Korean J Radiol.
2010 Feb;11(1):75-83. 10.3348/kjr.2010.11.1.75.
Contrast-Enhanced Harmonic Ultrasonography for the Assessment of Prostate Cancer Aggressiveness: a Preliminary Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ultrasound in Medicine, Xinhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, 1665 Kongjiang Road, Shanghai, 200092, P.R China. joychen1266@126.com
- 2Department of Ultrasound in Medicine, Sixth People's Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiaotong University, 600 Yishan Road, Shanghai, 200233, P.R China.
- 3Department of Pathology, Sixth People's Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiaotong University, 600 Yishan Road, Shanghai, 200233, P.R China.
- KMID: 1787017
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2010.11.1.75
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
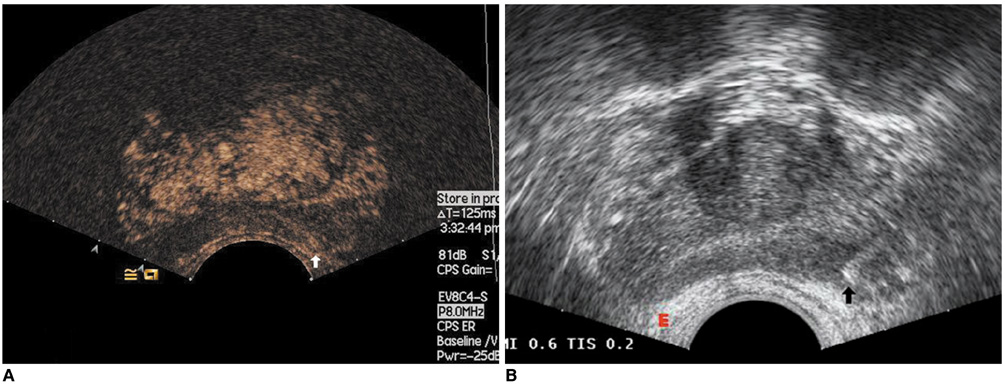
To determine whether contrast-enhanced harmonic ultrasonography can be used to predict the aggressiveness of prostate cancer. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Contrast-enhanced harmonic ultrasonography was performed in 103 patients suspected of prostate cancer before biopsy. Time intensity curves were reconstructed for systematic biopsy sites and sonographic abnormalities. The characteristics of the curves were described using hemodynamic indices including arrival time (AT), time-to-peak (TTP), and peak intensity (PI). The differences of hemodynamic indices between high-grade and low-grade cancer were analyzed and the correlations between the hemodynamic indices and biopsy Gleason score were studied.
RESULTS
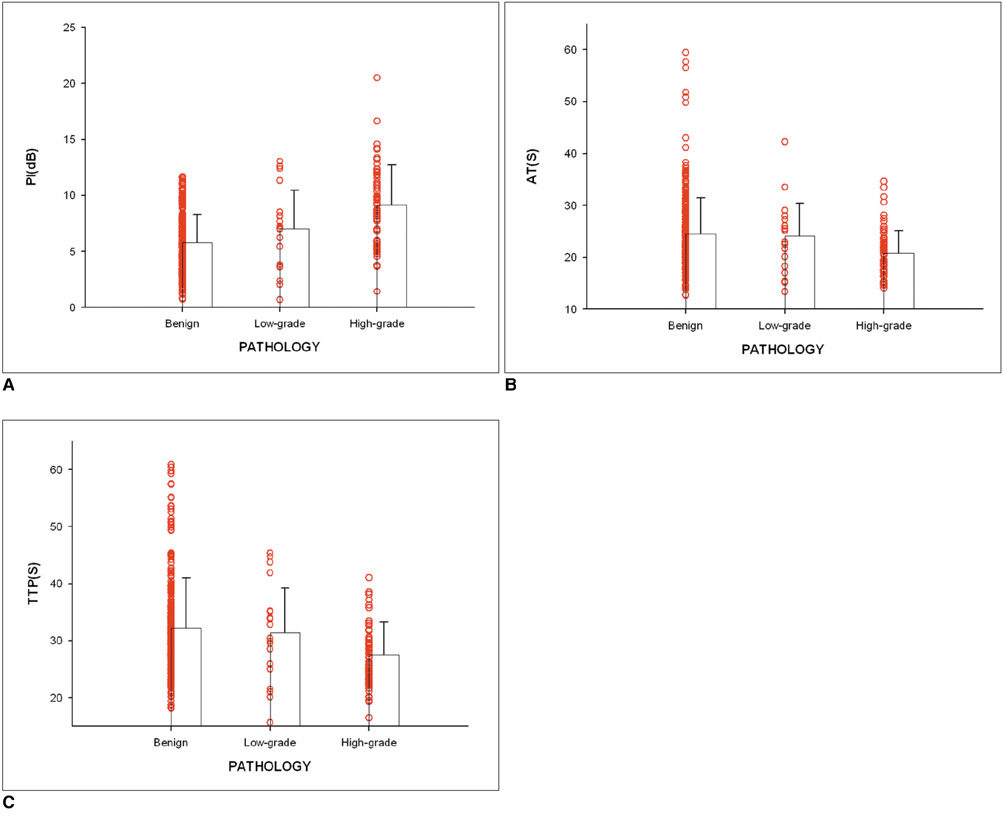
Prostate cancer was detected in 41 of 103 patients and there were significant differences in the hemodynamic indices between the biopsy sites of the non-malignant patients and prostate cancer lesions (p < 0.05). The prostate biopsies revealed 154 prostate cancer lesions, including 31 low-grade lesions and 123 high-grade lesions. The hemodynamic indices AT and TTP of high-grade tumors were significantly shorter than those of low-grade tumors (p = 0.001, 0.002). In addition, high-grade peripheral zone (PZ) tumors had higher PI than low-grade PZ tumors (p = 0.009). The PZ prostate cancer Gleason score correlated with PI, AT and TTP, with Spearman correlation coefficients of 0.223, -0.335, and -0.351, respectively (p = 0.013, < 0.001 and < 0.001).
