J Korean Med Sci.
2014 May;29(5):652-656. 10.3346/jkms.2014.29.5.652.
Pertussis Seroprevalence in Korean Adolescents and Adults Using Anti-Pertussis Toxin Immunoglobulin G
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. kjhan@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Vaccine Bio Research Institute, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Changwon Fatima Hospital, Changwon, Korea.
- KMID: 1786105
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2014.29.5.652
Abstract
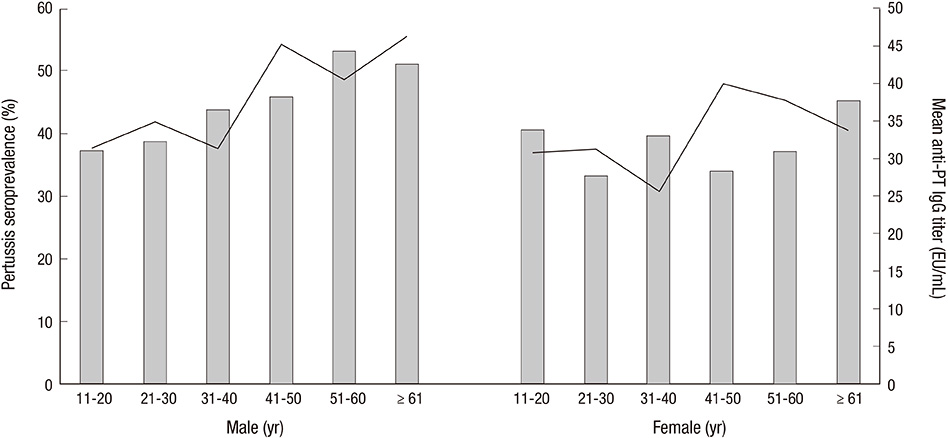
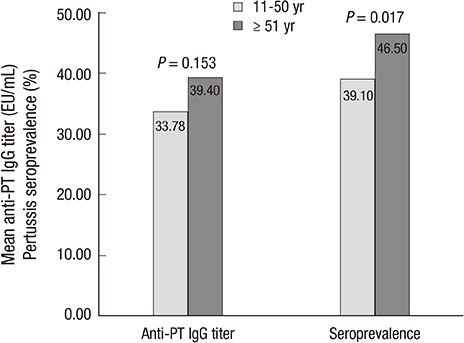
- This study was conducted to evaluate age-specific seroprevalence of pertussis in Korea and to formulate a strategy to prevent and reduce the incidence of pertussis. Residual serum samples of healthy adolescents and adults 11 yr of age or older were collected between July 2012 and December 2012, and anti-pertussis toxin (PT) IgG titers were measured using a commercial ELISA kit. We compared the mean anti-PT IgG titers and seroprevalence of pertussis of the six age groups: 11-20, 21-30, 31-40, 41-50, 51-60, and > or = 61 yr. A total of 1,192 subjects were enrolled. The mean anti-PT IgG titer and pertussis seroprevalence were 35.53 +/- 62.91 EU/mL and 41.4%, respectively. The mean anti-PT IgG titers and seroprevalence were not significantly different between the age groups. However, the seroprevalence in individuals 51 yr of age or older was significantly higher than in individuals younger than 51 yr (46.5% vs 39.1%, P = 0.017). Based on these results, a new pertussis prevention strategy is necessary for older adults.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Aging
Antibodies, Bacterial/*blood
Bordetella pertussis/*immunology
Child
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Female
Humans
Immunoglobulin G/*blood/immunology
Incidence
Male
Middle Aged
Pertussis Toxin/blood/*immunology
Pertussis Vaccine/immunology
Republic of Korea/epidemiology
Seroepidemiologic Studies
Vaccination
Whooping Cough/blood/*epidemiology
Young Adult
Antibodies, Bacterial
Immunoglobulin G
Pertussis Toxin
Pertussis Vaccine
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Seroprevalence of Pertussis in Healthcare Workers without Adult Pertussis Vaccine Use at a University Hospital in Korea
Won Suk Choi, Su Hyun Kim, Dae Won Park
J Korean Med Sci. 2018;33(50):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e321.Tetanus–diphtheria–acellular pertussis vaccination for adults: an update
Hyo-Jin Lee, Jung-Hyun Choi
Clin Exp Vaccine Res. 2017;6(1):22-30. doi: 10.7774/cevr.2017.6.1.22.
Reference
-
1. Hewlett EL, Edwards KM. Clinical practice: pertussis-not just for kids. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:1215–1222.2. Choe YJ, Park YJ, Jung C, Bae GR, Lee DH. National pertussis surveillance in South Korea 1955-2011: epidemiological and clinical trends. Int J Infect Dis. 2012; 16:e850–e854.3. Brooks DA, Clover R. Pertussis infection in the United States: role for vaccination of adolescents and adults. J Am Board Fam Med. 2006; 19:603–611.4. Güriş D, Strebel PM, Bardenheier B, Brennan M, Tachdjian R, Finch E, Wharton M, Livengood JR. Changing epidemiology of pertussis in the United States: increasing reported incidence among adolescents and adults, 1990-1996. Clin Infect Dis. 1999; 28:1230–1237.5. Pebody RG, Gay NJ, Giammanco A, Baron S, Schellekens J, Tischer A, Olander RM, Andrews NJ, Edmunds WJ, Lecoeur H, et al. The seroepidemiology of Bordetella pertussis infection in Western Europe. Epidemiol Infect. 2005; 133:159–171.6. Cassiday P, Sanden G, Heuvelman K, Mooi F, Bisgard KM, Popovic T. Polymorphism in Bordetella pertussis pertactin and pertussis toxin virulence factors in the United States, 1935-1999. J Infect Dis. 2000; 182:1402–1408.7. Crowcroft NS, Pebody RG. Recent developments in pertussis. Lancet. 2006; 367:1926–1936.8. Caro JJ, Getsios D, El-Hadi W, Payne K, O'Brien JA. Pertussis immunization of adolescents in the United States: an economic evaluation. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2005; 24:S75–S82.9. Tan T, Halperin S, Cherry JD, Edwards K, Englund JA, Glezen P, Greenberg D, Rothstein E, Skowronski D. Pertussis immunization in the global pertussis initiative North American region: recommended strategies and implementation considerations. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2005; 24:S83–S86.10. Van Rie A, Hethcote HW. Adolescent and adult pertussis vaccination: computer simulations of five new strategies. Vaccine. 2004; 22:3154–3165.11. Campins-Martí M, Cheng HK, Forsyth K, Guiso N, Halperin S, Huang LM, Mertsola J, Oselka G, Ward J, Wirsing von König CH, et al. Recommendations are needed for adolescent and adult pertussis immunisation: rationale and strategies for consideration. Vaccine. 2001; 20:641–646.12. Cherry JD, Grimprel E, Guiso N, Heininger U, Mertsola J. Defining pertussis epidemiology: clinical, microbiologic and serologic perspectives. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2005; 24:S25–S34.13. Rendi-Wagner P, Tobias J, Moerman L, Goren S, Bassal R, Green M, Cohen D. The seroepidemiology of Bordetella pertussis in Israel-estimate of incidence of infection. Vaccine. 2010; 28:3285–3290.14. Lee SY, Choi UY, Kim JS, Ahn JH, Choi JH, Ma SH, Park JS, Kim HM, Kang JH. Immunoassay of pertussis according to ages. Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2012; 19:55–60.15. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Communicable diseases surveillance yearbook 2008. Seoul: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2009.16. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Infectious diseases surveillance yearbook 2011. Seoul: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2012.17. Choi KM, Kim KH, Kim YJ, Kim JH, Park SE, Lee HJ, Eun BW, Jo DS, Choi EH, Hong YJ. Recommendation for the use of newly introduced Tdap vaccine in Korea. Korean J Pediatr. 2011; 54:141–145.18. De Greeff SC, de Melker HE, van Gageldonk PG, Schellekens JF, van der Klis FR, Mollema L, Mooi FR, Berbers GA. Seroprevalence of pertussis in the Netherlands: evidence for increased circulation of Bordetella pertussis. PLoS One. 2010; 5:e14183.19. Jenkinson D. Duration of effectiveness of pertussis vaccine: evidence from a 10 year community study. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1988; 296:612–614.20. Wendelboe AM, Van Rie A, Salmaso S, Englund JA. Duration of immunity against pertussis after natural infection or vaccination. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2005; 24:S58–S61.21. Senzilet LD, Halperin SA, Spika JS, Alagaratnam M, Morris A, Smith B. Sentinel Health Unit Surveillance System Pertussis Working Group. Pertussis is a frequent cause of prolonged cough illness in adults and adolescents. Clin Infect Dis. 2001; 32:1691–1697.22. Wright SW, Edwards KM, Decker MD, Zeldin MH. Pertussis infection in adults with persistent cough. JAMA. 1995; 273:1044–1046.23. Kwon HJ, Yum SK, Choi UY, Lee SY, Kim JH, Kang JH. Infant pertussis and household transmission in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2012; 27:1547–1551.24. Nelson JD. The changing epidemiology of pertussis in young infants: the role of adults as reservoirs of infection. Am J Dis Child. 1978; 132:371–373.25. Wendelboe AM, Hudgens MG, Poole C, Van Rie A. Estimating the role of casual contact from the community in transmission of Bordetella pertussis to young infants. Emerg Themes Epidemiol. 2007; 4:15.26. Forsyth K, Tan T, von König CH, Caro JJ, Plotkin S. Potential strategies to reduce the burden of pertussis. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2005; 24:S69–S74.27. Zhang Qi, Zheng H, Liu M, Han K, Shu J, Wu C, Xu N, He Q, Luo H. The seroepidemiology of immunoglobulin G antibodies against pertussis toxin in China: a cross sectional study. BMC Infect Dis. 2012; 12:138.28. Lai FY, Thoon KC, Ang LW, Tey SH, Heng D, Cutter JL, Phoon MC, Chow VT. Comparative seroepidemiology of pertussis, diphtheria and poliovirus antibodies in Singapore: waning pertussis immunity in a highly immunized population and the need for adolescent booster doses. Vaccine. 2012; 30:3566–3571.29. Lee SY, Kim JS, Ahn JH, Choi JH, Ma SH, Park JS, Kim HM, Kang JH. Immunoassay of diphtheria and tetanus according to ages. Infect Chemother. 2012; 44:62–66.30. Gergen PJ, McQuillan GM, Kiely M, Ezzati-Rice TM, Sutter RW, Virella G. A population-based serologic survey of immunity to tetanus in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1995; 332:761–766.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Pertussis Toxin on the Differentiation of B Lymphocytes in Lymph Node
- Investigation on the Immunity to Pertussis in the Korea
- Seroprevalence of Pertussis in Healthcare Workers without Adult Pertussis Vaccine Use at a University Hospital in Korea
- Pertussis Prevalence in Korean Adolescents and Adults with Persistent Cough
- Tetanus–diphtheria–acellular pertussis vaccination for adults: an update