J Korean Med Sci.
2011 Oct;26(10):1391-1393. 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.10.1391.
A Case of Pulmonary Alveolar Microlithiasis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. yskwon@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea.
- 3Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea.
- 4Department of Radiology, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 1786001
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2011.26.10.1391
Abstract
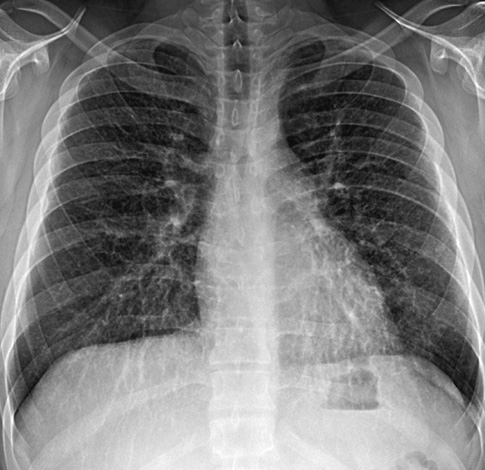
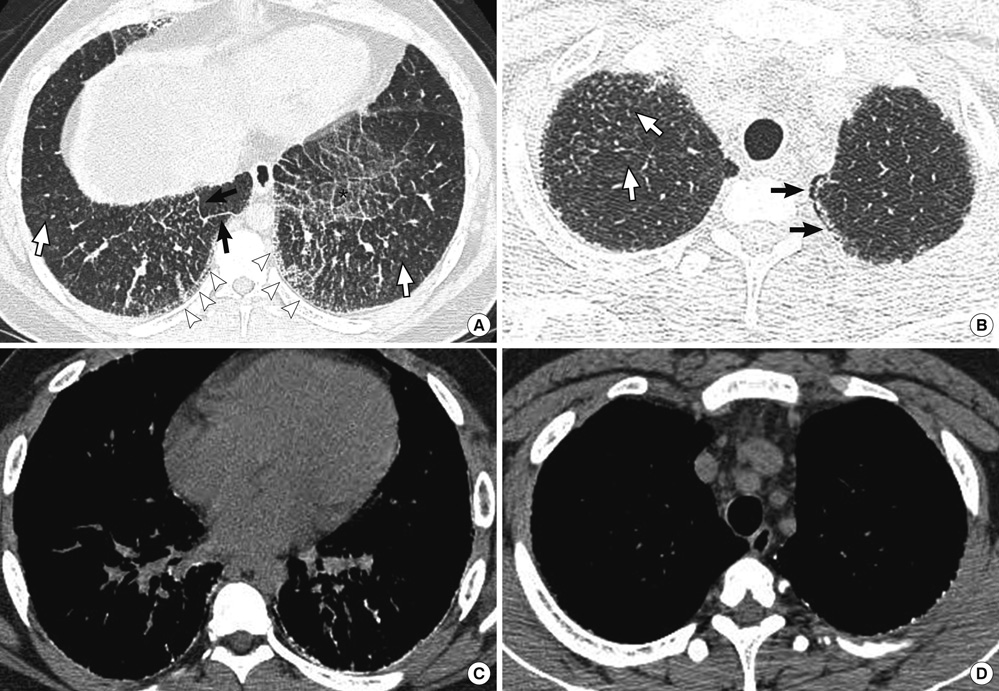
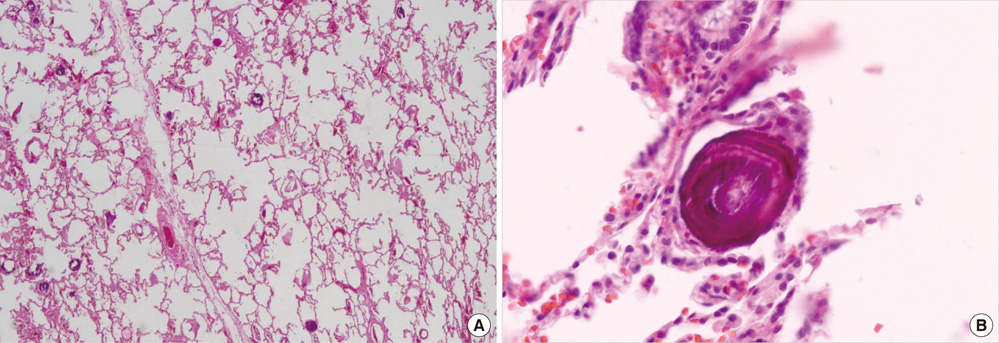
- Pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis (PAM) is a rare disease with unknown etiology and pathogenesis. It is characterized by diffuse, innumerable, and minute calculi, called microlithiasis in the alveoli. More than half of reported cases are asymptomatic at the time of diagnosis. We describe the first case of PAM in Korea. A 19-yr-old man without respiratory symptoms presented with interstitial thickening on the chest radiograph. His chest high resolution CT scan showed diffusely scattered, ill defined tiny micronodules and interstitial thickening. Open lung biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of PAM. He was followed up for 6 months without treatment, and no progression was noticed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Castellana G, Lamorgese V. Pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis. World cases and review of the literature. Respiration. 2003. 70:549–555.2. Lauta VM. Pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis: an overview of clinical and pathological features together with possible therapies. Respir Med. 2003. 97:1081–1085.3. Mariotta S, Ricci A, Papale M, De Clementi F, Sposato B, Guidi L, Mannino F. Pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis: report on 576 cases published in the literature. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2004. 21:173–181.4. Marchiori E, Gonçalves CM, Escuissato DL, Teixeira KI, Rodrigues R, Barreto MM, Esteves M. Pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis: high-resolution computed tomography findings in 10 patients. J Bras Pneumol. 