CONCLUSION
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound measurements of hemodynamic indices correlate with the prostate cancer Gleason score.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wilson NM, Masoud AM, Barsoum HB, Refaat MM, Moustafa MI, Kamal TA. Correlation of power Doppler with microvessel density in assessing prostate needle biopsy. Clin Radiol. 2004. 59:946–950.2. Volavsek M, Masera A, Ovcak Z. Incidental prostatic carcinoma. A predictive role of neoangiogenesis and comparison with other prognostic factors. Pathol Oncol Res. 2000. 6:191–196.3. Goldberg BB, Liu JB, Forsberg F. Ultrasound contrast agents: a review. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1994. 20:319–333.4. Halpern EJ. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging of prostate cancer. Rev Urol. 2006. 8:S29–S37.5. Ko EY, Lee SH, Kim HH, Kim SM, Shin MJ, Kim N, et al. Evaluation of tumor angiogenesis with a second-generation US contrast medium in a rat breast tumor model. Korean J Radiol. 2008. 9:243–249.6. Lee SH, Suh JS, Shin MJ, Kim SM, Kim N, Suh SH. Quantitative assessment of synovial vascularity using contrast-enhanced power Doppler ultrasonography: correlation with histologic findings and MR imaging findings in arthritic rabbit knee model. Korean J Radiol. 2008. 9:45–53.7. Frauscher F, Klauser A, Volgger H, Halpern EJ, Pallwein L, Steiner H, et al. Comparison of contrast enhanced color Doppler targeted biopsy with conventional systematic biopsy: impact on prostate cancer detection. J Urol. 2002. 167:1648–1652.8. Pelzer A, Bektic J, Berger AP, Pallwein L, Halpern EJ, Horninger W, et al. Prostate cancer detection in men with prostate specific antigen 4 to 10 ng/ml using a combined approach of contrast enhanced color Doppler targeted and systematic biopsy. J Urol. 2005. 173:1926–1929.9. Roy C, Buy X, Lang H, Saussine C, Jacqmin D. Contrast-enhanced color Doppler endorectal sonography of prostate: efficiency for detecting peripheral zone tumors and role for biopsy procedure. J Urol. 2003. 170:69–72.10. Mitterberger M, Pinggera GM, Horninger W, Bartsch G, Strasser H, Schäfer G, et al. Comparison of contrast enhanced color Doppler targeted biopsy to conventional systematic biopsy: impact on Gleason score. J Urol. 2007. 178:464–468.11. Bono AV, Celato N, Cova V, Salvadore M, Chinetti S, Novario R. Microvessel density in prostate carcinoma. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2002. 5:123–127.12. Bostwick DG, Wheeler TM, Blute M, Barrett DM, MacLennan GT, Sebo TJ, et al. Optimized microvessel density analysis improves prediction of cancer stage from prostate needle biopsies. Urology. 1996. 48:47–57.13. Borre M, Offersen BV, Nerstrøm B, Overgaard J. Microvessel density predicts survival in prostate cancer patients subjected to watchful waiting. Br J Cancer. 1998. 78:940–944.14. Goossen TE, de la Rosette JJ, Hulsbergen-van de Kaa CA, van Leenders GJ, Wijkstra H. The value of dynamic contrast enhanced power Doppler ultrasound imaging in the localization of prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 2003. 43:124–131.15. Emiliozzi P, Corsetti A, Tassi B, Federico G, Martini M, Pansadoro V. Best approach for prostate cancer detection: a prospective study on transperineal versus transrectal six-core prostate biopsy. Urology. 2003. 61:961–966.16. Emiliozzi P, Longhi S, Scarpone P, Pansadoro A, DePaula F, Pansadoro V. The value of a single biopsy with 12 transperineal cores for detecting prostate cancer in patients with elevated prostate specific antigen. J Urol. 2001. 166:845–850.17. Pinthus JH, Witkos M, Fleshner NE, Sweet J, Evans A, Jewett MA, et al. Prostate cancers scored as Gleason 6 on prostate biopsy are frequently Gleason 7 tumors at radical prostatectomy: implication on outcome. J Urol. 2006. 176:979–984.18. Steinberg DM, Sauvageot J, Piantadosi S, Epstein JI. Correlation of prostate needle biopsy and radical prostatectomy Gleason grade in academic and community settings. Am J Surg Pathol. 1997. 21:566–576.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Role of contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) and EUS elastography in pancreatic lesions
- Radiofrequency Ablation of Liver Cancer: Early Evaluation of Therapeutic Response with Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasonography
- Contrast-enhanced endoscopic ultrasonography: advance and current status
- Contrast-enhanced Harmonic Power Doppler Ultrasonography: Improved Depiction of Vascularity and Characterization of Flow Pattern in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Hepatic Hemangiomas: Spectrum of US Appearances on Gray-scale, Power Doppler, and Contrast-Enhanced US