis. 2002; 22:83–96.
Article4. Borzio M, Salerno F, Piantoni L, et al. Bacterial infection in patients with advanced cirrhosis: a multicentre prospective study. Dig Liver Dis. 2001; 33:41–48.
Article5. Thalheimer U, Triantos CK, Samonakis DN, Patch D, Burroughs AK. Infection, coagulation, and variceal bleeding in cirrhosis. Gut. 2005; 54:556–563.
Article6. Vilstrup H. Cirrhosis and bacterial infections. Rom J Gastroenterol. 2003; 12:297–302.7. Child CG, Turcotte JG. Surgery and portal hypertension. Major Probl Clin Surg. 1964; 1:1–85.8. Kamath PS, Wiesner RH, Malinchoc M, et al. A model to predict survival in patients with end-stage liver disease. Hepatology. 2001; 33:464–470.
Article9. Malinchoc M, Kamath PS, Gordon FD, Peine CJ, Rank J, ter Borg PC. A model to predict poor survival in patients undergoing trans-jugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts. Hepatology. 2000; 31:864–871.
Article10. Teh SH, Nagorney DM, Stevens SR, et al. Risk factors for mortality after surgery in patients with cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2007; 132:1261–1269.
Article11. Wiesner R, Edwards E, Freeman R, et al. Model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) and allocation of donor livers. Gastroenterology. 2003; 124:91–96.
Article12. Keats AS. The ASA classification of physical status–a recapitu-lation. Anesthesiology. 1978; 49:233–236.
Article13. Garrison RN, Cryer HM, Howard DA, Polk HC Jr. Clarification of risk factors for abdominal operations in patients with hepatic cirrhosis. Ann Surg. 1984; 199:648–655.
Article14. Mansour A, Watson W, Shayani V, Pickleman J. Abdominal operations in patients with cirrhosis: still a major surgical challenge. Surgery. 1997; 122:730–735.
Article15. Befeler AS, Palmer DE, Hoffman M, Longo W, Solomon H, Di Bisceglie AM. The safety of intra-abdominal surgery in patients with cirrhosis: model for end-stage liver disease score is superior to Child-Turcotte-Pugh classification in predicting outcome. Arch Surg. 2005; 140:650–654.16. Northup PG, Wanamaker RC, Lee VD, Adams RB, Berg CL. Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) predicts nontransplant surgical mortality in patients with cirrhosis. Ann Surg. 2005; 242:244–251.
Article17. Perkins L, Jeffries M, Patel T. Utility of preoperative scores for predicting morbidity after cholecystectomy in patients with cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004; 2:1123–1128.
Article18. Suman A, Barnes DS, Zein NN, Levinthal GN, Connor JT, Carey WD. Predicting outcome after cardiac surgery in patients with cirrhosis: a comparison of Child-Pugh and MELD scores. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004; 2:719–723.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Mortality scoring systems for liver transplant recipients: before and after model for end-stage liver disease score
- Important predictor of mortality in patients with end-stage liver disease
- Model for end-stage liver disease-3.0 vs. model for end-stage liver disease-sodium: mortality prediction in Korea
- New Scoring Systems for Severity Outcome of Liver Cirrhosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Current Issues Concerning The Child-Turcotte-Pugh Score and The Model of End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) Score
- Current Status of Deceased Donor Liver Transplantation for Alcoholic Liver Disease in Korea in MELD Era