J Korean Med Sci.
2014 Feb;29(2):243-247. 10.3346/jkms.2014.29.2.243.
Sleep Disturbances and Glucoregulation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea. sangwookkim@kangwon.ac.kr
- 2Department of Preventive Medicine, Kangwon National University Hospital, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1789982
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2014.29.2.243
Abstract
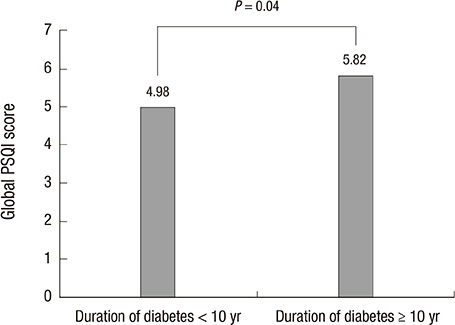
- We investigated the frequency of sleep disturbances and the association between sleep disturbances and glucoregulation in type 2 diabetic patients. The frequency of sleep disturbances in 614 type 2 diabetic patients was investigated using validated sleep questionnaires. There were 381 male and 233 female patients. The mean age was 59.7 +/- 11.1 yr; the mean body mass index was 24.9 +/- 4.4 kg/m2; the mean HbA1c was 7.8% +/- 1.5%; and the mean duration of diabetes was 10.3 +/- 8.4 yr. The questionnaires revealed insomnia in 48.2% of the patients while 8.5% reported excessive daytime sleepiness. A total of 49% of the patients was poor sleepers, while 28.5% had depression. Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that there was no significant association between HbA1c and other sleep disturbances, such as poor sleep, insomnia, and short duration of sleep. Sleep disturbances were very common in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, whereas there was no association between poor or short sleep and glucoregulation. Awareness and identifying sleep complaints in such patients are necessary to improve their quality of daily life.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Body Mass Index
Depression/epidemiology
Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2/complications/*diagnosis/drug therapy
Female
Hemoglobin A, Glycosylated/analysis
Humans
Hypoglycemic Agents/therapeutic use
Logistic Models
Male
Middle Aged
Quality of Life
Questionnaires
Sleep Disorders/*complications
Sleep Initiation and Maintenance Disorders/epidemiology
Hemoglobin A, Glycosylated
Hypoglycemic Agents
Figure
Reference
-
1. Buxton OM, Pavlova M, Reid EW, Wang W, Simonson DC, Adler GK. Sleep restriction for 1 week reduces insulin sensitivity in healthy men. Diabetes. 2010; 59:2126–2133.2. Schmid SM, Hallschmid M, Jauch-Chara K, Bandorf N, Born J, Schultes B. Sleep loss alters basal metabolic hormone secretion and modulates the dynamic counterregulatory response to hypoglycemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007; 92:3044–3051.3. Beihl DA, Liese AD, Haffner SM. Sleep duration as a risk factor for incident type 2 diabetes in a multiethnic cohort. Ann Epidemiol. 2009; 19:351–357.4. Chao CY, Wu JS, Yang YC, Shih CC, Wang RH, Lu FH, Chang CJ. Sleep duration is a potential risk factor for newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 2011; 60:799–804.5. Chaput JP, Després JP, Bouchard C, Astrup A, Tremblay A. Sleep duration as a risk factor for the development of type 2 diabetes or impaired glucose tolerance: analyses of the Quebec Family Study. Sleep Med. 2009; 10:919–924.6. Tuomilehto H, Peltonen M, Partinen M, Lavigne G, Eriksson JG, Herder C, Aunola S, Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi S, Ilanne-Parikka P, Uusitupa M, et al. Sleep duration, lifestyle intervention, and incidence of type 2 diabetes in impaired glucose tolerance: the Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:1965–1971.7. Hoevenaar-Blom MP, Spijkerman AM, Kromhout D, van den Berg JF, Verschuren WM. Sleep duration and sleep quality in relation to 12-year cardiovascular disease incidence: the MORGEN Study. Sleep. 2011; 34:1487–1492.8. Skaer TL, Sclar DA. Economic implications of sleep disorders. Pharmacoeconomics. 2010; 28:1015–1023.9. Ohayon MM. Epidemiology of insomnia: what we know and what we still need to learn. Sleep Med Rev. 2002; 6:97–111.10. Taub LF, Redeker NS. Sleep disorders, glucose regulation, and type 2 diabetes. Biol Res Nurs. 2008; 9:231–243.11. Donga E, van Dijk M, van Dijk JG, Biermasz NR, Lammers GJ, van Kralingen KW, Corssmit EP, Romijn JA. A single night of partial sleep deprivation induces insulin resistance in multiple metabolic pathways in healthy subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010; 95:2963–2968.12. Spiegel K, Tasali E, Leproult R, Van Cauter E. Effects of poor and short sleep on glucose metabolism and obesity risk. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2009; 5:253–261.13. Pallayova M, Donic V, Gresova S, Peregrim I, Tomori Z. Do differences in sleep architecture exist between persons with type 2 diabetes and nondiabetic controls? J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2010; 4:344–352.14. Ohkuma T, Fujii H, Iwase M, Kikuchi Y, Ogata S, Idewaki Y, Ide H, Doi Y, Hirakawa Y, Nakamura U, et al. Impact of sleep duration on obesity and the glycemic level in patients with type 2 diabetes: the Fukuoka Diabetes Registry. Diabetes Care. 2013; 36:611–617.15. Skomro RP, Ludwig S, Salamon E, Kryger MH. Sleep complaints and restless legs syndrome in adult type 2 diabetics. Sleep Med. 2001; 2:417–422.16. Ohayon MM, Hong SC. Prevalence of insomnia and associated factors in South Korea. J Psychosom Res. 2002; 53:593–600.17. Cunha MC, Zanetti ML, Hass VJ. Sleep quality in type 2 diabetics. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2008; 16:850–855.18. Shim U, Lee H, Oh JY, Sung YA. Sleep disorder and cardiovascular risk factors among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Korean J Intern Med. 2011; 26:277–284.19. Rajendran A, Parthsarathy S, Tamilselvan B, Seshadri KG, Shuaib M. Prevalence and correlates of disordered sleep in Southeast Asian indians with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab J. 2012; 36:70–76.20. Davies RJ, Stradling JR. The epidemiology of sleep apnoea. Thorax. 1996; 51:S65–S70.21. Lurie A. Obstructive sleep apnea in adults: epidemiology, clinical presentation, and treatment options. Adv Cardiol. 2011; 46:1–42.22. Young T, Palta M, Dempsey J, Skatrud J, Weber S, Badr S. The occurrence of sleep-disordered breathing among middle-aged adults. N Engl J Med. 1993; 328:1230–1235.23. Pamidi S, Tasali E. Obstructive sleep apnea and type 2 diabetes: is there a link? Front Neurol. 2012; 3:126.24. Schober AK, Neurath MF, Harsch IA. Prevalence of sleep apnoea in diabetic patients. Clin Respir J. 2011; 5:165–172.