2007. 33:552–557.5. Corut A, Senyigit A, Ugur SA, Altin S, Ozcelik U, Calisir H, Yildirim Z, Gocmen A, Tolun A. Mutations in SLC34A2 cause pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis and are possibly associated with testicular microlithiasis. Am J Hum Genet. 2006. 79:650–656.6. Samano MN, Waisberg DR, Canzian M, Campos SV, Pêgo-Fernandes PM, Jatene FB. Lung transplantation for pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis: a case report. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2010. 65:233–236.7. Shigemura N, Bermudez C, Hattler BG, Johnson B, Crespo M, Pilewski J, Toyoda Y. Lung transplantation for pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2009. 139:e50–e52.8. Stamatis G, Zerkowski HR, Doetsch N, Greschuchna D, Konietzko N, Reidemeister JC. Sequential bilateral lung transplantation for pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis. Ann Thorac Surg. 1993. 56:972–975.9. Gasparetto EL, Tazoniero P, Escuissato DL, Marchiori E, Frare E Silva RL, Sakamoto D. Pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis presenting with crazy-paving pattern on high resolution CT. Br J Radiol. 2004. 77:974–976.10. Hoshino H, Koba H, Inomata S, Kurokawa K, Morita Y, Yoshida K, Akiba H, Abe S. Pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis: high-resolution CT and MR findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1998. 22:245–248.11. Chung MJ, Lee KS, Franquet T, Muller NL, Han J, Kwon OJ. Metabolic lung disease: imaging and histopathologic findings. Eur J Radiol. 2005. 54:233–245.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Sandstorm Appearance of Pulmonary Alveolar Microlithiasis Incidentally Detected in a Young, Asymptomatic Male
- A Case of Pulmonary Alveolar Microlithiasis
- Bilateral Sequential Bronchopulmonary Lavage in One Stage for Recurred Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis: A case report
- A Case of 8 Year-old Boy with Testicular Microlithiasis Showing Bilateral Testicular Enlargement
- Anesthetic Management for Whole-Lung Lavage in a Patient with Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis